SUMMARY
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to the Endocrine System
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're exploring the endocrine system, which plays a crucial role in managing our body’s functions through hormones. Can anyone tell me what a hormone is?

Isn't a hormone a chemical messenger in the body?

Exactly, Student_1! Hormones are chemicals released from glands that travel through the bloodstream to target organs. This system helps regulate essential functions like metabolism and growth. Can someone name an endocrine gland?

The pituitary gland?

Good job, Student_2! The pituitary gland is known as the 'master gland' because it controls other endocrine glands. Let’s remember that with the acronym 'PG' for Pituitary Gland!

What does the pituitary gland control?

It regulates growth, blood pressure, and many other functions, as it secretes various hormones like growth hormone (GH). To sum up, the endocrine system is vital for maintaining body balance.
Functions of Major Glands
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's delve deeper into the major glands in the endocrine system. Starting with the thyroid gland, what hormone does it secrete?

It secretes thyroxine, which regulates metabolism.

That's correct! Remember, T4 for Thyroxine. It’s essential for metabolism. Now, what about the adrenal glands?

They produce adrenaline!

Exactly! Adrenal glands secrete adrenaline during stress, which is why they're often called the 'fight or flight' glands. How can we remember their role?

We can use 'AF' for Adrenal 'F'ight or flight!

Perfect, Student_2! The adrenal glands are crucial for responding to emergencies. Let's recap: Thyroid secretes T4 for metabolism and adrenals secrete adrenaline for stress response.
Hormonal Interactions
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let’s explore how hormones work together. For example, insulin and glucagon from the pancreas regulate blood sugar levels. Can someone explain how they do that?

Insulin lowers blood sugar by helping cells take in glucose, while glucagon raises it by stimulating glycogen breakdown.

Excellent, Student_3! We use 'IG' to remember Insulin decreases and Glucagon increases blood sugar. Hormonal balance is crucial for metabolism.

What happens if there’s an imbalance?

Great question! An imbalance can lead to conditions like diabetes. By understanding these interactions, we see that the endocrine system acts like a finely tuned orchestra.
Regulation and Feedback Mechanisms
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, let’s focus on how the endocrine system maintains homeostasis—can anyone explain feedback mechanisms?

Feedback mechanisms are processes that regulate hormone levels to maintain balance.

Exactly! There are positive and negative feedback loops. Can anyone give me an example of negative feedback?

Thyroid hormone regulation: When levels are high, TSH drops, and when they're low, TSH rises!

Great job, Student_1! This mechanism ensures a stable internal environment. To help remember, we can use 'N' for Negative feedback avoids too much of a hormone.
Conclusion and Summary Reiteration
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's summarize everything we've learned about the endocrine system! Who can name the major glands?

Hypothalamus, pituitary, thyroid, adrenal, pancreas, gonads!

Correct! Each gland is critical for hormonal balance. Remember the acrostics we created, PG for Pituitary Gland, AF for Adrenal Fight, and IG for Insulin/Glucagon. Why are these so important?

They maintain homeostasis and respond to changes in the body.

Exactly! By understanding the endocrine system, we recognize its vital role in health and well-being.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section details the human endocrine system, highlighting major glands, the hormones they produce, and their significant roles in regulating various body functions such as metabolism, growth, and homeostasis. It illustrates how hormones interact with their target tissues to maintain internal balance.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
The human endocrine system consists of various glands that produce hormones essential for regulating myriad physiological processes, including metabolism, growth, and reproductive functions. Key glands include the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, pineal gland, thyroid, parathyroid, thymus, adrenal glands, pancreas, and gonads (testis and ovary). Each of these glands plays a unique role in hormone production that collectively influences body homeostasis.
Major Hormones and Their Functions
- Hypothalamus: Produces releasing and inhibiting hormones that regulate the pituitary gland.
- Pituitary Gland: Contains the anterior (producing growth hormone, TSH, ACTH) and posterior parts (releases oxytocin and vasopressin), which control various body processes.
- Pineal Gland: Secretes melatonin for regulating circadian rhythms.
- Thyroid Gland: Produces thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) for metabolic regulation.
- Parathyroid Gland: Secretes parathyroid hormone (PTH) to regulate calcium levels in the blood.
- Thymus: Secretes thymosins that are vital for T-lymphocyte differentiation and immune response.
- Adrenal Gland: Composed of the adrenal cortex (producing glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids) and medulla (secreting adrenaline and noradrenaline) which manage stress responses.
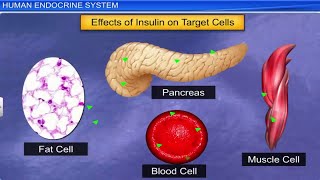
- Pancreas: Produces insulin and glucagon to regulate blood sugar levels.
- Testis: Secretes testosterone for male sex characteristics and spermatogenesis.
- Ovary: Produces estrogen and progesterone, crucial for female reproductive functions.
Additionally, non-endocrine organs such as the heart and kidneys secreting atrial natriuretic factor (reducing blood pressure) and erythropoietin (stimulating rbc formation) respectively, underscore the extensive role of hormones in maintaining homeostasis throughout the body.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of Hormones and Their Roles
Chapter 1 of 12
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
There are special chemicals which act as hormones and provide chemical coordination, integration and regulation in the human body. These hormones regulate metabolism, growth and development of our organs, the endocrine glands or certain cells.
Detailed Explanation
Hormones are special chemicals produced by endocrine glands. They play a crucial role in coordinating and regulating various functions in the body, including metabolism and growth. Each hormone has a specific target or function, making them vital for maintaining homeostasis in the body.
Examples & Analogies
Think of hormones like traffic signals that manage the flow of cars in a busy intersection. Just as traffic signals control when cars should stop or go to ensure smooth traffic, hormones regulate bodily functions to ensure everything works harmoniously.
Components of the Endocrine System
Chapter 2 of 12
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The endocrine system is composed of hypothalamus, pituitary and pineal, thyroid, adrenal, pancreas, parathyroid, thymus and gonads (testis and ovary).
Detailed Explanation
The endocrine system is made up of various glands responsible for producing and secreting hormones. Each gland has specific hormones and functions that contribute to overall body regulation. For instance, the hypothalamus controls many bodily functions by signaling the pituitary gland to release hormones.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine the endocrine system as a symphony orchestra, where each gland represents a musician. Each musician plays a specific instrument that contributes to a harmonious performance, similar to how each gland produces unique hormones that help the body function well.
Functions of Specific Glands
Chapter 3 of 12
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The pituitary gland is divided into three major parts, which are called as pars distalis, pars intermedia and pars nervosa. Pars distalis produces six trophic hormones. Pars intermedia secretes only one hormone, while pars nervosa (neurohypophysis) secretes two hormones. The pituitary hormones regulate the growth and development of somatic tissues and activities of peripheral endocrine glands.
Detailed Explanation
The pituitary gland, known as the 'master gland', has three sections, each producing different hormones. The pars distalis produces hormones that control other glands and many body functions, while the pars intermedia and nervosa have specialized roles. This hierarchical structure ensures precise control over growth and metabolism.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the pituitary gland as a manager who oversees a team. The manager (pituitary) delegates tasks to different team members (other glands) to keep the project (body functions) on track. When the manager does their job well, the entire team works smoothly.
Key Hormonal Functions
Chapter 4 of 12
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The pineal gland secretes melatonin, which plays a very important role in the regulation of 24-hour (diurnal) rhythms of our body (e.g., rhythms of sleep and state of being awake, body temperature, etc.).
Detailed Explanation
Melatonin is crucial for regulating sleep patterns, marking night and day in the body's biological clock. By doing so, it helps maintain various activities that are synchronous with circadian rhythms, ensuring that physiological processes like sleep and wakefulness occur at the right times.
Examples & Analogies
Consider melatonin as a conductor of a clock. Just as a conductor signals when to perform, melatonin signals your body when it's time to sleep or wake up, helping to maintain a natural daily rhythm.
Thyroid and calcium regulation
Chapter 5 of 12
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The thyroid gland hormones play an important role in the regulation of the basal metabolic rate, development and maturation of the central neural system, erythropoiesis, metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins and fats, menstrual cycle. Another thyroid hormone, i.e., thyrocalcitonin regulates calcium levels in our blood by decreasing it.
Detailed Explanation
The thyroid produces hormones that regulate various metabolic processes, including energy use and growth. Additionally, thyrocalcitonin manages calcium levels in the blood, which is essential for bone health and muscle function.
Examples & Analogies
Picture the thyroid as a thermostat that maintains temperature in a house. If the temperature gets too high or too low, the thermostat adjusts it. Similarly, the thyroid regulates the body's metabolic rate and calcium levels to keep everything running smoothly.
Role of the Parathyroid Hormone
Chapter 6 of 12
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The parathyroid glands secrete parathyroid hormone (PTH) which increases the blood Ca2+ levels and plays a major role in calcium homeostasis.
Detailed Explanation
Parathyroid hormone (PTH) reverses the actions of thyrocalcitonin by raising calcium levels in the blood. It does this by targeting bones and kidneys, ensuring that calcium stays available for vital bodily functions like muscle contraction and nerve signaling.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine PTH as a maintenance crew that ensures a steady supply of materials (calcium) for essential construction projects (like muscle and nerve function). Just like a crew monitors supply levels and adjusts as needed, PTH maintains calcium levels in the body.
Thymus and Immune Regulation
Chapter 7 of 12
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The thymus gland secretes thymosins which play a major role in the differentiation of T-lymphocytes, which provide cell-mediated immunity. In addition, thymosins also increase the production of antibodies to provide humoral immunity.
Detailed Explanation
The thymus is crucial for developing the immune system, particularly T-lymphocytes that fight infections. Thymosins ensure that the body is equipped with the right cells to respond to pathogens and maintain immunity through antibody production.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the thymus like a training camp for soldiers (T-lymphocytes). Just as a camp prepares soldiers mentally and physically for battles (fighting infections), the thymus equips immune cells with the knowledge and tools needed to combat threats.
Functions of the Adrenal Gland
Chapter 8 of 12
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The adrenal gland is composed of the centrally located adrenal medulla and the outer adrenal cortex. The adrenal medulla secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine. These hormones increase alertness, pupilary dilation, piloerection, sweating, heart beat, strength of heart contraction, rate of respiration, glycogenolysis, lipolysis, proteolysis.
Detailed Explanation
The adrenal gland is vital for the 'fight or flight' response, with the adrenal medulla releasing epinephrine and norepinephrine during stress. These hormones prepare the body for rapid action, increasing heart rate and energy availability.
Examples & Analogies
Consider the adrenal medulla as a fire alarm system. When triggered (stressed), the alarm (epinephrine/norepinephrine) prepares you to either fight the fire (handle the threat) or flee to safety. The body becomes energized and sharp, ready to respond.
Pancreatic Regulation of Blood Sugar
Chapter 9 of 12
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The endocrine pancreas secretes glucagon and insulin. Glucagon stimulates glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis resulting in hyperglycemia. Insulin stimulates cellular glucose uptake and utilisation, and glycogenesis resulting in hypoglycemia.
Detailed Explanation
The pancreas maintains blood sugar levels through two key hormones: glucagon and insulin. Glucagon raises blood sugar when it falls too low, while insulin lowers it by helping cells absorb glucose for energy.
Examples & Analogies
Picture the pancreas as a smart thermostat for blood sugar levels. When sugar levels drop (cold), glucagon kicks in to heat things up. When levels rise (hot), insulin cools it down by helping the body's cells take in the excess sugar.
Hormonal Functions in Male and Female Reproductive Systems
Chapter 10 of 12
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The testis secretes androgens, which stimulate the development, maturation and functions of the male accessory sex organs, appearance of the male secondary sex characters, spermatogenesis, male sexual behaviour, anabolic pathways and erythropoiesis.
Detailed Explanation
Testosterone and other androgens are crucial for male sexual development and reproductive functions. They stimulate growth and maturation of male reproductive tissues and influence behaviors and physical traits associated with masculinity.
Examples & Analogies
Think of androgens as the builders of a construction site (male reproductive traits). Just like builders are responsible for constructing the framework of a building, androgens shape male characteristics, including muscle growth and behavior.
Female Hormones and Their Roles
Chapter 11 of 12
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The ovary secretes estrogen and progesterone. Estrogen stimulates growth and development of female accessory sex organs and secondary sex characters. Progesterone plays a major role in the maintenance of pregnancy as well as in mammary gland development and lactation.
Detailed Explanation
Estrogen and progesterone are vital for female reproductive health. Estrogen is important for the development of female characteristics and tissues, while progesterone supports pregnancy and prepares the body for nurturing an infant.
Examples & Analogies
Consider estrogen as a gardener nurturing a garden (female characteristics). Just as a gardener encourages plants to blossom and thrive, estrogen promotes the development of female traits and reproductive abilities. Progesterone is like the irrigation system that supports life during pregnancy.
Additional Hormonal Functions and Their Roles
Chapter 12 of 12
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The atrial wall of the heart produces atrial natriuretic factor which decreases the blood pressure. Kidney produces erythropoietin which stimulates erythropoiesis. The gastrointestinal tract secretes gastrin, secretin, cholecystokinin and gastric inhibitory peptide.
Detailed Explanation
Various non-endocrine organs also play important roles in hormone production. For example, the heart produces atrial natriuretic factor, which regulates blood pressure, while the kidneys produce erythropoietin to stimulate red blood cell production. The gastrointestinal tract produces hormones that aid digestion.
Examples & Analogies
Think of this as a team sport where different players (organs) contribute to the overall performance (body functions). Each player has a specific role, like the heart and kidneys producing hormones to manage blood pressure and blood cell production.
Key Concepts
-
Hormones: Chemical messengers regulating body functions.
-
Endocrine Glands: Ductless glands that release hormones into the bloodstream.
-
Feedback Mechanisms: Processes to maintain hormone balance.
Examples & Applications
Insulin from the pancreas lowers blood sugar levels.
Thyroid hormones regulate metabolism and development.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Insulin lowers sugar down, glucagon brings it around.
Stories
Imagine a kingdom (the body) ruled by wise glands. The Pituitary King sends messages to the other glands to regulate growth and stress like a good ruler.
Memory Tools
PG - Pituitary Gland, AD - Adrenal for 'Adrenaline'!
Acronyms
T4 for Thyroxine to remember functions related to metabolism.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Hormone
A chemical substance produced by glands that regulates physiological processes in the body.
- Endocrine Gland
Glands that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream.
- Feedback Mechanism
A process that helps regulate hormonal levels to maintain homeostasis.
- Adrenaline
A hormone produced by adrenal glands that prepares the body for fight-or-flight responses.
- Insulin
A hormone produced by the pancreas that lowers blood sugar levels.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
