Built-in Java Annotations
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
@Override Annotation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will begin by discussing the @Override annotation. Can anyone tell me what it does?

Isn't it used to indicate that a method is overriding a method from a superclass?

Exactly! The @Override annotation alerts the compiler that this method is intended to override a method in its superclass, which helps catch errors if the method signatures do not match. Remember, using it enhances code clarity.

So, if we forget to use it, will it still work?

It might still work, but if there's a mistake in the method signature, you won't get a warning, which could lead to bugs. Always use @Override where applicable!

What’s a good way to remember its purpose?

You can think of 'Override' as 'Overly Clear,' because it makes your intention very clear! It’s a best practice to use this annotation.
@Deprecated Annotation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let’s look at the @Deprecated annotation. Who can explain why we use it?

I think it marks methods or classes that shouldn’t be used anymore because there are better alternatives.

That's correct! When a method is marked with @Deprecated, it serves as a warning to developers that they should avoid using it in new code because it may be removed in future versions. It's a way to communicate planned changes without breaking existing code.

Can we remove deprecated methods immediately?

Not immediately; they should be removed carefully, considering that existing code may still rely on them. Mantain documentation to guide developers properly.

What’s a good memory aid for @Deprecated?

Think of it as 'Do not use, it’s deprecated!' which fits perfectly!
@SuppressWarnings Annotation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s move on to @SuppressWarnings. What do you think this annotation does?

It tells the compiler to ignore certain warnings, right?

Absolutely! This is useful when you know a warning is acceptable, like using legacy code. It helps keep the console output clean from warnings you have intentionally ignored.

Is it safe to use it frequently?

Good question! While it helps manage warnings, using it excessively can hide potential issues. It’s better to resolve warnings when possible instead of just suppressing them. Remember, 'Suppressing doesn't solve!'
@FunctionalInterface Annotation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's explore the @FunctionalInterface. Can anyone share what it means?

It makes sure the interface has only one abstract method.

Exactly! This annotation is important for enabling lambda expressions in Java. It lets the compiler enforce that the interface can only have one abstract method.

So, if I add a second abstract method, will it throw an error?

Correct! If you do, the compiler will give you an error, helping maintain the intention of functional programming. An easy way to remember is, 'One function, one purpose.'
@SafeVarargs Annotation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let’s talk about @SafeVarargs. What can you tell me about this annotation?

It must do something with variable arguments, right?

Yes, exactly! This annotation suppresses warnings about unsafe operations on variable arguments, particularly in methods where you know you are being safe. It helps reduce unnecessary warnings.

Is it always safe to use?

It's safe when you are sure about the types you're working with in the varargs. Remember, 'Safety with Varargs!' is a good way to recall!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Built-in Java annotations are metadata annotations that provide critical information to the compiler and runtime environment. They play key roles in indicating method overrides, deprecations, suppressing warnings, and enforcing functional interface requirements.
Detailed
In Java, built-in annotations serve as metadata, providing essential information to the compiler or runtime environment without modifying the program's behavior. Each built-in annotation has a specific purpose:
- @Override: Indicates that a method overrides a method in its superclass, ensuring better readability and compiler checks.
- @Deprecated: Marks methods or classes that are outdated, warning developers that they should not be used in future code.
- @SuppressWarnings: Instructs the compiler to ignore specific warnings, allowing developers to manage potential issues without cluttering their code with extra warnings.
- @FunctionalInterface: Ensures that an annotated interface contains exactly one abstract method, aiding in the use of lambdas and making code safer with functional programming practices.
- @SafeVarargs: Suppresses warnings related to variable arguments, ensuring the code remains clean when using methods that take varargs. These built-in annotations are crucial for enhancing code quality, maintainability, and clarity.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of Built-in Annotations
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Java provides several built-in annotations that serve various purposes in programming. Here are some key built-in annotations:
- @Override: Indicates method overrides a superclass method
- @Deprecated: Marks a method or class as outdated
- @SuppressWarnings: Tells the compiler to suppress specific warnings
- @FunctionalInterface: Ensures the interface has exactly one abstract method
- @SafeVarargs: Suppresses unsafe varargs warnings
Detailed Explanation
Java has several built-in annotations that help to convey essential information about the code to both the compiler and other developers. These annotations serve specific roles and improve code readability and maintainability. For instance, '@Override' indicates that a method is intended to override a method from a superclass, helping ensure that the method signature matches and avoids errors. Similarly, '@Deprecated' signals that a method or class should no longer be used, informing developers to look for alternatives. The '@SuppressWarnings' annotation allows developers to suppress compiler warnings for specific cases, thereby keeping the code cleaner when they are certain that the warnings are not relevant.
Examples & Analogies
Think of these annotations like signposts in a park. Just as signposts provide vital information to visitors – directing them to paths, warning them of hazards, and indicating areas that should be avoided or are under maintenance – Java annotations guide developers and compilers to understand the intentions behind the code better. By using '@Override', developers ensure they don't accidentally change the behavior of inherited methods, much like ensuring you’re on the correct path in the park.
Purpose of Each Annotation
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- @Override: Helps in identifying erroneous attempts to override methods due to signature mismatches.
- @Deprecated: Serves as a clear indication to other developers regarding the lifespan of methods and classes.
- @SuppressWarnings: Useful particularly in complex codebases where warnings may be too general.
- @FunctionalInterface: Ensures the correct design of functional interfaces, facilitating lambda expressions.
- @SafeVarargs: Protects against potential heap pollution scenarios in methods that take varargs.
Detailed Explanation
Each built-in annotation has a distinct purpose that aligns with common programming needs. For instance, the '@Override' annotation not only provides documentation benefits but also helps in catching bugs by enforcing method signatures to match with the superclass. The '@Deprecated' annotation keeps the codebase clean, preventing future developers from using outdated methods that might not be supported in future versions. The '@SuppressWarnings' annotation allows developers to stay focused on actual problems without being distracted by trivial warnings, while '@FunctionalInterface' explicitly marks interfaces that are intended for functional programming, promoting the use of lambda expressions. Finally, '@SafeVarargs' serves an important role in preventing programming errors related to varargs.
Examples & Analogies
Consider annotations like safety labels on food products. Just as labels inform consumers about dietary concerns, whether something is gluten-free or might contain allergens, annotations provide essential information to developers. When you see '@FunctionalInterface', it’s like reading 'this product is gluten-free,' confirming that it is structured correctly and ready for specific uses – in this case, for passing lambda expressions.
Key Concepts
-
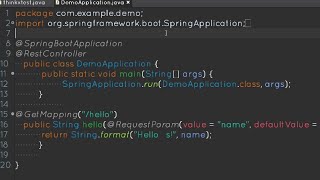
@Override: Used to indicate method overriding.
-
@Deprecated: Marks methods/classes that should no longer be used.
-
@SuppressWarnings: Tells the compiler to ignore specific warnings.
-
@FunctionalInterface: Requires that an interface contains exactly one abstract method.
-
@SafeVarargs: Suppresses unsafe varargs warnings.
Examples & Applications
Using @Override to denote a method that overrides an existing method in a superclass.
Annotating a method with @Deprecated when it is no longer the recommended approach.
Applying @SuppressWarnings to avoid compiler warnings for legacy method calls.
Defining an interface with @FunctionalInterface to make it eligible for lambda expressions.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Override with pride, it makes your code glide.
Stories
Imagine a legacy codebase with a deprecated method. Developers gather around and say, 'This one's out of service!'
Memory Tools
Remember D.O.S. for Deprecated, Override, Suppress - Discipline in Java Coding!
Acronyms
F.A.V.S
Functional Annotation for Variable Safety.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- @Override
An annotation indicating that a method overrides a method in its superclass.
- @Deprecated
An annotation marking a method or class as outdated and should not be used.
- @SuppressWarnings
An annotation that tells the compiler to ignore specific warnings.
- @FunctionalInterface
An annotation that ensures an interface contains exactly one abstract method.
- @SafeVarargs
An annotation that suppresses warnings related to variable arguments when types are ensured to be safe.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
