Meiosis II
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Overview of Meiosis II
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are going to learn about Meiosis II. It’s an essential part of the process that results in the formation of haploid cells from diploid cells. Can anybody tell me what haploid means?

Haploid means having a single set of unpaired chromosomes.

That's correct! During meiosis, we start with a diploid cell and end up with four haploid cells after two rounds of division. Let's dive into the stages of Meiosis II.
Prophase II
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

In Prophase II, the chromosomes begin to condense again, and the nuclear envelope that formed in Telophase I disappears. Why do you think it's important for the chromosomes to condense again?

So that they are easier to separate during the next phases?

Exactly! When chromosomes are compact, they are easier to manipulate. Now, what do we expect during Metaphase II?
Metaphase II and Anaphase II
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

During Metaphase II, the chromosomes align at the cell’s equator. Microtubules attach from each pole to the kinetochores. Can anyone explain what kinetochores do?

They are the points where the microtubules attach to the chromosomes.

Great! Following metaphase, we move on to Anaphase II where the centromeres split and sister chromatids separate. What happens next?

They move to opposite poles of the cell.

Exactly! And this sets us up for the final stage, Telophase II.
Telophase II and Conclusion
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

In Telophase II, what happens to the chromosomes?

They decondense, and a nuclear envelope forms around each set.

Correct! So by the end of meiosis II, we have produced four distinct haploid daughter cells. Can anyone summarize why meiosis is important?

It ensures genetic diversity through recombination and reduces chromosome number for gametes!

Well done! Remember, these processes are crucial for evolution and the survival of species.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Meiosis II follows meiosis I without any preceding DNA replication. It resembles mitosis in that each chromatid separates and is pulled toward opposite poles, leading to the formation of four unique gametes, each with a haploid set of chromosomes, thus ensuring genetic diversity.
Detailed
Meiosis II
In the process of meiosis, Meiosis II is the second division that occurs after an interkinesis phase. Unlike meiosis I, during which homologous chromosomes are separated, meiosis II separates the sister chromatids. The process includes four stages: Prophase II, Metaphase II, Anaphase II, and Telophase II.
Key Stages:
- Prophase II: The nuclear membrane disintegrates, and the chromosomes become more compact once again.
- Metaphase II: Chromosomes align at the equatorial plate, similar to metaphase in mitosis. Microtubules attach to the kinetochores of sister chromatids.
- Anaphase II: The centromeres divide, allowing sister chromatids to move towards opposite poles of the cell.
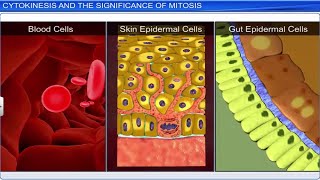
- Telophase II: The chromosomes reach the poles and a nuclear envelope begins to form around each set, following which cytokinesis occurs, producing four haploid daughter cells.
This reduction division crucially contributes to genetic variation among offspring, making it a significant process in sexual reproduction.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Prophase II
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Meiosis II is initiated immediately after cytokinesis, usually before the chromosomes have fully elongated. In contrast to meiosis I, meiosis II resembles a normal mitosis. The nuclear membrane disappears by the end of prophase II. The chromosomes again become compact.
Detailed Explanation
During the Prophase II stage of meiosis II, the process starts immediately after the completion of cytokinesis, where the cell has divided into two. At this point, the chromosomes, which are still visible, start to condense again, preparing for the next stage of division. The nuclear membrane that may have reformed during interkinesis breaks down, allowing the chromosomes to be active in the cytoplasm. The key point here is that meiosis II is like mitosis, a familiar process where single chromosomes (instead of homologous pairs) will line up and be separated.
Examples & Analogies
Think of Prophase II like getting ready for a race. Just like athletes put on their running gear and warm up again before the actual race, the chromosomes condense and prepare for the final stages of cell division, getting ready to separate and end up in their new 'cells'.
Metaphase II
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
At this stage the chromosomes align at the equator and the microtubules from opposite poles of the spindle get attached to the kinetochores of sister chromatids.
Detailed Explanation
In the Metaphase II stage, the prepared chromosomes align along the equatorial plane of the cell, known as the metaphase plate. Each chromosome consists of two sister chromatids that are attached at their centromeres. The key action here is the attachment of spindle fibers to kinetochores, which are special proteins on the centromere. This positioning is crucial because it ensures that when the chromatids are pulled apart in the next stage, each new cell will receive one of each chromatid.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine aligning different colored marbles on a table in a game. You carefully arrange each color so that when the time comes to pick them up (like pulling apart the chromatids), you ensure that each player (cell) gets one of each color. That way, everyone ends up with a balanced set!
Anaphase II
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Anaphase II begins with the simultaneous splitting of the centromere of each chromosome (which was holding the sister chromatids together), allowing them to move toward opposite poles of the cell by shortening of microtubules attached to kinetochores.
Detailed Explanation
During Anaphase II, the centromeres that hold the sister chromatids together are pulled apart, allowing each chromatid to be considered an individual chromosome again. The spindle fibers, which were attached to the kinetochores, shorten and pull the chromatids towards opposite ends of the cell. This ensures that each new daughter cell will receive the correct number of chromosomes.
Examples & Analogies
You can think of Anaphase II like a game of tug-of-war, where each team (the kinetochores) is pulling on the rope (the chromatids) to separate themselves from the other team. When the whistle blows (the centromeres split), both teams pull hard to their sides, ensuring they pull their side of the rope equally.
Telophase II
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Meiosis ends with telophase II, in which the two groups of chromosomes once again get enclosed by a nuclear envelope; cytokinesis follows resulting in the formation of tetrad of cells i.e., four haploid daughter cells.
Detailed Explanation
In Telophase II, each set of separated chromosomes reaches the opposite poles of the cell. At this stage, new nuclear membranes form around each group of chromosomes, leading to the restoration of the nuclei. Following this, cytokinesis occurs, leading to the division of the cytoplasm and the formation of four distinct haploid cells, each containing half the chromosome number of the original cell. This is essential for sexual reproduction, as these haploid cells can eventually fuse during fertilization.
Examples & Analogies
Think of Telophase II like the closing act of a play where all the actors (chromosomes) come back together and take their final bows in separate sections of the stage (the new cells). Each group prepares to exit the stage (the cell) on their own, ready to take on new roles as gametes in future acting (reproduction) adventures.
Key Concepts
-
Meiosis II consists of four stages: Prophase II, Metaphase II, Anaphase II, and Telophase II.
-
In Prophase II, the nuclear envelope disintegrates and chromosomes become compact.
-
During Metaphase II, chromosomes align at the equator and kinetochores attach to spindle fibers.
-
Anaphase II involves the separation of sister chromatids to opposite poles.
-
Telophase II results in the formation of four haploid daughter cells and reformation of the nuclear envelope.
Examples & Applications
Meiosis II is essential in the formation of gametes, allowing for genetic diversity in offspring.
In flowering plants, the meiotic process leads to the production of pollen and ovules, critical for reproduction.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, then Telophase, all in tune, bringing haploid cells in June.
Stories
In a laboratory, biologists watched chromosomes condense during Prophase II, align during Metaphase II, split apart in Anaphase II, and finish creating haploid cells by Telophase II, like a great genetic dance!
Memory Tools
PMAT for Meiosis II: Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase.
Acronyms
CHAMP for Chromosome events
for Condense
for Halve
for Align
for Move
for Polish
each phase preparing for the next.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- haploid
A cell with a single set of chromosomes (n).
- sister chromatids
Identical copies of a chromosome, connected at the centromere.
- kinetochore
Protein complex that forms at the centromere and attaches to spindle fibers.
- cytokinesis
The division of the cytoplasm to form two separate daughter cells.
- nuclear envelope
The double membrane that surrounds the nucleus in a cell.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
