Parathyroid Gland
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Overview of the Parathyroid Gland
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to discuss the parathyroid glands which are crucial for calcium metabolism in our bodies. Can anyone tell me where they are located?

They are located behind the thyroid gland, right?

Exactly! There are four parathyroid glands, and they secrete parathyroid hormone, commonly known as PTH. What role do you think PTH plays in our body?

It must have something to do with calcium levels?

Yes! PTH increases the calcium levels in the blood. Can anyone think of how it does that?

Doesn't it act on bones to release calcium?

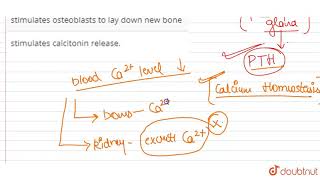
Correct! PTH stimulates the process of bone resorption, which releases calcium into the bloodstream. This is a significant mechanism of action. Remember the acronym 'BKR' for Bones, Kidneys, and Restoration. PTH acts on bones, kidneys, and helps in nutritional restoration by aiding absorption.

What does it do to the kidneys?

Great question! PTH also stimulates the reabsorption of calcium in the renal tubules, which means it prevents calcium from being lost in urine. Let’s sum up: PTH increases blood calcium levels by acting on bones, kidneys, and the intestines.
Mechanisms of PTH Action
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's dive deeper! What happens in the bones when PTH is secreted?

It causes resorption, but what does that mean?

Bone resorption means that the cells in the bone release calcium into the blood. This is something to remember— bone resorption increases calcium levels in the blood. Can anyone explain how this oxidation process might affect the body?

If bones are broken down for calcium, wouldn't that make bones weaker?

Exactly! Long-term elevation of PTH can weaken bones if not balanced with other hormones like TCT. What about its action in the intestines?

It probably enhances calcium absorption from food?

Correct again! PTH indirectly increases calcium absorption in the intestines by activating vitamin D. This is an essential aspect of maintaining calcium balance. Let’s summarize: PTH increases blood calcium by acting on bones, kidneys, and aiding nutrient absorption.
Regulation of PTH Secretion
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Lastly, how do you think the body regulates the secretion of PTH?

Maybe it depends on calcium levels in the blood?

Bingo! PTH secretion is primarily regulated by the levels of calcium ions in the blood. When calcium levels drop, PTH is secreted. What do you think happens once calcium levels rise?

Wouldn't the secretion decrease?

Exactly! This negative feedback ensures calcium homeostasis. Remember: 'Low calcium, high PTH.' Can anyone summarize the role of PTH for me?

PTH raises blood calcium by acting on bones to release calcium, kidneys to retain calcium, and intestines to absorb calcium!

Great summary! Remember that all these actions play a critical role in maintaining overall health.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Located behind the thyroid gland, the parathyroid glands play a crucial role in maintaining calcium homeostasis through the secretion of parathyroid hormone (PTH). PTH increases blood calcium levels by promoting bone resorption, enhancing renal calcium reabsorption, and increasing dietary calcium absorption.
Detailed
Parathyroid Gland
The parathyroid glands consist of four small glands located at the back of the thyroid gland. These glands are pivotal for calcium regulation due to their secretion of parathyroid hormone (PTH). The primary role of PTH is to elevate calcium levels in the blood when it is low by acting on bones, kidneys, and intestines.
- Bone: Stimulates bone resorption, leading to the release of calcium into the bloodstream.
- Kidneys: Increases reabsorption of calcium, reducing its excretion in urine.
- Intestines: Enhances calcium absorption from dietary sources processed in the intestines.
PTH works alongside thyrocalcitonin (TCT) to maintain calcium balance in the body, thus highlighting the importance of both hormones in physiological processes.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
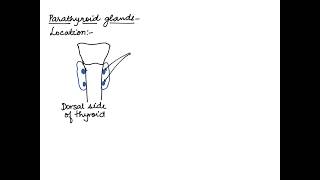
Location and Structure of Parathyroid Glands
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In humans, four parathyroid glands are present on the back side of the thyroid gland, one pair each in the two lobes of the thyroid gland.
Detailed Explanation
Humans have two pairs of parathyroid glands, making a total of four. They are situated on the backside of the thyroid gland, which is located in the neck. Each pair corresponds to one lobe of the thyroid. Their location is crucial as they work closely with the thyroid gland in regulating calcium levels in the body.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the parathyroid glands as small, diligent assistants to the larger boss (the thyroid gland). Their position behind the thyroid is like having dedicated helpers who monitor and manage calcium, ensuring that everything runs smoothly.
Function and Secretion of Parathyroid Hormone (PTH)
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The parathyroid glands secrete a peptide hormone called parathyroid hormone (PTH). The secretion of PTH is regulated by the circulating levels of calcium ions.
Detailed Explanation
The main hormone produced by the parathyroid glands is parathyroid hormone (PTH). This hormone plays a vital role in maintaining calcium homeostasis in the body. The glands carefully gauge the level of calcium in the blood, and when it drops too low, they release more PTH. This process ensures that the body maintains an adequate amount of calcium, necessary for various bodily functions, including muscle contraction and blood clotting.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a smart thermostat that controls the heating in your home. When it senses that the temperature drops, it turns on the heater. Similarly, when the parathyroid glands detect low calcium levels in the blood, they release PTH to increase calcium levels.
Effects of Parathyroid Hormone (PTH)
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Parathyroid hormone (PTH) increases the Ca2+ levels in the blood. PTH acts on bones and stimulates the process of bone resorption (dissolution/demineralisation). PTH also stimulates reabsorption of Ca2+ by the renal tubules and increases Ca2+ absorption from the digested food.
Detailed Explanation
PTH has several critical effects on the body. First, it triggers the bones to release calcium into the bloodstream by stimulating bone resorption. Second, it promotes the kidneys to reabsorb more calcium from the urine, reducing its loss. Lastly, it enhances calcium absorption in the intestines from the food we eat. Through these actions, PTH ensures that calcium levels in the blood remain stable and sufficient.
Examples & Analogies
Think of PTH as a manager overseeing calcium resources. When more calcium is needed, it instructs the body to not only release calcium from the storage unit (bones) but also to save as much as possible during cleanup (kidneys) and to gather more from supplies (food).
Role of PTH in Calcium Balance
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
It is, thus, clear that PTH is a hypercalcemic hormone, i.e., it increases the blood Ca2+ levels. Along with TCT, it plays a significant role in calcium balance in the body.
Detailed Explanation
PTH is termed a 'hypercalcemic hormone' because its overall effect is to elevate blood calcium levels. It works in conjunction with other hormones, such as thyrocalcitonin (TCT), which acts to lower calcium levels when they become too high. The balance between these hormones is essential for maintaining calcium homeostasis, which is vital for overall health.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a balanced scale that keeps track of calcium levels. PTH is like a weight added to one side to increase the amount of calcium, while TCT is like a counterweight that reduces it when necessary. Together, they ensure that the scale remains balanced, representing stable calcium levels in the body.
Key Concepts
-
Calcium Regulation: Parathyroid hormone (PTH) is crucial for increasing blood calcium levels.
-
Bone Resorption: PTH promotes bone resorption, releasing calcium into the bloodstream.
-
Kidney Function: PTH enhances renal reabsorption of calcium, reducing excretion.
-
Nutritional Importance: PTH indirectly increases calcium absorption from the intestines.
Examples & Applications
Example 1: Low blood calcium levels trigger increased PTH secretion.
Example 2: High levels of PTH lead to bone demineralization over time.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
PTH increases calcium, hear the call, bones release it, so we stand tall.
Stories
Imagine a kingdom (the body) where calcium is the treasure. PTH is the knight sent to gather treasure (calcium) from the castle (bones) and deliver it to the town (blood).
Memory Tools
Remember 'BKR' for PTH action: Bones release calcium, Kidneys reabsorb it, Restoration of dietary calcium.
Acronyms
Use 'CaP' for Calcium Parathormone - the hormone that raises calcium levels.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Parathyroid glands
Four small glands located behind the thyroid gland responsible for regulating calcium levels in the blood.
- Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
A peptide hormone secreted by the parathyroid glands that increases calcium levels in the blood.
- Bone resorption
The process by which bone tissue is broken down to release minerals, primarily calcium, into the bloodstream.
- Calcium homeostasis
The regulation of calcium levels in the body, primarily through the actions of hormones like PTH and TCT.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
