What is Reflection?
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Reflection
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are discussing Reflection in Java. Does anyone know what Reflection allows a program to do?

I think it lets a program inspect classes and objects at runtime.

Exactly! Reflection provides the ability to analyze and manipulate the internal structure of classes, including their methods and fields. It is crucial for flexibility in applications.

How do we access these class members?

Good question! We use the `java.lang.reflect` package. For instance, `getFields()` and `getDeclaredFields()` can be used to access class fields.

Does this mean we can also create objects dynamically?

Absolutely! With Reflection, we can instantiate classes at runtime using `getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance()`. This adds great power to our applications.

What about security? Is there any risk using Reflection?

Yes, and that's an important point. Using Reflection can expose private members, which could pose security risks. Always use it cautiously.

In summary, Reflection is a powerful tool for dynamic behavior but comes with trade-offs in terms of performance and security.
Core Package and Class Object
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s delve into the core packages for Reflection. What do you think the `java.lang.Class` package provides?

It probably holds the Class objects for all classes in Java.

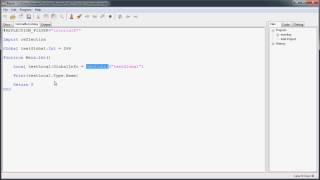
Correct! Each loaded class has a corresponding `Class` object that enables us to inspect its members. You can get a Class object using `Class.forName()`. Can anyone code an example?

Sure! `Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("java.util.ArrayList");`

Perfect! This statement retrieves the Class object for ArrayList. What can we do with this object?

We can access its methods and fields!

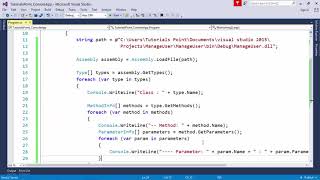
Exactly! You can access methods with `getMethods()` and fields with `getFields()`. Just remember to differentiate between declared and inherited members.

This is such an efficient way to check class members!

Yes indeed! And with great power comes responsibility—ensure you understand the implications of using such features.
Accessing Private Members
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Continuing, let’s talk about accessing private members of a class. Why might we want to do that?

To modify internal state or test methods that are otherwise inaccessible?

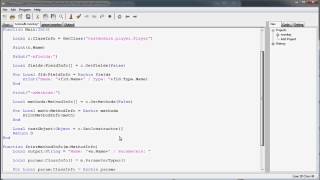
Exactly! Reflection allows us to do this. By setting accessible fields to true, we can manipulate private members. Can anyone show an example?

We can use `field.setAccessible(true);` to allow access to private fields.

Well said! So how would you modify a private field using Reflection?

First, get the Field object, set it accessible, and then set its value with `field.set(obj, value);`

That's spot on! This technique helps especially in testing frameworks where we need to control the behavior of classes without altering their design.

Does this mean it breaks encapsulation?

Correct again! That's why it’s best to use Reflection judiciously and consider design alternatives when possible.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Java Reflection is a powerful feature that provides the ability to inspect and modify classes and their members at runtime. This section covers its definition, core packages, and key concepts, highlighting its significance in developing dynamic Java applications.
Detailed
What is Reflection?
Reflection is a feature in Java that enables a program to analyze and manipulate its internal structure at runtime. It allows developers to inspect classes, objects, methods, and fields dynamically, providing flexibility and extensibility to Java applications.
Key Features of Reflection
- Core Package: Reflection capabilities are primarily found in the
java.lang.reflectandjava.lang.Classpackages. - Class Object: Each class in Java has an associated
Classobject, which can be created usingClass.forName(). Using this object, you can inspect class members, including fields, methods, and constructors, as well as access superclass and interfaces. - Dynamic Instantiation: Reflection allows for dynamic instantiation of objects with
getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance(), facilitating the creation of objects at runtime. - Accessing Fields and Methods: With Reflection, it's possible to access private fields and methods by using
setAccessible(true), thus enabling manipulation of otherwise inaccessible class members.
Importance of Reflection
Reflection is particularly useful in several contexts:
- Framework Development (e.g., Spring, Hibernate)
- Dynamic Testing Tools (e.g., JUnit)
- Proxies and Aspect-Oriented Programming (AOP)
However, developers should be aware of the limitations, such as performance overhead and security restrictions.
Youtube Videos

![[Advanced Programming Concepts] Reflection](https://img.youtube.com/vi/_nqPCc9SVwQ/mqdefault.jpg)




Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Reflection
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Reflection is the ability of a Java program to analyze and manipulate the runtime behavior of applications, particularly the internal structure of classes, objects, methods, and fields.
Detailed Explanation
Reflection is a feature in Java that allows developers to inspect and modify the behavior of their programs while they are running. This means that when you use reflection, you can look into classes, their attributes (also known as fields), methods, and even their relationships with other classes. In essence, reflection provides insights into the structure of your code, which is particularly useful for tasks like debugging or creating frameworks.
Examples & Analogies
Think of reflection like a doctor examining a patient's internal organs through an MRI scan. Just as a doctor can see what's going on inside without needing to open the body, reflection allows a Java program to see the internal components of its own classes and methods while running.
Core Packages for Reflection
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Reflection is provided by the java.lang.reflect and java.lang.Class packages.
Detailed Explanation
In Java, reflection is supported by specific packages, primarily java.lang.reflect and java.lang.Class. The java.lang.Class package contains the Class class, which is crucial since every class in Java is represented as an instance of this class. Meanwhile, the java.lang.reflect package provides classes and methods that allow you to inspect and manipulate the classes, fields, methods, and constructors of loaded classes in your program.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine the java.lang.Class package as a library catalog that tells you all the books (classes) you have in your library (the application). The java.lang.reflect package represents the tools you can use to examine each book in detail. You can see the pages (fields), chapters (methods), and even the index (constructors) without opening the actual book.
Key Concepts
-
Reflection: Inspecting and manipulating classes at runtime.
-
Class Object: An instance representing a loaded class.
-
Dynamic Instantiation: Creating objects at runtime using Reflection.
-
Access to Private Members: Utilizing setAccessible to modify private fields.
Examples & Applications
Using Class.forName("java.util.ArrayList") to obtain Class object of ArrayList.
Dynamically instantiating an object: Object obj = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();
Accessing a private field example: field.setAccessible(true); field.set(obj, 123);
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Reflection's a tool, oh so bright; it lets us see what's behind the light.
Stories
Imagine a magician (Reflection) who opens locked doors (private fields and methods) making the hidden visible to all.
Memory Tools
R.A.C.E. (Reflection, Analyze, Create, Extract) helps remember the functions of Reflection.
Acronyms
R.E.V.E.A.L. (Reflection Enables Visibility, Extensibility, And Longevity) shows the benefits of using Reflection.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Reflection
A Java feature that allows programs to analyze and manipulate the runtime behavior of classes.
- Class Object
An instance of the java.lang.Class class representing a loaded class.
- Access Private Members
The ability to access fields and methods that are declared private using Reflection methods.
- java.lang.reflect
A package that provides classes and interfaces for reflection in Java.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
