Place-and-Route Tools
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Place-and-Route
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Welcome, class! Today we're diving into the vital role of place-and-route tools in VLSI design. Can anyone tell me what you think these tools do?

Do they help with arranging the components on the chip?

Exactly, Student_1! They optimize the physical layout of the design. Specifically, they reduce things like wirelength. What do you think happens if the wirelength is too long?

It could cause issues with timing and power consumption, right?

Right again! Timing and power are critical factors that place-and-route tools manage. Remember the acronym TPA: Timing, Power, Area. This will help you recall the three key focuses of these tools.
Cadence Innovus
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's delve into Cadence Innovus. This tool automates placement and routing. Can anyone explain why automation in these tasks is beneficial?

It saves time and reduces human errors.

Exactly! It allows designers to focus on more critical aspects of design. Innovus also employs advanced algorithms to manage congestion. What do we mean by congestion?

It refers to areas where too many wires or components are packed together, which can cause delays or failures.

Correct! To handle congestion, Innovus optimizes timing closure and ensures signal integrity. These features streamline the VLSI design process significantly.
Synopsys IC Compiler II
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's look at Synopsys IC Compiler II. What features do you think make this tool a favorite among designers?

It must have good optimization for power and area.

Absolutely! This tool excels in physical design, providing high-quality placement and routing. Beyond that, it integrates machine learning for design rule checking. Why is this integration important, do you think?

Machine learning can help predict potential design issues before they happen, right?

Spot on! By using AI techniques, IC Compiler II enhances overall design reliability and accuracy.
Conclusion of Place-and-Route Tools
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

To wrap up, why are place-and-route tools so essential in VLSI design?

They optimize design for timing, power, and area, helping to create more efficient chips.

Exactly! Remember the tools we talked about: Cadence Innovus and Synopsys IC Compiler II, each with unique strengths. Always consider TPA when designing!

This session really helped clarify how these tools work together!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section discusses place-and-route tools that automate the placement and routing process in VLSI design, highlighting tools such as Cadence Innovus and Synopsys IC Compiler II. It emphasizes their roles in optimizing timing, power, and area, along with advanced features that support congestion management and design rule checks.
Detailed
Place-and-Route Tools
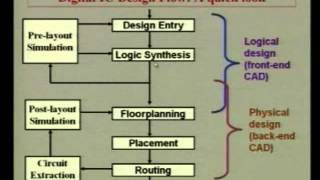
Place-and-route tools are critical components of the VLSI design process, focusing on optimizing the physical layout of integrated circuits. These tools aim to minimize wirelength while ensuring that a design meets its timing, power, and area specifications. In this section, we specifically examine two predominant tools:
- Cadence Innovus: This tool automates the placement and routing of designs, applying advanced algorithms to manage congestion, achieve timing closure, and analyze signal integrity. Innovus is designed to optimize the overall design for important factors like timing performance, power consumption, and the area utilized on the chip.
- Synopsys IC Compiler II: Another widely used tool, IC Compiler II provides high-quality physical design solutions, encompassing placement, routing, and power optimization. This tool harnesses machine learning techniques for improved design rule checking (DRC) and layout versus schematic (LVS) verification, ensuring compliance with complex design standards.
These tools are significant as they enable designers to automate complex tasks and improve the overall efficiency of the design process, thereby accelerating design turnaround times and enhancing product performance.
Youtube Videos
Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Place-and-Route Tools
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Place-and-route tools are crucial in ensuring the physical layout of the VLSI design is optimal, minimizing wirelength and ensuring that timing and power requirements are met.
Detailed Explanation
Place-and-route tools play a vital role in the final stages of VLSI design. After high-level synthesis and logic synthesis, the design needs to be physically laid out on silicon. These tools help with two main tasks: placing components on the chip and routing interconnections between them. The main objectives are to minimize the length of wires (wirelength) to reduce delays and power consumption and to ensure that the design meets all timing and power specifications.
Examples & Analogies
Think of place-and-route tools like the floor plan of a large event hall. Just as an event planner decides where to place tables, chairs, and stages to ensure that guests can move around easily and that everything is accessible, place-and-route tools strategically position components (like transistors and gates) on a chip. A well-designed layout reduces congestion and improves performance, much like a well-organized event layout enhances guest experience.
Cadence Innovus
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Cadence Innovus: This tool automates the placement and routing of designs, optimizing for timing, power, and area. Innovus incorporates advanced algorithms for congestion management, timing closure, and signal integrity analysis.
Detailed Explanation
Cadence Innovus is a specialized tool designed for the place-and-route phase of VLSI design. It uses automated processes to determine the best positions for circuit elements and to create pathways for electrical signals. Innovus considers multiple factors such as how fast signals need to travel (timing), how much power the design consumes (power optimization), and how compactly everything fits on the chip (area efficiency). It also addresses issues like congestion (areas where too many signals are competing for space) and ensures that signals arrive at their destinations without interference (signal integrity).
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a busy highway intersection where too many cars are trying to enter at the same time. A traffic management system works like Innovus by optimizing traffic flow. It directs cars to less congested routes and ensures that traffic lights are synchronized to minimize delays. Similarly, Innovus manages the pathways for electrical signals to prevent bottlenecks and ensure smooth operation of the chip.
Synopsys IC Compiler II
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Synopsys IC Compiler II: IC Compiler II is widely used for physical design, offering high-quality placement, routing, and power optimization. It also provides advanced machine learning techniques to handle design rule checking (DRC) and layout versus schematic (LVS) verification.
Detailed Explanation
Synopsys IC Compiler II is another powerful tool for the physical design of VLSI circuits. Like Innovus, it automates the placement and routing of components on a chip, ensuring a high-quality layout that meets performance criteria. This tool is noted for its ability to optimize power consumption while maintaining speed and area efficiency. Additionally, IC Compiler II incorporates machine learning to enhance its capabilities in checking design rules and verifying that the physical layout matches the intended circuit design. This reduces the chances of errors that could occur when manufacturing the chip.
Examples & Analogies
You can think of IC Compiler II as an architect using sophisticated design software to create a building layout. The architect optimizes the use of space, ensuring that the building not only looks good but also functions well under various conditions. The software helps the architect ensure compliance with regulations (design rules) and that the final blueprints faithfully represent the original design intentions (layout versus schematic verification), similar to how IC Compiler II ensures that the chip is ready for production without issues.
Key Concepts
-
Placement: The physical arrangement of components on a chip.
-
Routing: The process of connecting different components on a chip using wires.
-
Optimization: The adjustment of design parameters to achieve the best performance outcomes.
-
Automation: The use of technology to perform tasks without human intervention.
Examples & Applications
Cadence Innovus can significantly reduce the time spent on routing by automating repetitive tasks.
Synopsys IC Compiler II's machine learning capabilities allow it to learn from previous designs, improving future design processes.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In place and route, make it neat, minimize wire, avoid defeat!
Stories
Imagine a builder designing a complex bridge. Each beam and connection must be placed with care to ensure the bridge stands strong, just like VLSI designs need careful placement and routing to function perfectly.
Memory Tools
Remember 'TPA' for Timing, Power, Area focus in place-and-route tasks.
Acronyms
In VLSI design, think 'CAIN' for Cadence Innovus, Area, Integration, and Neatness.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- PlaceandRoute Tools
Software applications that automate the placement and routing of components in VLSI design to optimize physical layout.
- Timing Closure
The process of ensuring that a design meets its timing requirements, especially for clocked circuits.
- Signal Integrity
The quality of the electrical signals in a circuit, which can be affected by various factors including interference and distortion.
- Congestion Management
Techniques used by place-and-route tools to prevent overcrowding of components or wires, which can lead to performance issues.
- Design Rule Checking (DRC)
Verification of a design’s compliance with certain prescribed design rules to avoid manufacturing errors.
- Layout vs. Schematic (LVS)
A process of comparing a circuit’s physical layout to its schematic to ensure consistency and correctness.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
