Genesis of Periodic Classification
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Dobereiner's Triads
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to explore the early classification of elements, starting with Johann Dobereiner's work in the early 1800s. Can anyone tell me what he observed?

He noticed groups of three elements that had similar properties and atomic weights?

Exactly! These groups are called triads. Dobereiner found that the middle element's atomic weight was roughly the average of the other two. Can someone think of examples of these triads?

Lithium, sodium, and potassium?

Good! These three are part of a triad. Remember this pattern of periodicity; it's foundational. Can you see a trend here?

It seems like similar properties repeated every three elements?

Correct! This laid a groundwork that others would build on. Let's summarize: Dobereiner introduced us to the idea of periodic relationships among elements.
Newlands' Law of Octaves
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Following Dobereiner, we have John Newlands who proposed his Law of Octaves. What was unique about his approach?

He arranged elements by increasing atomic weight and found that properties repeated every eighth element, like musical octaves?

Exactly! His concept likened the periodicity in elements to musical notes. However, he faced criticism for only fitting up to calcium. Why do you think that was?

Because not all elements fit neatly into that pattern after calcium?

Spot on! Newlands’ Law of Octaves was foundational, winning him recognition with the Davy Medal later on. Let's conclude this session by highlighting: Newlands expanded the idea of periodicity but needed more flexibility.
Mendeleev and the Periodic Law
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's talk about Dmitri Mendeleev, often credited with crafting the first modern Periodic Table. What made his work stand out?

He organized elements by both properties and atomic weights, and left gaps for undiscovered elements!

Exactly! Mendeleev's foresight in predicting properties of undiscovered elements, like Eka-aluminium and Eka-silicon, was groundbreaking. Can you summarize Mendeleev’s contribution?

He systematically arranged elements based on properties and atomic weight, predicting new elements' characteristics.

Well said! His contributions solidified the concept of periodicity. Remember, Mendeleev's work was critical in developing a scientific approach to classifying elements.
Modern Periodic Law
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let’s discuss how the Periodic Law evolved. What is the modern version of the periodic law?

It's that the properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic numbers instead of atomic weights.

Right! This change arose after Henry Moseley highlighted the significance of atomic numbers over atomic mass. Why do you think this shift was important?

It provided a more accurate and consistent way to classify elements based on a fundamental property—protons.

Exactly! This advancement underscored the periodic relationship in a more reliable framework, enhancing the use of the Periodic Table in chemistry. Let’s summarize: The transition from Mendeleev to Modern Periodic Law was essential for the advancement of chemical classification.
Significance of Periodic Classification
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

To wrap up our discussion, why do you think a comprehensive understanding of periodic classification is crucial in chemistry?

It helps us predict the properties of elements and understand chemical behavior based on their position in the Periodic Table.

Exactly! The periodic classification allows students and scientists to rationalize chemical behaviors and anticipate patterns, making it a cornerstone of chemistry. What is one key takeaway from today?

The development of the Periodic Table shows the evolution of scientific understanding and the importance of classification in science.

Great summary! This understanding enriches our grasp of the natural world and its underlying principles.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section outlines the historical progression of the classification of elements, starting with Johann Dobereiner's triads, followed by Newlands' Law of Octaves, and culminating in Mendeleev and Meyer's contributions to the Periodic Law. It emphasizes the importance of atomic weights and later, atomic numbers in organizing elements, showcasing the significance of periodicity in chemical properties.
Detailed
Genesis of Periodic Classification
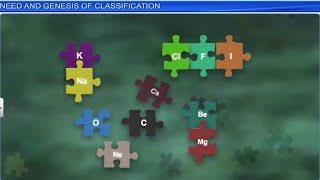
The classification of elements into groups and the development of the Periodic Law were pivotal moments in the history of chemistry. Early efforts by scientists such as Johann Dobereiner in the early 1800s first noted the trend among elements through his identification of triads—groups of three elements with similar properties and atomic weights. Dobereiner's observations laid the groundwork for further exploration of periodicity.
In 1865, John Alexander Newlands advanced the idea with his Law of Octaves, noting that every eighth element shared similarities, analogous to the octaves in music. Although his theories faced skepticism, he later received recognition for his contributions. The true foundation of the Periodic Law was laid by Dmitri Mendeleev and Lothar Meyer, who independently proposed that arranging elements by atomic weights revealed periodic trends in their properties. Mendeleev’s version was particularly innovative as he prioritized chemical properties over strict adherence to atomic weight order, leaving gaps for undiscovered elements and predicting their properties effectively. Thus, this section illustrates the critical milestones and personalities in the evolution of the Periodic Table, culminating in the Modern Periodic Law founded on atomic number and electronic configuration.
Youtube Videos





Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Early Classification by Dobereiner
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Classification of elements into groups and development of Periodic Law and Periodic Table are the consequences of systematising the knowledge gained by a number of scientists through their observations and experiments. The German chemist, Johann Dobereiner in early 1800’s was the first to consider the idea of trends among properties of elements. By 1829 he noted a similarity among the physical and chemical properties of several groups of three elements (triads). In each case, he noticed that the middle element of each of the triads had an atomic weight about halfway between the atomic weights of the other two. Also the properties of the middle element were in between those of the other two members.
Detailed Explanation
Johann Dobereiner was a pioneering chemist who first recognized patterns in the properties of elements. He grouped elements into sets of three called triads. For each triad, he noticed that the middle element had an atomic weight that was approximately the average of the other two elements' atomic weights. This observation suggested that there were relationships among the elements that could help in understanding their properties. Dobereiner's work laid the groundwork for more systematic approaches to element classification.
Examples & Analogies
Think of trying to group your friends by their interests. If you have three friends who all like sports, music, and art, you might notice that one of them likes all three activities in a balanced way, while the other two prefer just one. This is similar to how Dobereiner saw that the middle element of his triads had properties that were 'in between' the other two.
Newlands and the Law of Octaves
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The English chemist, John Alexander Newlands in 1865 profounded the law of octaves. He arranged the elements in increasing order of their atomic weights and noted that every eighth element had properties similar to the first element. The relationship was just like every eighth note that resembles the first in octaves of music. Newlands’s Law of Octaves seemed to be true only for elements up to calcium. Although his idea was not widely accepted at that time, he, for his work, was later awarded Davy Medal in 1887 by the Royal Society, London.
Detailed Explanation
John Newlands built upon Dobereiner's observations and proposed the 'Law of Octaves.' He arranged the known elements in a sequence based on increasing atomic weights. Newlands discovered that every eighth element had similar properties, likening this pattern to musical octaves. While this pattern was clear for the first 20 elements, it didn't hold true for all elements, leading to criticism of his method. Despite this, Newlands' work marked an important step in the classification of elements and was later recognized with an award.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine playing a piano. Every eighth note sounds kind of similar to the first note. Just as music has patterns and structures, Newlands showed that elements have their own patterns in their properties when ordered by weight.
Mendeleev and Periodic Law
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The Periodic Law, as we know it today owes its development to the Russian chemist, Dmitri Mendeleev (1834-1907) and the German chemist, Lothar Meyer (1830-1895). Working independently, both the chemists in 1869 proposed that on arranging elements in the increasing order of their atomic weights, similarities appear in physical and chemical properties at regular intervals. Mendeleev arranged elements in horizontal rows and vertical columns of a table in order of their increasing atomic weights in such a way that the elements with similar properties occupied the same vertical column or group.
Detailed Explanation
Dmitri Mendeleev significantly advanced the classification of elements. He created a comprehensive table where elements were arranged by increasing atomic weight. In this table, elements displaying similar properties were placed in the same columns, or groups. Mendeleev's work provided a structured approach to chemistry, demonstrating that elements are not random but instead exhibit periodic behaviors based on their atomic characteristics.
Examples & Analogies
Think about arranging your collection of books by genre. You might place all the mystery novels in one section, all the science fiction in another, and so on. Just like how Mendeleev organized elements with similar properties together, you would group books with similar themes, making it easier to find what you're looking for.
Mendeleev's Predictions
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
While Dobereiner initiated the study of periodic relationship, it was Mendeleev who was responsible for publishing the Periodic Law for the first time. He fully recognized the significance of periodicity and used a broader range of physical and chemical properties to classify the elements. Mendeleev proposed that some elements were still undiscovered and, therefore, left several gaps in the table. He predicted the existence and properties of these elements, such as gallium and germanium, demonstrating the predictive power of his classification.
Detailed Explanation
Mendeleev's approach to the Periodic Table was groundbreaking. He not only categorized the known elements but also left spaces for those that had not yet been discovered. This foresight led to the successful prediction of elements like gallium and germanium, showcasing that the periodic classification could be used as a tool for future scientific discovery. It was a remarkable testament to the idea that understanding trends in chemistry can lead to predicting what we have yet to find.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a treasure map where some of the treasures are marked, but there are blank spaces where you think more prizes might be hidden. If you can guess where the next big treasure could be based on what you already know about the layout of the map, just like Mendeleev predicted the elements, you're using your understanding of patterns to forecast future discoveries!
Key Concepts
-
Periodic Table: A systematic organization of elements based on their properties and atomic numbers.
-
Periodic Law: The concept that the properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic number.
-
Triads: Groups of three elements with similar properties identified by Dobereiner.
-
Law of Octaves: Newlands' hypothesis connecting the properties of elements every eighth one.
-
Eka-Aluminium: Mendeleev's predicted element later identified as Gallium.
Examples & Applications
Dobereiner's triad of lithium, sodium, and potassium showcases similar chemical properties.
Newlands’ Law of Octaves exemplifies the relationship between every eighth element.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Triads grouped together, like peas in a pod; Chemical patterns emerge, giving scientists a nod.
Stories
Imagine a chef, Dobereiner, who makes a soup with three key ingredients, ensuring that the middle ingredient balances the flavors, just like elements in his triad.
Memory Tools
Remember: T for Triads and T for Three. They always match in chemistry.
Acronyms
Use DOI for Dobereiner, Octaves (Newlands), and Innovation (Mendeleev) to recall the pioneers of periodic classification.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Periodic Table
A tabular arrangement of the chemical elements, organized by atomic number and properties.
- Triads
Groups of three elements with similar properties, where the middle element has an atomic weight roughly the average of the other two.
- Law of Octaves
John Newlands' observation that every eighth element displayed similar properties.
- Periodic Law
The concept stating that properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic number.
- EkaAluminium
A name Mendeleev gave to the predicted element gallium.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
