Basic Serialization Example
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Serialization
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will explore serialization through a very basic example. Can anyone tell me what serialization is?

Isn’t it about converting an object into a byte stream?

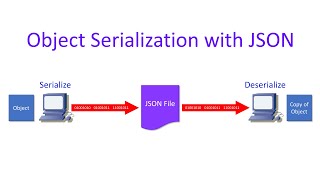
Exactly! Serialization is the process where an object is transformed into a byte stream for storage or transmission. Why do you think this process is essential?

To save objects into files or send them over a network?

Correct! This process facilitates persistent storage and object transmission, which is crucial in many applications.
The Student Class Example
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's analyze the Student class example. This class implements `Serializable`. What does that imply?

It means the class can be serialized, right?

Precisely! Without this marker interface, our object wouldn’t be eligible for serialization. Let's look at the code more closely.

I see it has two fields: id and name. Are both of them serialized?

Yes, indeed! Both fields must either be primitive types or also serializable. If not, serialization will fail. Now, let’s see what happens when we serialize an instance of the Student class.
Using ObjectOutputStream
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

In the main method, we create a `FileOutputStream` for our output file. Can anyone tell me the purpose of the `ObjectOutputStream`?

It lets us write the object data to the file?

Exactly! The `ObjectOutputStream` takes care of converting our object into a sequence of bytes. Then we have the `writeObject` method; can anyone tell me what it does?

It writes the serialized object to the output stream.

Correct! Once the object is written, we close the streams to free resources. That's crucial in Java to avoid memory leaks.
Importance of Serialization in Java
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Why do you think serialization is such an important feature in Java?

It simplifies saving and sharing complex data.

Exactly, it supports not just file storage but also network communications, such as Java RMI. Now, what are some practical scenarios where you might use this?

Like in distributed applications where objects need to be sent over the network?

Yes! Very well said. This is foundational knowledge for writing scalable Java applications.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section provides a clear, practical example of how to serialize a Java object using the Student class. It explains the necessary classes and methods, particularly focusing on ObjectOutputStream, to facilitate serialization.
Detailed
Basic Serialization Example
In this section, we delve into a simple example of serialization in Java utilizing a custom Student class. Serialization denotes the conversion of an object's state into a byte stream, which can then be persisted or transmitted. The provided code snippet includes a basic Student class that implements the Serializable interface. The main focus is on using FileOutputStream and ObjectOutputStream to write the object's data to a file named student.ser.
The code initiates by instantiating a Student object with an ID and name, followed by the demonstration of serialization through the ObjectOutputStream’s writeObject method. Upon execution, the serialized object signifies the transformation of the Student object into a stream of bytes. This example lays a foundational understanding crucial for further exploration of serialization and deserialization concepts in distributed systems.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Defining the Student Class
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
class Student implements Serializable {
int id;
String name;
Student(int id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
}
Detailed Explanation
In this chunk, we are defining a class called Student. This class implements the Serializable interface, which makes it eligible for serialization. The class has two fields: id, which is an integer, and name, which is a string. The constructor initializes these fields when a new Student object is created.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the Student class as a student profile. Just like every student has an ID number and a name that identifies them in a school database, this class captures the same information in a structured format.
Creating an Object and Serializing It
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
public class SerializeDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Student s1 = new Student(1, "Rahul");
FileOutputStream fout = new FileOutputStream("student.ser");
ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(fout);
out.writeObject(s1);
out.close();
fout.close();
System.out.println("Object has been serialized");
}
}
Detailed Explanation
This chunk contains the SerializeDemo class, which includes the main method where the serialization process takes place. We create a Student object named s1 with an ID of 1 and the name 'Rahul'. We then set up a FileOutputStream to write to a file named student.ser. The ObjectOutputStream is used to convert the Student object into a byte stream that can be saved into the file. After writing the object to the file, we close the output streams.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you are packing a physical file containing a student’s information into a box (the file on your computer). The FileOutputStream acts like the box, and the ObjectOutputStream is the act of wrapping the information neatly before placing it inside the box. Once the box is closed and stored, you cannot access the information until it’s opened again.
Key Concepts
-
Serialization: The process of converting an object into a byte stream for storage or transmission.
-
Serializable: A marker interface that indicates a class can be serialized.
-
ObjectOutputStream: A Java class used for writing objects to an output stream.
Examples & Applications
The Student class example illustrates how to implement serialization in Java by using the Serializable interface and ObjectOutputStream.
In the example, a Student object with id and name is serialized into a file called student.ser using Java I/O classes.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Serialize to save and share, a byte stream is beyond compare!
Stories
Once upon a time, a Java object wanted to travel far. To do this, it transformed into bytes, packed its bags and went on its way, ready to be sent or stored.
Memory Tools
S.O.B: Serialization Over Bytes.
Acronyms
S.E.N.D. - Serialize, Encode, Network, Deliver!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Serialization
The process of converting an object's state into a byte stream.
- Deserialization
The process of reconstructing an object from a byte stream.
- Serializable
A marker interface in Java indicating a class is eligible for serialization.
- ObjectOutputStream
A Java class that lets you write objects to an output stream.
- FileOutputStream
A Java class that handles writing data to a file output stream.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
