Anaphase II
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Anaphase II
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are going to dive into Anaphase II of meiosis! Can anyone tell me what happens during this phase?

Isn't it when the chromatids are pulled apart?

Exactly, Student_1! In Anaphase II, the centromeres split, and the sister chromatids move towards opposite poles of the cell. This separation is crucial for producing four haploid daughter cells. What does haploid mean?

It means having half the number of chromosomes.

Correct! Remember, during meiosis, we reduce the chromosome number by half, and Anaphase II is a key stage in achieving this.
Key Events of Anaphase II
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's discuss the key events of Anaphase II. Can anyone list them for me?

The centromeres split and chromatids move to the opposite poles, right?

That's right, Student_3! The leading edge of each chromosome directs toward the poles, helping organize the separation process. How does this lead to genetic diversity?

Well, it ensures that each gamete has a unique set of chromosomes, contributing to variation.

Great point, Student_4! So, the movement of chromatids not only ensures the correct distribution but also fosters genetic diversity.
The Importance of Anaphase II
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's summarize the importance of Anaphase II. Why do you think this phase matters in sexual reproduction?

Because it helps create gametes with the right number of chromosomes!

Exactly! Proper chromosome segregation in Anaphase II is crucial to ensure that fertilization can restore the diploid number. Any mistakes here could lead to issues like Down syndrome.

So, if something goes wrong during Anaphase II, it can impact the next generation?

Definitely! Understanding these processes is fundamental to grasping how heredity and variation work.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In Anaphase II of meiosis, the centromeres of each chromosome split simultaneously, allowing the sister chromatids to separate and migrate towards opposite poles of the cell. This stage is crucial for ensuring that each daughter cell receives the correct number of chromosomes.
Detailed
During Anaphase II, which is the third stage of Meiosis II, the sister chromatids, each now referred to as daughter chromosomes, begin their movement toward opposite poles of the cell. This phase is marked by the simultaneous splitting of the centromeres, which aligns the chromatids for their crucial separation. The tension from the spindle fibers pulls the sister chromatids apart, ensuring that as they move toward each pole, they maintain directionality with the centromere leading the way, allowing for organized and non-random chromosomal distribution. This step is essential for maintaining genetic integrity in the resulting gametes.
Youtube Videos


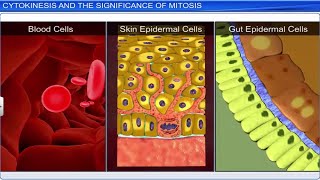





Key Concepts
-
Chromatid Separation: Sister chromatids are separated during Anaphase II.
-
Centromere Splitting: This key event allows chromatids to move toward opposite poles.
-
Importance of Genetic Diversity: Accurate chromosome segregation contributes to genetic variation in gametes.
Examples & Applications
In human meiosis, Anaphase II leads to the formation of four haploid gametes from a single diploid cell.
Errors during Anaphase II can cause genetic disorders, such as Down syndrome, due to incorrect chromosome numbers in the resulting gametes.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In Anaphase II, chromatids go, split from their links, and on they flow.
Stories
Imagine two friends, tied together with a string, pulling in opposite directions in a race. This is what sister chromatids do when their centromere splits!
Memory Tools
CCS - Chromatids, Centromeres, Separate: Remember the three key actions during Anaphase II.
Acronyms
A2C - Anaphase II
Chromatid Separation!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Anaphase II
The stage in Meiosis II where sister chromatids are separated and move to opposite poles of the cell.
- Centromere
The region of the chromosome where the two sister chromatids are joined together.
- Sister chromatids
Identical copies of a chromosome, connected at the centromere.
- Haploid
A cell that contains one complete set of chromosomes, half the number of chromosomes from the diploid state.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
