Exception Propagation
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Exception Propagation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we will discuss exception propagation. Can anyone tell me what happens when an error occurs in a method?

Does the program just crash?

Good question! If not handled, the exception can cause the program to crash, but if we have exception propagation, it gets passed to the calling method.

So it moves up to the method that called it?

Exactly! This is useful because it allows us to handle errors at a higher level. Let's consider our example of `methodA` calling `methodB`. If `methodB` throws an exception, `methodA` can be designed to handle it.

What's the advantage of this approach?

It centralizes error management and ensures our program doesn't fail abruptly, allowing smoother user experiences.

Can we use `throws` keyword for this?

Precisely! Using the `throws` keyword enables a method to declare the exceptions it can propagate, requiring the caller to deal with them.

To summarize, exception propagation allows for a cleaner and more organized way to manage errors in Java. Remember: it’s like passing the baton in a relay race!
Practical Examples of Exception Propagation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let’s put our knowledge into practice by looking at some code examples. What do you think happens when an exception isn't caught in `methodB`?

It goes up to `methodA`?

Right! Suppose `methodB` throws an `IOException`. How would we write `methodA`?

Would we add `throws IOException` in the method signature?

Correct! This tells anyone calling `methodA` that they need to handle this exception.

So how would you catch it in `methodA`?

You could use a try-catch block. If `methodB` throws an exception, you catch it and handle it in `methodA`. Let’s conclude with a quick recap.

Always remember, when an exception propagates, it can either be handled at the point of call or declared with `throws` to be managed higher up the stack.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
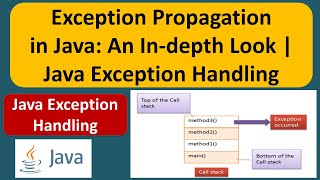
In Java, when a method throws an exception that is not caught within the method itself, it propagates up to the calling method. This allows for centralized error handling, making programs more robust and preventing abrupt crashes.
Detailed
Exception Propagation
Exception propagation is a key concept in exception handling, particularly in Java. When an exception occurs in a method and is not handled, it automatically moves up the call stack to the method that invoked it. This allows methods to signal to their callers that something has gone wrong without needing to handle the exception within themselves. As a practical example, if methodA calls methodB, and methodB throws an exception like IOException, methodA must either catch the exception or declare that it too can throw the exception. This flow is significant in keeping code clean and manageable. In summary, understanding exception propagation is essential for developing error-tolerant applications.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Basics of Exception Propagation
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
If an exception is not caught in the current method, it propagates to the calling method.
Detailed Explanation
This means that if a method encounters an exception and does not handle it (using try-catch), that exception 'travels upward' to the method that called it. This is known as propagation. Essentially, the calling method can either handle the exception or allow it to propagate further up the call stack.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you are in a factory and you are tasked with assembling a product. If you find a broken part but don't fix it, you pass the issue to your supervisor. If they ignore it, it goes all the way up to the manager. In this analogy, you represent the method processing the product, the supervisor represents the calling method, while the manager represents the main program handling overall operations.
Method Call Example
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
void methodA() {
methodB();
}
void methodB() throws IOException {
// throws exception
}
Detailed Explanation
Here, we have two methods: methodA and methodB. methodA calls methodB. In methodB, there's a potential to throw an IOException. Because methodB is set up to throw this exception, if it does occur and methodB doesn't handle it, the exception will propagate back to methodA.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a restaurant where one chef (methodA) asks another chef (methodB) to prepare a dish. If the second chef encounters a problem (like missing ingredients) and doesn’t address it, he informs the head chef (the calling method) about the issue. Instead of solving it, he passes the responsibility up the chain.
Key Concepts
-
Exception Propagation: The process of an exception being passed to the calling method.
-
throws Keyword: Declares that a method can throw exceptions, prompting callers to handle them.
Examples & Applications
When methodA calls methodB, and methodB throws an IOException, it propagates to methodA for handling.
By using throws in a method declaration, we inform the callers that error handling is necessary.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
If the error's there, don't despair, it just might pass beyond repair.
Stories
Imagine a ball being tossed up; if it’s not caught, it flies up to the next person.
Memory Tools
Remember 'P-E-R-A': Propagation, Exception, Return, Action.
Acronyms
PE - Propagation of Exceptions.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Exception Propagation
The mechanism by which an exception that is not handled in a method is passed up to the calling method.
- throws
A keyword in Java used to indicate that a method can throw exceptions, requiring the caller to handle them.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
