HUMAN ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to the Endocrine System
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will delve into the human endocrine system, which consists of glands that secrete hormones to regulate various body functions. Can anyone tell me what hormones are?

Hormones are chemicals released by glands that send messages to different parts of the body.

Exactly! Hormones act as intercellular messengers. They are produced in minute amounts but have significant effects. Can anyone name one of the endocrine glands?

The pituitary gland!

Right! The pituitary is often called the 'master gland' because it controls other endocrine glands. Remember the acronym HPTA: Hypothalamus, Pituitary, Thyroid, Adrenal, which highlights major glands in the system.

What about the pancreas? Does it produce hormones too?

Yes! The pancreas functions as both an endocrine and exocrine gland. It produces insulin and glucagon, which regulate blood sugar levels. Let's summarize: the endocrine system includes glands that release hormones to maintain homeostasis.
Roles of Major Endocrine Glands
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s examine the functions of specific endocrine glands. Who can explain what the hypothalamus does?

It regulates many bodily functions and controls the pituitary gland.

Correct! The hypothalamus releases releasing and inhibiting hormones. What about the thyroid gland?

It produces thyroid hormones that regulate metabolism.

Exactly! If there's an iodine deficiency, it can lead to hypothyroidism or goitre. Remember the thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck! What do we know about the adrenal glands?

They produce adrenaline and cortisol, right?

Yes! Adrenaline prepares the body for 'fight or flight' responses. So, important takeaway: Each gland has unique roles but collectively ensures physiological balance.
Hormonal Regulation and Mechanisms
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let’s talk about how these hormones work. Can someone explain what happens when a hormone reaches its target?

The hormone binds to a specific receptor on the target cell.

Exactly! This binding creates a hormone-receptor complex. What do we call hormones that use membrane-bound receptors versus those with intracellular receptors?

Peptide hormones use membrane-bound receptors, while steroid hormones use intracellular receptors.

That's correct! And remember, the effects are often long-lasting due to gene expression changes. Let's also use the acronym RAMP: Receptor, Action, Mechanism, Physiological effect to remember their action process.
Effects of Hormonal Imbalance
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's talk about what happens when hormone levels are imbalanced. Can anyone provide an example?

Diabetes is a great example because it involves insulin imbalance.

Absolutely! Without proper insulin, blood glucose levels can rise, leading to serious health concerns. Can anyone think of another condition related to hormonal regulation?

Cretinism, caused by a lack of thyroid hormones in infancy, can affect growth and mental development.

Great! These examples highlight the importance of balance in the endocrine system. Remember the mnemonic, BAD for Blood sugar, Androgens, Deficiency diseases!
Summary and Review
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

As we wrap up our session today, let's review what we've learned about the endocrine system. Who can list the major glands?

Hypothalamus, pituitary, thyroid, adrenal, pancreas, gonads, parathyroid, thymus!

Correct! And what roles do they play?

They regulate metabolism, growth, stress responses, and reproductive functions!

Exactly right! Don’t forget the key concepts we discussed: the way hormones interact with target cells and the consequences of hormonal imbalances. Remembering easy mnemonics can help solidify this information. Keep up your studies!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The endocrine system includes structures like the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thyroid, and adrenal glands, each secreting specific hormones that control various physiological processes. These hormones regulate metabolism, growth, development, and responses to stress, playing crucial roles in maintaining overall health.
Detailed
Human Endocrine System Overview
The human endocrine system comprises various ductless glands and tissues that produce hormones as chemical messengers. These hormones travel through the bloodstream to distant target organs, affecting physiological functions such as metabolism, growth, and reproductive processes. Key components of this system include the hypothalamus, which controls the pituitary gland's hormone release, and major glands such as the thyroid, adrenal glands, pancreas, parathyroid, thymus, and gonads (testes and ovaries). Each gland serves specific roles: the pituitary gland releases hormones that influence other glands, the thyroid regulates metabolism, and adrenal glands release stress hormones, among others. Furthermore, certain non-endocrine tissues also secrete hormones vital for bodily functions, emphasizing the comprehensive nature of hormonal regulation in human physiology.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of the Endocrine System
Chapter 1 of 8
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The endocrine glands and hormone producing diffused tissues/cells located in different parts of our body constitute the endocrine system. Pituitary, pineal, thyroid, adrenal, pancreas, parathyroid, thymus and gonads (testis in males and ovary in females) are the organised endocrine bodies in our body. In addition to these, some other organs, e.g., gastrointestinal tract, liver, kidney, heart also produce hormones.
Detailed Explanation
The human endocrine system consists of various glands and tissues that produce hormones. These hormones act as messengers that regulate physiological functions in the body. Key glands include the pituitary, pineal, thyroid, adrenal glands, pancreas, parathyroid, thymus, and the reproductive organs (testes and ovaries). Interestingly, other organs like the gastrointestinal tract, liver, kidneys, and heart also produce hormones which play pivotal roles in bodily functions.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the endocrine system as a complex orchestra. Each gland plays a unique instrument (produces specific hormones) that contributes to the overall harmony (body functions). Just as a conductor ensures that all musicians play in sync, the hormones help coordinate all bodily functions.
The Hypothalamus
Chapter 2 of 8
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The hypothalamus is the basal part of diencephalon, forebrain and it regulates a wide spectrum of body functions. It contains several groups of neurosecretory cells called nuclei which produce hormones. These hormones regulate the synthesis and secretion of pituitary hormones. The hormones produced by hypothalamus are of two types, the releasing hormones (which stimulate secretion of pituitary hormones) and the inhibiting hormones (which inhibit secretions of pituitary hormones).
Detailed Explanation
The hypothalamus is a small region in the brain that serves as a crucial link between the nervous system and the endocrine system. It produces releasing hormones that trigger the pituitary gland to release its hormones, as well as inhibiting hormones that prevent hormone secretion from the pituitary. This balancing act is vital for maintaining homeostasis in the body.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine the hypothalamus as a thermostat in a house. When it gets too cold (low hormone levels), it signals the heating system (pituitary gland) to turn on (release hormones). When it's warm enough, it tells the heating system to turn off, ensuring a comfortable environment (homeostasis).
The Pituitary Gland
Chapter 3 of 8
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The pituitary gland is located in a bony cavity called sella tursica and is attached to hypothalamus by a stalk. It is divided anatomically into an adenohypophysis and a neurohypophysis. The adenohypophysis consists of two portions, pars distalis and pars intermedia. The pars distalis region of pituitary, commonly called anterior pituitary, produces hormones such as growth hormone (GH), prolactin (PRL), thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH), luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle stimulating hormone (FSH).
Detailed Explanation
The pituitary gland, often termed the 'master gland,' is essential in regulating many bodily functions through hormone production. It has two parts: the anterior pituitary, which produces several key hormones like growth hormone and TSH, and the posterior pituitary, which stores and releases hormones produced by the hypothalamus, such as oxytocin and vasopressin.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the pituitary gland as the manager of a factory, where it oversees the production and distribution of various products (hormones) that the factory (body) needs to function efficiently. Just as a manager oversees different departments in a factory, the pituitary manages various endocrine functions by releasing specific hormones.
The Pineal Gland and Melatonin
Chapter 4 of 8
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The pineal gland is located on the dorsal side of forebrain. Pineal secretes a hormone called melatonin. Melatonin plays a very important role in the regulation of a 24-hour (diurnal) rhythm of our body.
Detailed Explanation
The pineal gland, a small gland located in the brain, produces melatonin, which is crucial for regulating sleep-wake cycles and other circadian rhythms. The secretion of melatonin increases with darkness and decreases with light, helping to signal the body when it is time to sleep and when to be awake.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine melatonin as a traffic light for your body's sleep schedule. When it gets dark outside, the pineal gland turns the light to 'red,' signaling it is time to wind down and sleep. When morning comes and light floods in, the light turns 'green' indicating that it's time to wake up and be alert.
The Thyroid Gland and Its Hormones
Chapter 5 of 8
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The thyroid gland is composed of two lobes which are located on either side of the trachea. The thyroid gland hormones play an important role in the regulation of the basal metabolic rate, development and maturation of the central neural system, erythropoiesis, and metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins and fats.
Detailed Explanation
The thyroid gland produces hormones such as thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which are vital for regulating metabolism, energy production, and growth. These hormones influence nearly every cell in the body and are essential for the proper functioning of the nervous system, especially during development.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the thyroid gland as an engine regulator in a car. Just like an engine needs to run at the right speed to function correctly, your body needs the right levels of thyroid hormones to maintain energy, metabolism, and overall health. Too much or too little can lead to problems, similar to how an improperly tuned engine can cause a car to stall or race.
The Adrenal Gland
Chapter 6 of 8
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Our body has one pair of adrenal glands, one at the anterior part of each kidney. The adrenal medulla secretes hormones called adrenaline and noradrenaline, which are rapidly secreted in response to stress and emergency situations.
Detailed Explanation
The adrenal glands consist of the adrenal cortex and adrenal medulla. The adrenal medulla releases adrenaline and noradrenaline, which prepare the body for 'fight or flight' responses during stressful situations. This includes increasing heart rate, energy availability, and blood flow to vital organs.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the adrenal glands as the body’s emergency response team. Just like firefighters rush to tackle a fire, when you're faced with danger or stress, your adrenal glands quickly release hormones like adrenaline to prepare your body for action, ensuring you can react swiftly and effectively.
The Pancreas and Blood Sugar Regulation
Chapter 7 of 8
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
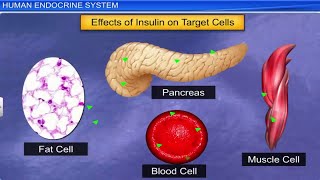
Pancreas is a composite gland that acts as both exocrine and endocrine gland. The endocrine pancreas consists of ‘Islets of Langerhans’. The α-cells secrete glucagon, while the β-cells secrete insulin.
Detailed Explanation
The pancreas plays a dual role by producing digestive enzymes (exocrine function) and hormones (endocrine function). The Islets of Langerhans contain α-cells that produce glucagon to raise blood sugar levels and β-cells that produce insulin to lower blood sugar. Together, these hormones maintain glucose homeostasis in the body.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine the pancreas as a thermostat and a furnace working together. When blood sugar levels drop, glucagon is like turning on the furnace to heat things up (raise blood sugar). When blood sugar levels are high, insulin acts like a thermostat, signaling the furnace to cool off by helping cells absorb glucose, maintaining a stable environment.
The Gonads: Testis and Ovary
Chapter 8 of 8
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Testis performs dual functions as a primary sex organ as well as an endocrine gland. Testis is composed of seminiferous tubules and stromal or interstitial tissue. The Leydig cells produce a group of hormones called androgens mainly testosterone.
Detailed Explanation
The gonads, which include the testes in males and ovaries in females, are responsible for producing sex hormones. Testes produce androgens like testosterone, which influence male characteristics and spermatogenesis, while ovaries produce estrogens and progesterone, regulating female traits and menstrual cycles.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the testes and ovaries as a factory where different products are made. The testes produce male hormones (like testosterone) that help build male traits (like deeper voices, muscles), while the ovaries produce female hormones (like estrogen) that help develop female traits (like breasts, regular menstrual cycles). Each factory produces what is needed to ensure the development of gender-specific characteristics.
Key Concepts
-
Hormones: Chemical signals produced by glands to regulate bodily functions.
-
Endocrine Glands: Ductless glands responsible for hormone release.
-
Hypothalamus: Brain region that controls the endocrine system.
-
Pituitary Gland: Master gland influencing other endocrine glands.
-
Thyroid Gland: Regulates metabolism and development.
-
Adrenal Glands: Release hormones involved in stress response.
-
Insulin and Glucagon: Hormones that regulate blood sugar levels.
Examples & Applications
Insulin decreases blood glucose levels while glucagon increases them.
The adrenal medulla produces adrenaline during stress, preparing the body for 'fight or flight'.
The thyroid gland's dysfunction can lead to conditions like hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Hormones rule, they set the pace, Bringing balance to every space.
Stories
Imagine a kingdom where hormones are like royal messengers, traveling from the glands to every part of the body, delivering important messages that maintain balance and harmony. Without them, the kingdom would fall into chaos!
Memory Tools
HPA for Hypothalamus, Pituitary, Adrenal—remembering the stress response system timeline.
Acronyms
SAG for Steroid, Amino-acid derivatives, Glycoproteins—types of hormones based on their structure.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Hormone
Chemical substances produced by endocrine glands that regulate various physiological processes in the body.
- Endocrine Glands
Ductless glands that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream.
- Hypothalamus
A region of the brain that controls the pituitary gland and regulates various bodily functions.
- Pituitary Gland
The master gland that regulates other endocrine glands and releases various hormones.
- Thyroid Gland
An endocrine gland that regulates metabolism through the secretion of thyroid hormones.
- Adrenal Gland
Glands that produce hormones like adrenaline and cortisol, regulating stress responses.
- Insulin
A hormone produced by the pancreas that regulates blood glucose levels.
- Glucagon
A hormone produced by the pancreas that increases blood glucose levels.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
