Introduction to AMBA (Advanced Microcontroller Bus Architecture)
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Overview of AMBA
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Good morning class! Today we are going to delve into AMBA, or the Advanced Microcontroller Bus Architecture. Can anyone explain what AMBA is?

It's a bus standard from ARM, right?

Exactly! AMBA is designed for connecting components in ARM-based SoCs. It allows different parts of a system like CPUs and memory to communicate effectively. Can anyone tell me one of the key features of AMBA?

I think it supports high performance?

That's correct! AMBA provides high performance, flexibility, and scalability. Remember this with the acronym 'PFS' - Performance, Flexibility, and Scalability. Let’s move on to discuss some details about the interconnect protocols. What do you think the benefits of having a scalable architecture are?
Importance of AMBA
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we understand what AMBA is, why do you think it’s so important for SoCs?

It must help add or remove components easily without changing the entire system!

Right! This scalability makes it easier for designers to adapt their systems. The second major point is performance - AMBA's protocols minimize latency and maximize bandwidth. Can anyone explain how this might benefit real-time processing?

This would allow for smoother and faster data handling in applications that need instant feedback, like gaming or automotive systems.

Great point! In summary, AMBA not only facilitates effective communication within SoCs but also adapts efficiently to changing design needs.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The Advanced Microcontroller Bus Architecture (AMBA) by ARM provides a flexible and scalable framework for integrating multiple subsystems in ARM-based systems. The architecture supports various interconnect protocols, enhancing performance, bandwidth, and real-time data processing capabilities in complex electronic systems.
Detailed
Introduction to AMBA (Advanced Microcontroller Bus Architecture)
The Advanced Microcontroller Bus Architecture (AMBA) is a pivotal bus standard developed by ARM, primarily aimed at creating efficient connections among various components in ARM-based System-on-Chips (SoCs). AMBA's design emphasizes a high-performance, flexible architecture that is scalable, allowing for easy integration of subsystems such as CPUs, memory storage, I/O peripherals, and custom accelerators.
Overview of AMBA
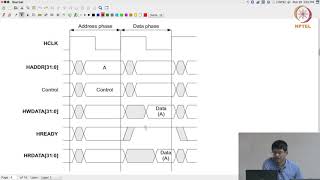
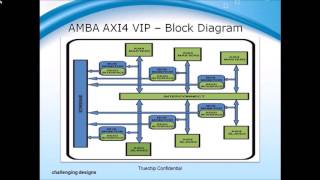
AMBA defines a comprehensive set of interconnects and protocols optimized for communication within SoCs, including several bus protocols, with the Advanced eXtensible Interface 4 (AXI4) being notably the most advanced and prevalent for applications demanding high performance.
Importance of AMBA
- Scalability: AMBA's architecture allows designers to modify SoC designs effortlessly by adding or removing components without disturbing the overall system structure.
- Performance: Its interconnect protocols are designed to ensure high bandwidth with low latency and efficient data transfers, crucial for systems that necessitate real-time processing capabilities.
In summary, AMBA plays a vital role in shaping modern electronic systems that must integrate various functional subsystems while maintaining robust performance characteristics.
Youtube Videos

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of AMBA
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The AMBA (Advanced Microcontroller Bus Architecture) is a widely used bus standard developed by ARM for connecting different components within an ARM-based SoC. It provides a high-performance, flexible, and scalable architecture for integrating various subsystems such as the CPU, memory, I/O peripherals, and custom accelerators.
Detailed Explanation
AMBA, or Advanced Microcontroller Bus Architecture, is a bus standard created by ARM. It serves as a connection system within System on Chips (SoCs) that are built on ARM architecture. SoCs integrate multiple components like the CPU, memory, and various peripherals into one chip. The AMBA architecture is designed to be high-performance, flexible, and scalable, meaning it can efficiently connect various elements while allowing for easy growth and modification of the system.
Examples & Analogies
You can think of AMBA like a highway system in a city. Just as roads connect different areas of a city (homes, shops, schools), AMBA connects different components of an SoC. A well-designed highway can handle many vehicles at once, making traffic efficient, similar to how AMBA allows fast communication between processors and memory.
Importance of AMBA: Scalability and Performance
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Why AMBA is Important:
- Scalability: AMBA supports scalable SoC designs, allowing designers to easily add or remove components without changing the underlying architecture.
- Performance: AMBA’s interconnect protocols are designed to deliver high bandwidth, low latency, and efficient data transfer, making them suitable for complex systems that require real-time processing.
Detailed Explanation
AMBA is significant for two main reasons: scalability and performance. Scalability means that designers can modify the system by easily adding or removing components, adapting to new needs without needing to redesign the entire system. Performance refers to AMBA's protocols, which ensure that data moves quickly and efficiently, reducing delays (latency) and maximizing data transfer capacity (bandwidth). This is crucial for applications that need quick responses, such as video processing or real-time gaming.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine building a LEGO city. If you start with a small house and later want to add a school or a park, you should be able to easily connect those new structures without tearing down the house. This flexibility in adding parts represents AMBA's scalability. Moreover, if your LEGO city has cars that zoom quickly from place to place, that speed and efficiency in movement represent the high performance that AMBA offers in data transfer.
Key Concepts
-
AMBA - A standard for connecting components in ARM-based SoCs.
-
Scalability - The ability of an architecture to grow or adapt.
-
Performance - The efficiency and speed of data handling in a system.
Examples & Applications
AMBA allows a designer to modify an SoC by adding a new memory component without redesigning the whole architecture.
A system using AMBA can quickly process data from sensors and send it to a CPU due to its low-latency protocols.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
AMBA is the architecture, smooth and bright, keeping all components in tight.
Stories
Once upon a time in a microchip world, AMBA connected different components like CPUs and memories elegantly, ensuring they communicated smoothly.
Memory Tools
PFS: Performance, Flexibility, scalability - remember these traits of AMBA.
Acronyms
AMBA - Architecture for Microcontrollers and Bus Activities.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- AMBA
Advanced Microcontroller Bus Architecture, a bus standard developed by ARM for connecting components within an ARM-based SoC.
- SoC
System-on-Chip, an integrated circuit that consolidates all components of a computer or other electronic system into a single chip.
- Interconnects
The communication channels that enable different components of a system to exchange data.
- AXI4
Advanced eXtensible Interface 4, a high-performance bus protocol within the AMBA standard.
- Scalability
The capability to expand or modify the system's capabilities without major redesign.
- Performance
The ability of a system to execute tasks efficiently, typically characterized by speed and responsiveness.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
