Metaphase II
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Metaphase II
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we are going to discuss Metaphase II. This is a crucial step in meiosis, where the chromosomes are aligned in preparation for separation. Who can tell me why this alignment is important?

I think it's important so that each new cell can get the right number of chromosomes.

Exactly! We want each gamete to receive one copy of each chromosome, ensuring genetic diversity. This phase signifies the transition before the chromatids are pulled to opposite poles.

How do the spindle fibers attach to the chromosomes?

Good question! Spindle fibers attach to the kinetochores at the centromere where the sister chromatids are held together. This is crucial for the separation process.
Key Events of Metaphase II
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

In Metaphase II, chromosomes align at the equator of the cell, forming the metaphase plate. Can anyone explain what happens next?

The chromatids will be separated during the next phase, Anaphase II.

Correct! The alignment ensures that when anaphase II starts, each chromatid will go to opposite ends of the cell. This is how we maintain the chromosome number.

Is there anything unique about how this happens in meiosis compared to mitosis?

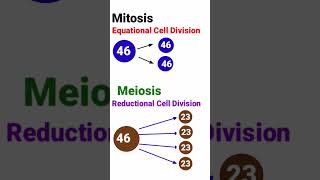
Yes, during mitosis, chromosomes align just like in metaphase, but meiosis specifically halves the chromosomal number across two rounds of division. This is key to sexual reproduction.
Significance of Metaphase II
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's discuss why Metaphase II is vital for genetic variability. Who can share how this phase affects the end results of meiosis?

It ensures that when the gametes are formed, they have a mix of genetic information.

Absolutely! This shuffling of genetic material during meiosis increases variability, which is crucial for evolution and adaptation.

Can you summarize what we’ve learned about Metaphase II?

In summary, during Metaphase II, chromosomes align at the metaphase plate, and spindle fibers attach to kinetochores, setting the stage for the accurate division of chromatids, paving the way for genetic diversity.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
During Metaphase II of meiosis, the chromosomes are lined up at the cell's equatorial plate, with spindle fibers attaching to the kinetochores of sister chromatids. This phase is pivotal for ensuring that each resulting gamete receives just one copy of each chromosome, maintaining the haploid nature necessary for sexual reproduction.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
In Metaphase II, which follows the first meiotic division, the two daughter cells (dyads) that were formed during meiosis I are now ready for their own division. The key events are characterized by the alignment of chromosomes along the metaphase plate. Each chromosome consists of two sister chromatids connected at the centromere. As the cell prepares for division, microtubules extend from opposite spindle poles, attaching to the kinetochores of these chromatids. The arrangement along the metaphase plate is crucial for the equal distribution of chromatids into the resulting gametes at anaphase II. This orderly alignment ensures that genetic material is accurately passed on, highlighting the importance of metaphase in the broader context of meiosis, which reduces the chromosomal number to half, preparing for fertilization.
Youtube Videos





Key Concepts
-
Metaphase II: a stage in meiosis characterized by the alignment of chromosomes at the equatorial plate.
-
Spindle Fibers: Attach to kinetochores during metaphase, crucial for chromatid separation.
-
Equatorial Plate: The plane where chromosomes align to ensure equal distribution during division.
Examples & Applications
During the formation of gametes, Metaphase II ensures that paternal and maternal chromosomes are evenly distributed.
In humans, a typical cell undergoes meiosis to produce haploid gametes with varied genetic combinations.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In Metaphase II, they line up true, Chromatids are ready to part for you!
Stories
In a bustling marketplace, chromosomes gather in perfect rows, each attached to a spindle fiber, eagerly waiting to be separated like pairs of shoes for the next big race.
Memory Tools
K.E.E. - Kinetochore attaches, Equatorial plane aligns, ready for separation!
Acronyms
MAP - Metaphase, Alignment, Preparation for division.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Metaphase II
A stage in meiosis where chromosomes align at the equatorial plate, preparing for separation.
- Chromatid
One half of a duplicated chromosome, joined together at the centromere.
- Kinetochore
A protein structure located at the centromere of a chromosome where spindle fibers attach.
- Spindle fibers
Microtubule structures that segregate chromosomes during cell division.
- Equatorial plate
The imaginary plane where chromosomes align during metaphase.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
