AXI4 Protocol Performance Features
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
High Bandwidth
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's start with discussing high bandwidth in AXI4. High bandwidth means the ability to transfer a lot of data quickly. AXI4 achieves this through concurrent data transfers—who can tell me what that means?

I think concurrent data transfers mean that multiple data streams can happen at the same time, right?

Exactly! Think of it like multiple lanes on a highway. Each lane can carry traffic simultaneously, preventing bottlenecks. How does this impact memory and peripheral operations?

It should mean that both can operate quickly, reducing wait times for data retrieval and processing.

Correct! The more data we can handle at once, the faster the overall system operates. Remember, 'Burst for bandwidth'—an acronym B4B can help you remember this!

So, the more bursts and channels we use, the more efficient the data transfer?

Yes, precisely! This is crucial for high-performance applications. Let's summarize: AXI4’s high bandwidth enables high data throughput through concurrent transfer.
Low Latency
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let's talk about low latency in AXI4. Low latency refers to the minimal delay in data processing. Why do you think this is important?

Because in applications like gaming or driving systems, delays can cause problems or inefficiencies.

Exactly! AXI4 uses pipelining, which allows operations to start before previous ones are finished. Can someone explain how this reduces latency?

If one action can start before the one before it has finished, it keeps the flow of data moving. It’s like a factory assembly line!

Great analogy! And remember, 'Pipeline equals performance'—a mnemonic that can help you recall this concept. So our summary: AXI4 ensures low latency through pipelined transactions.
Transaction Ordering
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's dive into transaction ordering! Why is it important to guarantee order in transactions?

It probably helps keep data organized and maintains integrity, especially if the data's related.

Yes! AXI4 guarantees ordering within the same channel. Can someone explain how this might look in practice?

If you have multiple read requests, you need them to be handled in the order they were received to make sure the data comes back correctly.

Exactly! But across different channels, AXI4 allows flexibility. So, remember: 'Order for output'—this mnemonic will help you remember the importance of transaction ordering.
Multiple Master and Slave Configurations
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let’s discuss multiple master and slave configurations. Why is supporting multiple masters and slaves beneficial?

It allows for more complex systems, right? Like multiple CPUs accessing memory at the same time!

Exactly! This scalability is key for large SoCs. What challenges might arise with multiple sources requesting data?

There could be conflicts when two masters request the same slave at once, which needs to be managed.

Great point! AXI4 handles this with efficient arbitration techniques. As a summary: AXI4’s architecture achieves flexibility through its support for multiple masters and slaves.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The AXI4 protocol enhances data transfer performance through high bandwidth capabilities by facilitating concurrent data transfers, reducing latency with pipelined transactions, and ensuring transaction ordering for system efficiency. It also allows for flexible configurations with multiple master and slave devices.
Detailed
Detailed Summary of AXI4 Protocol Performance Features
The AXI4 protocol is engineered to optimize overall data transfer performance in ARM-based SoCs through various performance features, which include:
- High Bandwidth:
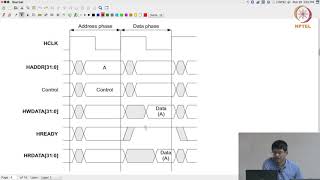
- AXI4 significantly enhances data throughput by enabling multiple concurrent data transfers, or bursts, across different channels. This capability maximizes bus utilization and boosts bandwidth utilization for both memory and peripheral operations, ensuring that systems can handle high data load efficiently.
- Low Latency:
- One of the hallmark features of AXI4 is its pipelining and a burst transaction model, which are crucial for minimizing delays in read and write operations. This is particularly important for applications requiring real-time data processing, such as automotive or multimedia systems where swift data handling is imperative.
- Transaction Ordering:
- AXI4 guarantees transaction ordering within a single channel, which helps maintain data integrity while allowing flexible transaction processing across different channels. This feature supports the simultaneous handling of multiple read and write transactions, which boosts the overall efficiency of a system.
- Support for Multiple Master and Slave Configurations:
- The AXI4 protocol is scalable and adaptable, capable of supporting various configurations with multiple master and slave entities. This flexibility is essential for large systems that incorporate multiple processors, memory controllers, and diverse peripherals, facilitating advanced functionalities in complex SoCs.
In summary, the AXI4 protocol's performance features contribute to creating high-performance, scalable, and efficient communication architectures essential for modern SoC designs.
Youtube Videos

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
High Bandwidth
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
AXI4 supports high data throughput by allowing multiple data transfers (bursts) to occur concurrently on different channels. This maximizes the utilization of the bus and increases the bandwidth for memory and peripheral operations.
Detailed Explanation
The AXI4 protocol is designed to achieve high bandwidth, meaning it can transfer a lot of data quickly. It does this by allowing several transfers, known as burst transactions, to happen at the same time on different pathways (channels) within the system. This simultaneous transfer capability helps to fully use the available bus, making it possible to process various operations at once rather than waiting for one operation to finish before starting another.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a multi-lane highway where many cars can travel at the same time. If each lane can accommodate different types of vehicles (like trucks, cars, and motorcycles), the entire highway can move a lot of traffic efficiently. Similarly, AXI4 uses multiple channels like lanes on a highway to allow data to flow freely and quickly.
Low Latency
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
AXI4 uses pipelining and a burst-based transaction model to minimize delays between read and write operations. This is essential for systems that require real-time data processing, such as multimedia or automotive systems.
Detailed Explanation
Low latency refers to the quick response time in data processing. The AXI4 protocol minimizes delays through two key techniques: pipelining and burst transactions. Pipelining allows multiple operations to be set up at once, so the next operation can start while the first one is still being completed. Burst transactions enable sending a group of data in a single operation instead of one piece at a time. Together, these features ensure a smooth, fast flow of information, particularly important in applications that need immediate processing like video games or car navigation systems.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a food assembly line in a restaurant. If each chef is able to start on their next dish while waiting for the previous one to cook, and they can prepare multiple dishes at once, the entire process runs faster. In the same way, the AXI4 protocol’s techniques allow systems to handle data without waiting, keeping everything moving efficiently.
Transaction Ordering
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
AXI4 guarantees transaction ordering within the same channel but allows flexible ordering across channels. This means that multiple read and write transactions can be processed simultaneously, improving overall system efficiency.
Detailed Explanation
Transaction ordering is crucial for ensuring correct data processing. In AXI4, transactions that occur within the same channel are guaranteed to happen in the order they were initiated. However, transactions across different channels can be processed in any order, which provides flexibility. This setup lets the system handle multiple data requests at the same time, enhancing its efficiency and allowing it to adapt to various workloads without delays.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a busy restaurant where orders come in. If the kitchen makes sure to handle each table's orders in the order they were placed (like a channel), that's similar to ordering within a channel in AXI4. However, if the kitchen can make multiple tables' appetizers while also preparing main courses for other tables (across different channels), it shows how the AXI4 protocol can have flexible ordering, leading to quicker overall service.
Support for Multiple Master and Slave Configurations
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
AXI4 supports multiple masters and slaves in an interconnect system, making it highly flexible and scalable for large SoCs with multiple processors, memory controllers, and peripherals.
Detailed Explanation
In an AXI4 system, 'masters' are components that request data (like processors), and 'slaves' are those that provide data (like memory or peripherals). The protocol can accommodate several masters and slaves simultaneously, which means multiple components can communicate and share resources effectively. This capability makes the AXI4 architecture adaptable for complex systems with many processing units and devices, enhancing scalability as new components can be integrated as needed.
Examples & Analogies
Think of an office with multiple employees (masters) needing to interact with different filing cabinets (slaves). If several employees can access their respective cabinets at the same time without interfering with each other, that's similar to how AXI4 handles multiple communication requests simultaneously. This setup allows for an efficient workflow as more employees are added without requiring major changes to the office layout.
Key Concepts
-
High Bandwidth: Refers to the ability of AXI4 to handle numerous data transfers at once, improving throughput.
-
Low Latency: Ensures quick response times between reads and writes, essential for real-time data processing.
-
Transaction Ordering: Maintains the order of transactions within channels, ensuring data integrity.
-
Multiple Master and Slave Configurations: Supports flexible and scalable designs within SoCs.
Examples & Applications
In multimedia applications, such as video streaming, AXI4’s high bandwidth allows for large data packets to be processed efficiently, ensuring smooth playback.
In automotive systems, low latency provided by AXI4 is crucial for real-time processing of sensor data to avoid delay in reactions.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
To gain the speed for packets fast, use AXI4, it’s designed to last.
Stories
Imagine a train station with multiple tracks, where trains arrive at once. Each line takes different routes to ensure no one waits long—representing high bandwidth through concurrent data transfers.
Memory Tools
P.O.B. - Pipeline, Order and Bandwidth—remember these three for AXI4 performance!
Acronyms
B4B - Bursts for Bandwidth, a tool to help remember why AXI4's design is effective.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- High Bandwidth
The capacity to transfer large amounts of data quickly through multiple simultaneous channels.
- Low Latency
The minimal delay between request and response in data processing.
- Transaction Ordering
The sequence in which transactions are processed; important for maintaining data integrity.
- Multiple Master and Slave Configurations
A system design that allows several masters and slaves to communicate and share resources efficiently.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
