Thymus
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to the Thymus
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will learn about the thymus gland. Can anyone tell me where it is located?

Isn't it located between the lungs?

That's correct! The thymus is situated between the lungs and behind the sternum. It's an essential part of our immune system.

What does the thymus do exactly?

Great question! The thymus secretes hormones called thymosins, which help with the differentiation of T-lymphocytes, crucial for our immune response.

What are T-lymphocytes?

T-lymphocytes, or T-cells, are a type of white blood cell vital for cell-mediated immunity. They help protect our body against infections.

So, the thymus helps in making these T-cells?

Exactly! It plays a significant role in developing these immune cells. Remember that the thymus gland is often called the 'school of T-cells' because it's where they mature.

In summary, the thymus is located between the lungs, produces thymosins, and is essential for T-cell maturation, contributing to our immune defenses.
Function of Thymosins
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's explore how thymosins work in our immune system. What role do you think they play in T-cell differentiation?

Do they help T-cells become activated?

Not directly, but they enable the differentiation process. Thymosins signal certain precursor cells in the bone marrow to develop into T-lymphocytes.

And what happens after they mature?

Once matured, the T-cells migrate to peripheral organs like the lymph nodes, where they respond to infections or foreign substances.

I read that the thymus degenerates as you age. Does that affect immunity?

Absolutely! As the thymus shrinks and produces less thymosin, the production of T-cells slows down, leading to a weakened immune response in older individuals.

To summarize, thymosins are key in T-lymphocyte differentiation, and their production decreases with age, impacting immune system efficiency.
Thymus and Immune System Aging
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll discuss how the thymus gland changes with age. What do you think happens as we get older?

Does it stop working?

Not entirely, but its size reduces and it produces less thymosin, which can lead to a decrease in T-lymphocyte production.

So, older people might get sick more often because of a weaker immune system?

Yes! This reduction in T-cells can make older adults more susceptible to infections and diseases.

Are there any ways to boost the immune system as we age?

While we can't reverse thymus degeneration, healthy lifestyle choices like balanced nutrition and regular exercise can support a strong immune system.

In summary, as we age, the thymus decreases in size and function, leading to fewer T-cells and potentially weaker immune responses.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Located between the lungs and behind the sternum, the thymus gland is vital for developing the immune system. It secretes thymosins, which promote the differentiation of T-lymphocytes, essential for cell-mediated immunity, and also aid in antibody production. With age, the thymus degenerates, decreasing thymosin production and weakening immune responses.
Detailed
Thymus
The thymus gland is a lobular structure situated between the lungs, behind the sternum, and above the aorta. It plays a crucial role in the development of the immune system. The primary function of the thymus is to secrete thymosins, a group of peptide hormones that are essential for the differentiation and maturation of T-lymphocytes. These T-cells are vital components of the adaptive immune response, providing cell-mediated immunity.
In addition to promoting T-lymphocyte development, thymosins also facilitate the production of antibodies, which contribute to humoral immunity, thereby playing a dual role in the immune system. Importantly, the thymus undergoes degeneration as an individual ages, leading to a reduction in thymosin production. This decline has significant implications for the immune system, as older individuals often experience weakened immune responses.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Location and Structure of the Thymus
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
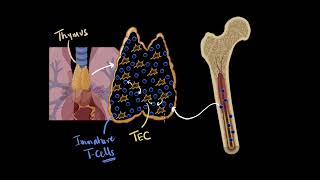
The thymus gland is a lobular structure located between lungs behind sternum on the ventral side of aorta.
Detailed Explanation
The thymus gland is situated in the upper chest, located between the lungs and just behind the sternum (breastbone). It has a lobular structure, meaning it is divided into smaller sections, which helps organize the hormones it produces for immune function. The position of the thymus is important because it is close to the heart and lungs, which are vital organs that also interact with the immune system.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the thymus like a training camp for soldiers, located strategically behind the front lines (the heart and lungs) where they learn to fight off enemies (diseases). The interaction with nearby organs allows for swift responses when faced with threats.
Function of the Thymus
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The thymus plays a major role in the development of the immune system. This gland secretes the peptide hormones called thymosins.
Detailed Explanation
The thymus is crucial in developing the body's immune system. It produces special hormones known as thymosins, which are necessary for differentiating T-lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). These T-lymphocytes are vital for cell-mediated immunity, which helps the body fight off infections and diseases. In other words, the thymus helps train the immune system to recognize and attack pathogens (like bacteria and viruses).
Examples & Analogies
Imagine the thymus as a school where T-lymphocytes are students learning how to recognize and combat different germs. Just like soldiers need training to understand their enemy, T-lymphocytes need thymosins from the thymus to become effective defenders of the body.
Immune Function and its Importance
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Thymosins play a major role in the differentiation of T-lymphocytes, which provide cell-mediated immunity. In addition, thymosins also promote production of antibodies to provide humoral immunity.
Detailed Explanation
Thymosins are vital for two types of immunity: cell-mediated and humoral immunity. Cell-mediated immunity involves T-lymphocytes directly attacking infected or cancerous cells, while humoral immunity is about producing antibodies that neutralize pathogens in the body fluids. The thymus gland ensures that T-lymphocytes are properly trained and developed to effectively handle various infections. Without a functional thymus, the body may struggle to mount appropriate immune responses.
Examples & Analogies
Consider the immune system as a team of first responders. The thymus acts like a training facility that not only prepares the rapid responders (T-lymphocytes) for on-the-ground confrontations but also teaches them to call for backup by producing antibodies (humoral immunity). This teamwork is essential for a strong defense against diseases.
Thymus Degeneration and Immune Response
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Thymus is degenerated in old individuals resulting in a decreased production of thymosins. As a result, the immune responses of old persons become weak.
Detailed Explanation
As people age, the thymus gradually shrinks in size and is less effective in producing thymosins. This degeneration leads to a decline in the production and activity of T-lymphocytes. Consequently, older adults may have weaker immune responses, making them more susceptible to infections and diseases. This reflects the importance of thymosin production for maintaining a robust immune system throughout life.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a once-busy firehouse (the thymus) that becomes less staffed (due to degeneration) as it ages, resulting in slower responses to fires (infections). As the firehouse diminishes, the community (body) can struggle more to fight off fires, highlighting the vital need for a well-functioning thymus, especially in older adults.
Key Concepts
-
Thymus: Essential for T-cell development and immune system function.
-
Thymosins: Hormones that promote the differentiation of T-lymphocytes.
-
T-cells: Play a crucial role in the adaptive immune response.
-
Immune system aging: Reduced thymus function leads to a weaker immune response in older adults.
Examples & Applications
Thymosin production is crucial for the body's ability to fight off viral infections.
As individuals age, they may experience more frequent infections due to decreased T-cell production.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Thymus in the chest, where T-cells go to rest.
Stories
Once upon a time, in a land where T-cells were born, a special school called the thymus taught them how to fight battles against invaders.
Memory Tools
Remember T for Thymus, T-cells, and Thymosins – they all work together for immunity!
Acronyms
T's in T-cell differentiation
for Thymus
for Thymosins
for T-cells!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Thymus
A lobular gland located between the lungs that plays a crucial role in immune system development.
- Thymosins
Peptide hormones secreted by the thymus that are essential for T-lymphocyte differentiation and immune function.
- TLymphocytes (Tcells)
A type of white blood cell involved in cell-mediated immunity.
- Cellmediated immunity
An immune response mechanism that involves T-cells attacking infected or cancerous cells.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
