Integration of Advanced VLSI CAD Tools
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Tool Interoperability
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will explore tool interoperability in advanced VLSI CAD tools. Can anyone explain what interoperability means?

It means how different CAD tools can work together smoothly.

Absolutely right! Tool interoperability is crucial because it allows changes in one phase of design, like synthesis, to reflect in placement and routing automatically. This helps minimize errors. What might be a benefit of this?

It reduces the manual work we have to do!

Exactly! Less manual intervention leads to fewer mistakes. Can anyone give an example of how losing this integration could impact a project?

If a change isn't reflected, it could cause timing issues later on, right?

Correct! Always remember, 'One change, many impacts!' That's a good memory aid for understanding integration in design flows.
Data Management
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Moving on to data management in our CAD tools, what challenges do you think we face with managing design data?

Probably handling the huge amounts of data generated during the design process?

Exactly! VLSI designs generate vast amounts of data. This requires efficient systems for storage and retrieval. What solutions can we use to handle this?

We can use cloud-based systems!

Spot on! Cloud platforms not only store data but also allow for collaborative working. How does version control fit into this?

It helps us keep track of design changes and ensures we don’t lose previous versions.

Well said! Thus, an effective data management system is crucial to ensure consistency in design iterations. Remember, "Data consistency is design efficiency!"
Automated Design Flows
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's discuss automated design flows. What do we mean by that?

It's where the design process can run from start to finish without much human input.

Exactly! This automation allows designers to focus more on optimization instead of tedious tasks. What are some specific objectives we can optimize during these flows?

Power and area are two big ones!

Absolutely correct! Automated design flows greatly reduce time-to-market. Can anyone summarize why this is beneficial for companies?

It means they can release products faster and stay ahead in the market.

Exactly! Remember, 'Speed in automation leads to success in innovation!'
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The integration of multiple sophisticated CAD tools is essential in modern VLSI design. This integration facilitates seamless automation of tasks, effective data management, and the establishment of automated design flows that contribute to reduced time-to-market for products.
Detailed
Integration of Advanced VLSI CAD Tools
The integration of advanced VLSI CAD tools is pivotal in streamlining the design process. These tools function cohesively within a unified environment, where tasks are automated and specifications are consistently met. Key aspects covered in this section include:
- Tool Interoperability: This allows different stages of the design flow—such as synthesis, placement, routing, and verification—to communicate effectively, ensuring modifications in one area are reflected in others, thus reducing potential errors and decreasing manual adjustments.
- Data Management: As designs become increasingly complex, the role of robust data management systems becomes critical. Effective data management ensures that large volumes of design data are adequately processed and stored. Cloud-based solutions and version control systems are vital in managing design iterations and maintaining consistency throughout the design lifecycle.
- Automated Design Flows: Modern CAD tools support automated design flows, enabling the execution of entire design cycles without manual intervention. This automation significantly enhances productivity and minimizes the time needed to bring new products to market by focusing on optimizations for specific objectives such as power, area, and timing.
Youtube Videos
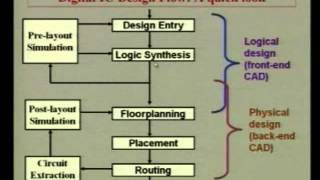
Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Tool Interoperability
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Integration between tools such as synthesis, placement, routing, and verification ensures that changes in one stage of the design flow are automatically propagated to subsequent stages. This eliminates errors and reduces manual intervention.
Detailed Explanation
Tool interoperability refers to the ability of different CAD tools to work together seamlessly. In VLSI design, you have various stages such as synthesis, placement, routing, and verification. When these tools are integrated, any change made in one stage is automatically updated across the other stages. This reduces human error which can occur when teams manually input changes into different tools. For example, if a design change is made during synthesis, the placement and routing tools can automatically adjust without needing additional input. This leads to a much more efficient workflow and helps maintain design integrity throughout the development process.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a relay race where each runner must pass a baton. If they don't communicate well or the baton is dropped, the team loses time and risk disqualification. In VLSI design, if one tool fails to update the changes across others, it's akin to dropping the baton—leading to delays and potential errors.
Data Management
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Advanced VLSI CAD tools require effective data management to store and process large amounts of design data. This includes the use of cloud-based platforms for distributed processing and version control systems to manage design iterations and maintain design consistency.
Detailed Explanation
Data management is crucial in VLSI design because projects often generate enormous amounts of data. Advanced CAD tools need to handle this data efficiently. Cloud-based platforms allow designers to access and process this data from different locations, enabling collaboration among teams who may be geographically dispersed. Additionally, version control systems help track changes in design iterations. This ensures that every version of the design is saved, allowing teams to revert to previous versions if needed, thus maintaining consistency and preventing loss of crucial data.
Examples & Analogies
Think of data management like a library. In a library, books are organized in a way that makes it easy to find them. If the library doesn’t have a system, books can get lost, and it becomes difficult to manage. Similarly, effective data management ensures that all design data is organized, current, and accessible, making the design process smoother.
Automated Design Flows
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Modern CAD tools support automated design flows, which allow designers to run end-to-end design cycles automatically, optimizing for specific goals such as power, area, and timing. These automated flows significantly reduce time-to-market for new products.
Detailed Explanation
Automated design flows streamline the process of VLSI design by allowing designers to set up a sequence of tasks that run automatically from start to finish. This includes synthesis, placement, routing, and verification, all optimized for goals like power consumption, area utilization, and timing constraints. With automation, designers can reduce the time it takes to get a product to market because they don't have to spend extensive manual effort on each stage of the design process. Instead, they can focus on refining the design and strategizing improvements.
Examples & Analogies
Consider an assembly line in a factory. Once everything is set up, the assembly line can produce products quickly and efficiently without constant oversight, allowing for faster production. In the same way, automated design flows enable rapid development of VLSI designs, similar to how an assembly line produces products efficiently.
Key Concepts
-
Interoperability: The capacity of tools to communicate and operate together seamlessly.
-
Data Management: The storage and processing systems that facilitate design data handling.
-
Automated Design Flows: Systems that enable automatic execution of design tasks and processes.
Examples & Applications
Once changes to circuit designs in one tool can immediately reflect in another tool, this enhances workflow efficiency.
Using version control systems in data management allows teams to revert to previous design states easily.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In CAD, tools must connect, interoperability we respect.
Stories
Imagine engineers at a workstation, collaborating effortlessly as their CAD tools share data. This harmonious team exemplifies interoperability, allowing them to reach their goals quickly.
Memory Tools
Remember: I.D.A (Interoperability, Data Management, Automated flows) for CAD tools integration!
Acronyms
C.A.D = Connect, Automate, Design in VLSI flows.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Interoperability
The ability of different CAD tools to work together without conflicts.
- Data Management
The processes used to collect, store, and process design data effectively.
- Automated Design Flows
Processes that allow design cycles to run automatically from start to finish.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
