Programming Paradigms
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Procedural Programming
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we’re going to dive into procedural programming, which is the foundational paradigm for many languages. Can anyone tell me what they think procedural programming involves?

I think it’s about writing code in steps, right? Like listing instructions?

Exactly! Procedural programming involves a sequential flow of control where you write procedures or functions that follow a logical series of steps. Can you think of an example, Student_2?

Like calculating the factorial of a number using a loop?

Great example! It helps us understand how we can build complexity in a structured manner. Remember the acronym 'SIMPLE' for procedural programming: **S**tep-by-step, **I**nstructions, **M**athematical, **P**rocedures, **L**oops, **E**xecution. What do you think?

That’s helpful! It’s a neat way to remember the key aspects!

Exactly! By mastering this paradigm, you'll have a strong base to tackle more advanced concepts.
Object-Oriented Programming
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's discuss Object-Oriented Programming or OOP. Does anyone know what key concepts are involved in OOP?

I think it’s about objects and classes, right?

Right! OOP revolves around creating classes, which can encapsulate data and functionality. What are some characteristics of OOP?

Encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism!

Exactly! Remember the acronym **EIP**: **E**ncapsulation, **I**nheritance, **P**olymorphism. These principles allow us to create complex systems while managing code complexity effectively. Can anyone explain how inheritance can be useful?

It lets us create new classes based on existing ones, so we don't have to rewrite code!

Perfectly put! Inheritance promotes code reusability, making your applications easier to maintain.
Functional Programming
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, we’ll look at Functional Programming. Who here can describe what functional programming focuses on?

It focuses on using functions as the primary building blocks, without changing state.

Exactly! It's all about immutability and stateless functions. Think of the mnemonic **FIRST**: **F**unctions, **I**mmutability, **R**educers, **S**tate-free, **T**ransformations. Why do you think this can be beneficial, Student_1?

Because it can help eliminate side effects, making the code easier to debug?

Yes! Functional programming can lead to more predictable and reliable code, which is especially important in larger applications.
Event-Driven Programming
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let's dive into Event-Driven Programming. What context do you think this paradigm is most suitable for?

Applications where multiple events happen at once, like GUI apps?

Correct! This paradigm lets applications react to user actions. Remember the acronym **REACT**: **R**esponsive, **E**vent, **A**ctions, **C**allbacks, **T**riggered. How do you think this impacts user experience?

It makes the applications feel more dynamic and interactive!

Exactly! Users expect their interactions to yield immediate feedback, and event-driven programming enables that flexibility.
Concurrent & Parallel Programming
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Lastly, let's discuss Concurrent and Parallel Programming. Why might a developer use these techniques?

To handle multiple tasks at the same time and improve performance?

Exactly right! Let’s remember the guideline **MTP**: **M**ulti-threading, **T**asks, **P**erformance. Can anyone think of an application scenario where this might be essential?

Rendering a video might use parallel processing to speed it up.

Great example! Using concurrent programming techniques can significantly enhance performance in computationally intensive applications.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
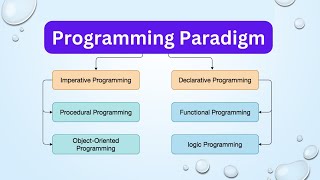
This section discusses the foundational procedural programming paradigm in basic programming and contrasts it with more intricate advanced programming paradigms such as Object-Oriented Programming (OOP), Functional Programming, Event-Driven Programming, and Concurrent & Parallel Programming. It emphasizes their distinct purposes and applications for complex systems.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Basic Programming Paradigm: Procedural Programming
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Basic Programming Paradigm: Procedural Programming
- Focuses on step-by-step instructions.
- Example: Writing a function to calculate factorial using loops.
Detailed Explanation
Procedural programming is a programming paradigm that organizes code into procedures or routines. It involves giving the computer a sequence of tasks to perform, with clear and defined steps. For instance, to calculate a factorial of a number, you would use a loop to multiply the number by itself and by all lower numbers down to one. This makes the flow of execution linear and straightforward.
Examples & Analogies
Think of procedural programming like following a recipe in a cookbook. Just as a recipe lists out steps to create a dish in a specific order, procedural programming does the same for tasks in code, leading the computer through each step systematically.
Advanced Paradigms Overview
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Advanced Paradigms:
1. Object-Oriented Programming (OOP):
- Encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism.
- Useful for building complex systems (e.g., game engines, enterprise applications).
2. Functional Programming:
- Stateless and immutable functions.
- Examples: Haskell, Scala, functional features in Python and JavaScript.
3. Event-Driven Programming:
- Common in GUI and web applications.
- Event listeners and callback functions.
4. Concurrent & Parallel Programming:
- Use of threads, processes, async-await, etc.
- Boosts performance for computation-heavy tasks.
Detailed Explanation
Advanced programming paradigms provide more flexibility and power in writing code compared to simple procedural programming. Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) allows for modeling real-world entities using classes and objects, helping to manage complexity. Functional programming focuses on composing functions and avoiding state changes, which can lead to fewer bugs. Event-driven programming is essential for applications that react to user actions, while concurrent and parallel programming harness multiple threads and processes to enhance performance, especially for tasks that require significant computation power.
Examples & Analogies
Consider advanced programming paradigms like tools in an artist's toolkit. A chef (programmer) can use different tools (paradigms) for different dishes (projects). When making a complex cake (building a system), using OOP is like combining various ingredients (features) where each has a role. When optimizing a busy restaurant workflow (concurrent programming), the chef may multitask (use threads) to manage several orders at once.
Key Concepts
-
Procedural Programming: A step-by-step approach to coding via functions.
-
Object-Oriented Programming: Uses objects and classes for data encapsulation and code reuse.
-
Functional Programming: Emphasizes pure functions and immutability.
-
Event-Driven Programming: Program execution based on events, enhancing interactivity.
-
Concurrent & Parallel Programming: Techniques for improving performance through simultaneous task execution.
Examples & Applications
A function written in Python that calculates the factorial of a number using loops.
An OOP-based program that models a car with properties like color and speed, and methods like accelerate and brake.
A simple event-driven JavaScript program that changes a button's color when clicked.
A parallel algorithm that processes large datasets in chunks to speed up computation and data analysis.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In PROCess, we follow a linear path, with loops and steps, avoiding math's wrath!
Stories
Imagine a teacher guiding students through a maze (procedural programming), then introducing them to a library of books (OOP), where each book has its own story and is part of a larger narrative.
Memory Tools
Remember 'EIP' for OOP: Encapsulation, Inheritance, Polymorphism.
Acronyms
Use REACT** for Event-Driven Programming
R**esponsive
**E**vent
**A**ction
**C**allback
**T**riggered.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Procedural Programming
A programming paradigm that follows a sequence of steps or instructions.
- ObjectOriented Programming (OOP)
A paradigm that uses objects to encapsulate data and functionality, emphasizing the use of classes and inheritance.
- Functional Programming
A programming style that treats computation as the evaluation of mathematical functions and avoids changing state or mutable data.
- EventDriven Programming
A paradigm in which the flow of the program is determined by events such as user actions or sensor outputs.
- Concurrent Programming
Executing multiple sequences of operations at the same time.
- Parallel Programming
A form of computation in which many calculations or processes are carried out simultaneously.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
