Prophase
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Chromatin Condensation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

In prophase, the chromatin condenses to form mitotic chromosomes. Can anyone tell me why this condensation is so important?

It makes the chromosomes visible for separation during mitosis!

Exactly! Think of them as tightly packed files in a cabinet, making it easier to handle during the move or transition. Now, how many chromatids does each chromosome consist of during prophase?

Two chromatids.

Well done! Each is linked at the centromere, which we'll need to remember moving forward.
Centrosome Movement
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

During prophase, the centrosome duplicates and moves towards opposite poles. Why do we say that it's crucial for the next stages?

They help in forming the spindle fibers that are essential for chromosome movement!

Exactly! They radiate out microtubules called asters, forming the mitotic apparatus. Can anyone recall what that structure does?

It organizes and helps pull the chromosomes apart!

Correct! Remember, a good way to recall is: 'Centrosomes arrange, chromosomes change.'
Disintegration of the Nuclear Envelope
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

As prophase progresses, we see the nuclear envelope start to disintegrate. Why is this process vital for mitosis?

It allows the microtubules to access the chromosomes to pull them apart!

Yes! Without the breakdown of this barrier, the mechanics of mitosis wouldn't work effectively. What happens to the nucleolus during this phase?

It also disappears!

Correct! Visually, by the end of prophase, we should not see the nuclear envelope or nucleolus when under a microscope.
Spindle Formation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

The mitotic spindle forms during prophase. How does this formation influence the overall process of mitosis?

It helps align the chromosomes during metaphase and separates them during anaphase!

Exactly! Remember, 'the spindle’s grace assures equal space' — this helps us remember the spindle's role in aligning and separating chromosomes.
Review of Prophase
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's summarize the key points from prophase. Who can list them out?

1. Chromatin condenses into chromosomes. 2. The centrosomes move apart. 3. The nuclear envelope disintegrates.

Great job! And what significance does this phase have for the overall mitosis process?

It prepares everything for the proper alignment and separation of chromosomes.

Exactly! Knowing the sequence and importance of prophase helps us understand the subsequent stages better.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
During prophase, chromosomal material condenses into visible chromosomes, each consisting of two chromatids. The centrosomes move to opposite poles of the cell, and the nuclear envelope begins to disintegrate, preparing for the subsequent stages of mitosis.
Detailed
Prophase
Prophase is the initial stage of karyokinesis, which is the nuclear division during mitosis, occurring following DNA synthesis in the S phase of the cell cycle. In this phase, several critical events take place:
- Chromatin Condensation: The chromatin fiber condenses to form distinct mitotic chromosomes, each consisting of two sister chromatids connected at a region known as the centromere.
- Centrosome Movement: The centrosome, which has duplicated during the S phase, begins migrating towards opposite poles of the cell. Each centrosome radiates microtubules, creating a structure called the mitotic spindle.
- Nuclear Envelope Disintegration: As prophase progresses, the nuclear envelope, along with the nucleolus, begins to break down, leading to the dispersal of nuclear contents into the cytoplasm.
- Spindle Formation: The aster arrays of microtubules formed by the centrosomes and the spindle fibers indicate the setup for chromosome alignment in later phases of mitosis. At the end of prophase, the chromosomal material is compacted, making it easier to visualize under a microscope.
The significance of prophase cannot be understated as it sets the groundwork for successful chromosome segregation and ensures genetic fidelity in daughter cells.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Prophase
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Prophase which is the first stage of karyokinesis of mitosis follows the S and G phases of interphase.
Detailed Explanation
Prophase is recognized as the first stage of karyokinesis (the division of the nucleus during cell division called mitosis). This stage occurs after the S phase (where DNA is replicated) and the G phases (growth phases) of interphase, which is the period between cell divisions.
Examples & Analogies
Think of preparing for a big performance. Before the show (representing mitosis), the cast must go through practice sessions (interphase) where they learn their lines (S phase) and strengthen their skills (G phases) before stepping onto the stage (prophase).
Chromatin Condensation
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In prophase, chromosomal material becomes untangled during the process of chromatin condensation.
Detailed Explanation
During prophase, the chromatin (the relaxed form of DNA) condenses into visible chromosomes. This is a crucial step because it helps organize the chromosomes for accurate separation later. Each chromosome is made up of two chromatids joined at a central part known as the centromere.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine organizing a messy drawer. When you condense and organize your belongings into neat sections (condensation), it becomes easier to find pairs of socks or tools (chromatids) later when you need them.
Centrosome Movement
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The centrosome, which had undergone duplication during the S phase of interphase, now begins to move towards opposite poles of the cell.
Detailed Explanation
The centrosomes are structures that play a significant role in cell division. After duplicating during the S phase, they move to opposite ends (poles) of the cell during prophase. This movement is essential because it helps in setting up the mitotic spindle that is necessary for chromosome separation later in mitosis.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the centrosome as a director of a play. When the director positions themselves on opposite sides of the stage (the poles), they can communicate better to guide the actors (chromosomes) on where to move during the performance.
Formation of the Mitotic Apparatus
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Each centrosome radiates out microtubules called asters. The two asters together with spindle fibers forms mitotic apparatus.
Detailed Explanation
As the centrosomes move to opposite poles, they extend microtubules, which are structural components of the cell. These microtubules, called asters, help form the spindle apparatus. This apparatus is crucial for guiding the chromosomes during cell division.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine setting up a stage for a play. The poles are like the light rigging on either side that holds the lights in place (asters), while the cables made to connect them represent the spindle fibers that will help illuminate the performance.
Disappearance of Cellular Structures
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
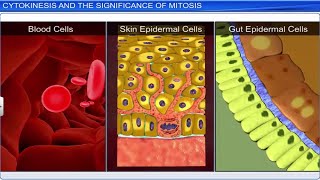
Cells at the end of prophase, when viewed under the microscope, do not show golgi complexes, endoplasmic reticulum, nucleolus and the nuclear envelope.
Detailed Explanation
During prophase, various cellular structures begin to disappear as the cell prepares to divide. Specifically, the nuclear membrane dissolves, along with other organelles like the Golgi apparatus and the nucleolus. This disappearance is vital for allowing the chromosomes to be freely moved during mitosis.
Examples & Analogies
Visualize getting ready for a family move. Before packing begins, furniture and decorations (organelles) are taken down to clear the space (cell division) for easy movement. Only the essentials, like family members (chromosomes), are left to be organized in the new layout (daughter cells).
Key Concepts
-
Chromatin Condensation: The process during prophase where chromatin fibers become tightly packed into visible chromosomes.
-
Centrosome Function: Centrosomes organize microtubules that will form the mitotic spindle critical for chromosome movement.
-
Nuclear Envelope Breakdown: The disintegration of the nuclear envelope allows microtubules to interact with chromosomes.
-
Structure of Mitotic Spindle: The spindle apparatus is formed from microtubules that help align and separate chromosomes.
Examples & Applications
Example 1: In animal cells, prophase is marked by the formation of visible chromosomes, which can be seen under a microscope as distinct structures.
Example 2: During prophase of plant cells, similarly, chromosomes condense and the nuclear envelope disintegrates, allowing for mitotic spindle formation.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In prophase we see,
Stories
Imagine a busy office (the cell) preparing for a big move. As the files (chromatin) get organized and packed neatly into boxes (chromosomes), the entrance (nuclear envelope) opens, allowing movers (spindle fibers) to set up all around.
Memory Tools
C for Condense, C for Centrosome, and D for Disintegrate (the nuclear envelope).
Acronyms
CCCD - Chromatin Condenses, Centrosome moves, Nuclear envelope Disintegrates.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Prophase
The first stage of mitosis, characterized by chromatin condensation and disappearance of the nuclear envelope.
- Centromere
The region where two sister chromatids are joined together.
- Chromatid
One of the two identical halves of a duplicated chromosome.
- Centrosome
An organelle that is the main microtubule organizing center of the cell.
- Mitotic spindle
A structure composed of microtubules that segregates chromosomes into daughter cells during cell division.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
