Nested try Blocks
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Nested Try Blocks Structure
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Good morning, class! Today, we're diving into nested try blocks. Can someone remind me what a try block does?

It's used to define a block of code that may throw exceptions!

Exactly! Now, a nested try block is essentially a try block placed inside another try block. Why do you think this could be useful?

Maybe to handle different types of errors differently?

Right! By nesting, we can manage exceptions at different levels, keeping our code organized. Can anyone give me a simple example where this would be handy?

Like when reading files? You could try to open a file in the inner block and catch that error there, while the outer block could handle issues like file not found.

Exactly! Let's look at a code illustration to see how this works.
Localized Handling in Nested Try Blocks
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Yesterday, we touched on nesting. Now, let's dive deeper into localized error handling. Why is it important to isolate exceptions?

So that we can focus on specific errors without affecting the overall program flow?

Precisely! Each `try` can handle its specific exceptions. For instance, if you're trying to parse data inside the nested block but encounter issues, which `catch` block will execute?

The inner one, right? Because it’s closer to where the error happens.

Exactly! The outer catch block will only execute if the inner try block fails and the exception is not caught there. This structure helps programmers manage errors in a clean way. Let’s clarify this with an example.
Best Practices for Nested Try Blocks
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

With nested try blocks comes responsibility! What are some best practices we should follow?

We should always handle exceptions explicitly and not leave things to default behavior.

Great point! Also, never forget to clean up resources in the `finally` block. What happens if you don’t handle an exception properly in the inner block?

It could cause unwanted crashes or bugs in the application?

Absolutely! Ensure every scenario is covered to maintain application stability. Let’s summarize our learning today.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section explains how nested try blocks work in Java, allowing for the separation of error handling in complex code. By placing try blocks within each other, developers can localize exception management effectively. This organized approach enhances code readability and maintainability, which is essential in robust application development.
Detailed
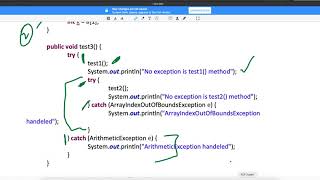
Nested Try Blocks
In Java programming, it’s possible to place one try block inside another, which can help in handling exceptions more efficiently. This creates a scenario where developers can manage different levels of exceptions, making the code cleaner and more maintainable.
Key Points:
-
Structure: A nested
tryblock consists of an outertryblock that includes an innertryblock. Each block can have its owncatchstatements for handling different types of exceptions. -
Localized Exception Handling: By nesting
tryblocks, specific sections or operations that may generate errors can be isolated, allowing more precise error management. The outertrycan handle exceptions that the inner block might not, or vice versa. - Example Structure:
This layout is particularly useful when different parts of the code might throw exceptions that need different handling methods. The outer catch block can deal with exceptions from the entire inner structure while the inner block addresses more specific exceptions.
Significance
The ability to use nested try blocks enhances the robustness and reliability of Java applications, ensuring that issues can be managed more seamlessly and with less disruption to the overall flow of the program.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Nested try Blocks
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
You can have try blocks inside try blocks for localized exception handling.
Detailed Explanation
In Java, you can create a try block within another try block, known as a nested try block. This allows developers to handle exceptions more selectively and locally within a block of code, improving error management in complex scenarios. The outer try block can be used to catch exceptions that may occur in both the outer and the inner blocks, allowing for a clear distinction in exception handling for different sections of the code.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you are in a two-story building. If something goes wrong on the first floor (like a spill), you might have a safety measure (an inner try block) to handle it immediately without allowing the problem to escalate to the second floor (the outer try block). If issues occur on the second floor (like a fire), you still have safety measures in place to manage that situation separately.
Structure of Nested try Blocks
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
try {
try {
// Nested risky code
} catch (Exception e) {
// Inner exception handling
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// Outer exception handling
}
Detailed Explanation
The provided code snippet illustrates the structure of nested try blocks. The outer try block encloses the inner try block, which contains risky code that may throw exceptions. If any exception occurs in the inner try block, it is caught and handled by the corresponding inner catch block. If the inner block is successful but the outer block still has risks, exceptions from the outer block can be caught by its own catch block. This double-layered approach provides a robust way to handle errors and manage exceptions effectively.
Examples & Analogies
Think of this code structure like a layered defense in a video game, where the player has several levels of protection. If an enemy attacks at the first level (the inner try), the player has an immediate defense (the inner catch) to deal with it. Yet, if this attack somehow bypasses the first level, the second level (the outer try) also has a defense (the outer catch) prepared to respond to any additional threats.
Benefits of Using Nested try Blocks
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Using nested try blocks helps in localized exception handling.
Detailed Explanation
One of the primary benefits of using nested try blocks is that it allows for localized handling of exceptions. By segmenting different parts of the code into separate try blocks, developers can isolate problematic sections, making the debugging process easier. It also provides clarity on where to handle specific errors, enhancing code readability and maintainability.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a team of firefighters tackling a house fire. If they enter a room (inner try) and find a small fire, they can address it immediately. However, if there’s an even bigger fire in the hallway (outer try), they still have a plan to handle that separately. This systematic approach allows them to efficiently deal with multiple issues without causing a bigger problem.
Key Concepts
-
Nested Try Blocks: Allows a try block to be defined within another try block for sophisticated exception management.
-
Local Exception Handling: Facilitates targeted handling of exceptions in specific sections of the code.
-
Try-Catch Structure: Basic framework for defining error handling in Java.
Examples & Applications
Example 1: Using nested try blocks to read a file and parse its contents. If the file cannot be found, an IOException can be caught in the outer block, while parsing errors can be caught in the inner block.
Example 2: Using nested try blocks when connecting to a database where the outer block manages connection exceptions and the inner block handles SQL exceptions.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Nested try, oh what a try, exceptions here and there, catch them quick, with careful flair!
Stories
Imagine two doctors in a busy hospital. One specializes in broken bones (inner try), and the other in all other ailments (outer try). The first doctor only manages localized problems, while the second handles broader issues that weren't fixed.
Memory Tools
Use NEST for Nested Exception: N - Nested; E - Ensure specificity; S - Separate handling; T - Try again if needed!
Acronyms
NEST
Nested Error Handling Strategy for Tracking.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Nested try Blocks
A programming construct where one try block is placed inside another try block, allowing for complex exception management.
- Local Exception Handling
The practice of managing exceptions in a specific, localized section of code to provide focused error handling.
- Outer Catch
The catch block that handles exceptions thrown by the outer try block.
- Inner Catch
The catch block that handles exceptions thrown by the inner try block.
- Finally Block
A block that executes after try-catch blocks, regardless of whether an exception occurred.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
