AXI4-Lite and AXI4-Stream Variants
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to AXI4-Lite
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll dive into AXI4-Lite, a simplified version of the AXI4 protocol. Can anyone tell me what you think could be the benefits of a simplified protocol?

It might be easier to implement and manage, right?

Absolutely! AXI4-Lite reduces complexity. This variant supports only single transactions, which means it's perfect for low-throughput tasks. For example, it's commonly used with control registers. How do you think single transactions impact system performance?

It should lower the overhead, right? Less overhead means faster operations.

Exactly! Additionally, because it lacks burst capability, it is efficient for specific applications. To remember this, think of AXI4-Lite as the 'single serve' option in a restaurant—simple and straightforward. Any other questions on AXI4-Lite?
AXI4-Stream Applications
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, moving on to AXI4-Stream, which is designed for continuous data streams. Student_3, what do you think unidirectional data flow means in this context?

I think it means data only moves in one direction, like a one-way street?

Great analogy! This design is ideal for applications like video processing or networking traffic where continuous data comes in. Can anyone tell me how low latency can be crucial for these applications?

Low latency means data gets processed faster, which is essential for real-time experiences like watching a live video stream.

Exactly right! The efficiency of AXI4-Stream lets us manage high data flows optimally. To sum it up, remember AXI4-Stream as a 'fast lane' for data. Does anyone want to add anything?
Comparison of AXI4 Variants
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

In this session, let’s compare AXI4-Lite and AXI4-Stream. Student_1, what features do you think make AXI4-Lite suitable for certain applications?

It has low overhead and is used for simple control registers.

Correct! Meanwhile, AXI4-Stream excels in high-throughput situations. Student_2, can you distinguish the use cases for both variants?

AXI4-Lite is used in control registers; AXI4-Stream is for streaming data, like videos.

That's a perfect summary. Both variants are crucial within the AXI4 framework, catering to different needs. Can anyone give me a final thought on how these variants contribute to system performance?

They allow specific functionality by optimizing resources for the task at hand!

Exactly! This is how AXI4 enhances SoC designs efficiently.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
AXI4-Lite presents a simplified interface for single data transactions, ideal for low-throughput control registers, while AXI4-Stream is tailored for continuous data streams in high-bandwidth applications like video processing. Both variants enhance system performance and efficiency by addressing specific requirements in SoC designs.
Detailed
AXI4-Lite and AXI4-Stream Variants
Overview
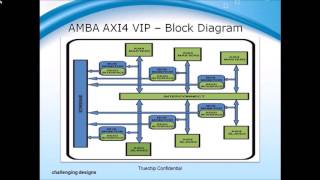
In the world of SoC designs, the AXI4 protocol extends its utility through various specialized variants, notably AXI4-Lite and AXI4-Stream. Each of these variants is tailored to meet distinct application requirements, thereby enhancing system performance and resource allocation.
AXI4-Lite
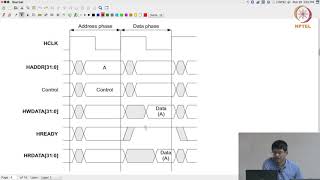
AXI4-Lite is a streamlined version of AXI4 designed to facilitate single data transfers without the complexities of burst transactions. This simplicity makes it particularly suitable for functionality such as low-throughput control registers or simpler peripherals that do not require extensive data handling.
Key Features of AXI4-Lite
- Single Transaction: Each transfer is a standalone operation, reducing overhead.
- Low Overhead: The simplified control interface minimizes the resources needed for management.
- No Burst Capability: As burst transactions are unnecessary in its use cases, this feature is intentionally omitted to maintain simplicity.
AXI4-Stream
In contrast, AXI4-Stream is specifically crafted for continuous data flows typical in applications requiring high bandwidth, such as video and audio processing or networking traffic.
Key Features of AXI4-Stream
- Unidirectional Data Flow: The protocol allows for data to flow in one direction, optimizing throughput.
- High Throughput: Designed for the simultaneous handling of data streams, enhancing efficiency.
- Low Latency: The architecture supports rapid data transfers, which is critical for real-time applications.
Conclusion
Both AXI4-Lite and AXI4-Stream prove to be essential variants within the AXI4 framework, each catering to specific use cases. They enhance the overall adaptability and capability of SoC designs by streamlining control or optimizing data flow depending on application needs.
Youtube Videos

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to AXI4 Variants
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
AXI4 has several variants that offer simplified or specialized versions of the protocol for specific use cases.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk introduces the reader to the concept of AXI4 variants. It highlights that AXI4 has different versions tailored to meet specific needs in various scenarios. By using these simpler or specialized protocols, designers can choose the one that best fits their application without the complexities of the full AXI4 protocol.
Examples & Analogies
Think of AXI4 like a multi-tool, where each tool (variant) is designed for a particular purpose. Just as a simple screwdriver is ideal for inserting screws and a wrench is better for turning nuts, the variants of AXI4 serve specific purposes—making it easier for designers to select the right tool for their specific problem.
AXI4-Lite Overview
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
AXI4-Lite:
- A simplified version of AXI4 that supports single data transfers without the burst capabilities of AXI4.
- Use Cases: AXI4-Lite is often used for low-throughput control registers or peripherals where the full capabilities of AXI4 are not needed.
- Key Features: Single transaction, low overhead, simple control interface, and no burst capability.
Detailed Explanation
AXI4-Lite is a lightweight version of the AXI4 protocol designed for simpler operations. It is ideal for scenarios where only single data transfers are needed, rather than complex data bursts. This makes it well-suited for controlling registers and simpler peripherals, where the overhead of full AXI4 features would be unnecessary and inefficient.
Examples & Analogies
Consider AXI4-Lite like a single-lane road designed for minimal traffic. It’s straightforward and doesn’t need all the complexities of a multi-lane highway designed for high-speed traffic. This makes it perfect for scenarios where traffic is light, just like how AXI4-Lite efficiently handles simple tasks without unnecessary complications.
AXI4-Stream Overview
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
AXI4-Stream:
- AXI4-Stream is designed for continuous data streams, such as video data, audio data, or network traffic.
- Use Cases: AXI4-Stream is used in high-bandwidth applications like video processing, data acquisition, or network interfaces.
- Key Features: Supports unidirectional data flow, high throughput, and low-latency data transfer for stream-based applications.
Detailed Explanation
AXI4-Stream is specifically designed for transferring continuous data streams effectively. It addresses the needs of high-bandwidth applications, where large amounts of data need to be constantly pushed through the system, such as in multimedia applications. AXI4-Stream supports a one-way flow of data, which optimizes it for these types of scenarios while ensuring minimal delay.
Examples & Analogies
Think of AXI4-Stream as a water pipe designed specifically for steady, uninterrupted flow. Just like a large water pipe can deliver a consistent stream of water efficiently and with minimal resistance, AXI4-Stream allows for smooth and rapid data transfer in applications requiring the constant flow of information, like video streaming or real-time data feeds.
Key Concepts
-
AXI4-Lite: A simplified AXI4 protocol for low-throughput applications.
-
AXI4-Stream: A protocol for continuous data flows requiring high throughput and low latency.
-
Single Transaction: An independent data transfer operation in AXI4-Lite.
-
Unidirectional Data Flow: A data flow feature in AXI4-Stream that enhances efficiency.
Examples & Applications
AXI4-Lite is typically used in control registers for devices where data throughput is minimal, such as configuring system parameters.
AXI4-Stream can be used in streaming applications like video processing where large amounts of data need to be continually transferred without delays.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
AXI4-Lite is a single byte, for simple needs it’s just right.
Stories
Imagine AXI4-Lite as a small shop serving one customer at a time, while AXI4-Stream is like a fast food drive-through, sending out many orders in a row.
Memory Tools
Think of 'LITE' for AXI4-Lite as 'Less Input Time Efficiency' to remember its simplicity.
Acronyms
Use 'SLOW' for AXI4-Lite to remember 'Single transfer, Low Overhead, Weak burst capability'.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- AXI4Lite
A simplified version of the AXI4 protocol that supports single data transfers without burst capabilities, typically used for low-throughput control registers.
- AXI4Stream
A protocol variant designed for continuous data streams, allowing high throughput and low-latency transfer, ideal for applications like video processing.
- Single Transaction
An operation where data is transferred only once without the complexity of burst capabilities.
- Unidirectional Data Flow
A data transfer method where data travels in one direction only, optimizing throughput in streaming applications.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
