Benefits of Using Software Tools
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Rapid Prototyping
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

One of the foremost benefits of using software tools is rapid prototyping. Can anyone explain what that means?

Does it mean that we can create a model quickly without going through all design steps?

Exactly, Student_1! Rapid prototyping allows us to create a basic version of our design quickly to test ideas and performance. This speeds up the overall design cycle.

Can you give an example of rapid prototyping in signal processing?

Sure! For instance, in MATLAB, you can quickly develop and test different filtering techniques using simulation tools instead of designing and building hardware filters. Great job, everyone!
Visualization and Debugging
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s talk about visualization. Why is it important in signal processing?

It helps us to see the signals and understand their patterns better.

Absolutely, Student_3! Visualization allows us to interpret complex data easily. It can reveal trends in behavior that aren't obvious from raw data. What about debugging—any thoughts on how it assists us?

It helps us find mistakes or errors in our simulations.

Great point, Student_4! Debugging support in software helps us understand signal flow and locate problems quickly, saving significant time and resources. Recap: Rapid prototyping and visualization streamline our design process!
Cost-effectiveness
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's move to another benefit: cost-effectiveness. Why do you think using software tools can be more cost-effective?

Because we don’t need to buy physical hardware for every experiment?

Exactly, Student_1! Software tools reduce the necessity for physical components, cutting down costs on hardware purchases and maintenance. Can anyone think of how this might affect project timelines?

It would save time since setting up hardware can take a long time!

Right again! With less time spent on setup, we can focus more on design and testing. Remember, implementing software tools ultimately leads to resource efficiency.
Scalability of Algorithms
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let’s touch on scalability. What does it mean for algorithms to be scalable?

It means we can change them later to work with different hardware without starting from scratch.

Exactly! Scalability allows designs to easily adapt to varying hardware capabilities. This flexibility is crucial, especially when project requirements evolve over time.

So, it's more about being prepared for future changes?

Yes! Flexibility is key in modern design processes. To summarize today’s sessions: rapid prototyping, visualization, debugging, cost-effectiveness, and scalability are all vital benefits of using software tools!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The benefits of using software tools in signal processing include faster prototyping, better visualization of complex concepts, effective debugging support, cost reduction by minimizing hardware needs, and scalable algorithms for advanced applications.
Detailed
Benefits of Using Software Tools
In today's digital landscape, the application of software tools in engineering and technology has revolutionized signal processing and communication systems. These tools offer a multitude of advantages crucial for modern-day tasks. This section explores the five key benefits of using software tools:
- Rapid Prototyping: Software tools enable engineers to swiftly develop and test prototypes, significantly speeding up the design cycle. This efficient approach allows for quick iterations and refinements.
- Visualization: Abstractions in signal processing can often be complex and hard to understand. However, visualization features provided by these tools enhance the interpretation and modeling of signals, leading to a clearer understanding of their behavior and properties.
- Debugging Support: Monitoring signal flows and identifying errors becomes straightforward with software tools. Their robust debugging capabilities empower engineers to detect issues early in the design process, ensuring higher reliability and performance.
- Cost-effective: The deployment of software solutions can help reduce dependence on physical hardware. This not only brings down costs related to hardware acquisition and maintenance, but also related to time spent on setting up physical test environments.
- Scalability: With software tools, algorithms designed can be easily scaled to meet specific hardware requirements later in the development process, providing flexibility and adaptability to changing project demands.
In summary, the appropriate use of software tools is pivotal not just for increased efficiency but also for fostering innovation in signal processing and communication system design.
Youtube Videos

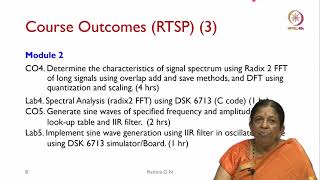

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Rapid Prototyping
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Rapid Prototyping: Speeds up design cycle.
Detailed Explanation
Rapid prototyping refers to the quick creation of a model or prototype of a system or component. In the context of software tools for signal processing, this means that engineers and developers can quickly test their ideas and algorithms in a simulated environment. By using software tools, they can make changes and see the results in real-time without having to build physical models. This significantly reduces the time taken to iterate designs and helps in discovering the most effective solutions faster.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a chef trying out new recipes. Instead of making the entire dish every time, they might just prepare small test portions to see how the flavors work together. Similarly, engineers use rapid prototyping to test their signal processing designs quickly without committing to expensive and time-consuming hardware builds.
Visualization
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Visualization: Enhances understanding of abstract concepts.
Detailed Explanation
Visualization in signal processing software tools refers to the graphical representation of data and signals. By visualizing signals, developers can better understand complex patterns and behaviors that may not be evident through numerical data alone. Software tools can generate graphs and plots that illustrate how a signal behaves over time or how it responds to different algorithms, making it easier for users to interpret the results.
Examples & Analogies
Think of how a weather map visualizes temperature or storm systems. Just as a map helps people understand the weather at a glance, visualization tools help engineers comprehend complex signal data instantly rather than sifting through endless numbers. It provides a clearer picture of what is happening.
Debugging Support
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Debugging Support: Easily monitor signal flow and errors.
Detailed Explanation
Debugging support in software tools allows users to analyze and troubleshoot their algorithms efficiently. It includes features that enable real-time monitoring of signal flow, showing where errors might occur in the processing chain. Developers can pinpoint issues in their designs before moving to physical implementations, which can be costly and time-consuming.
Examples & Analogies
Consider debugging like fixing a plumbing issue in your home. If there's a leak, you can visually inspect the pipes to find out where the problem is. Similarly, software tools provide a way to inspect the signal paths and identify issues without needing to dismantle complex hardware setups.
Cost-effective Solutions
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Cost-effective: Reduces need for extensive physical hardware.
Detailed Explanation
Using simulation and analysis software significantly cuts down on costs associated with the development of signal processing systems. By allowing users to test multiple scenarios and designs within a software framework, the dependence on expensive physical components is reduced, which not only saves money but also minimizes waste and the inventory of materials needed.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine planning a garden using a digital garden design tool instead of physically planting each seed. By visualizing the layout, you avoid spending money on plants that might not work well together. Similarly, simulation tools help engineers design systems without having to invest in every single piece of hardware initially.
Scalability
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Scalability: Algorithms can be scaled to hardware later.
Detailed Explanation
Scalability in the context of software tools refers to the ability to adapt and expand algorithms for different hardware setups. Developers can create algorithms in a flexible software environment, and later, when moving to physical implementation, they can adjust and optimize these algorithms according to the specific hardware they will use. This ensures that designs can grow and evolve with technological advancements.
Examples & Analogies
Think of scalability like a musician who can play in a small coffee shop but can also adapt their sound for a big concert venue. The core of the music remains the same, but the execution may change to suit the environment. Similarly, algorithms created in software tools can be adjusted to work on various hardware platforms without losing their effectiveness.
Key Concepts
-
Rapid Prototyping: Speeding up design processes by quickly developing models.
-
Visualization: Enhancing the understanding of complex signals through graphical representation.
-
Debugging Support: Facilitating error detection during the design phase.
-
Cost-effectiveness: Reducing expenses by minimizing hardware requirements.
-
Scalability: Allowing algorithms to adapt to various hardware setups.
Examples & Applications
Using MATLAB to create simulations of filters to quickly test their performance before final hardware implementation.
Leveraging visualization tools to plot signal waveforms, helping engineers to see real-time responses and understand signal behavior.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Rapid prototyping, designs take flight, speed in sight, making ideas bright.
Stories
Imagine a chef who quickly tosses ingredients together to find the right recipe. This is akin to rapid prototyping, where speed helps discover solutions.
Memory Tools
Remember 'D.R.C.S.' for Benefits: Debugging, Rapid prototyping, Cost-effective, Scalability.
Acronyms
VDSC for Visualization, Debugging support, Scalability, Cost-effective solutions.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Rapid Prototyping
The process of quickly creating a model or prototype of a system to test concepts and functionality.
- Visualization
The representation of data in graphical formats to enhance comprehension.
- Debugging
The process of identifying, isolating, and fixing problems within a software model or system.
- Costeffective
A characteristic of a process or action that achieves desired results without incurring significant expenses.
- Scalability
The ability of a system or algorithm to handle growth or changes in demand without significant changes to its structure.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
