Ocean Floor Configuration
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Ocean Floor Structure
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to learn about the ocean floor's structure. It can be segmented into three major divisions: continental margins, deep-sea basins, and mid-ocean ridges.

What exactly are continental margins?

Great question! Continental margins are the areas where land meets the ocean, including features like shelves and trenches.

Why are they important?

They help us understand the relationship between land and sea, crucial for studying ocean currents and ecosystems.
Abyssal Plains
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let's talk about abyssal plains. These are vast, flat areas of the ocean floor.

How are they formed?

They form from sediments that accumulate over time, creating incredibly flat sea beds. They can be crucial for studying marine life.

So, they collect a lot of sediments?

Yes! They collect sediments that drift down from nearby landmasses and the surrounding ocean floor.
Mid-Ocean Ridges
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's discuss mid-ocean ridges, the longest mountain range on Earth located underwater.

What makes them special?

These ridges are sites of volcanic activity, indicating how tectonic plates interact.

So they're related to plate tectonics?

Exactly! The Earth’s lithosphere dynamics greatly shape ocean floor configurations.
Distribution of Earthquakes and Volcanoes
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

The ocean floor's structure explains the distribution of earthquakes and volcanoes.

How do they connect?

Areas near mid-ocean ridges often experience earthquakes and volcanic activity due to tectonic movements.

That's interesting! So does that mean mid-ocean ridges are active?

Yes! They are highly active and central to understanding Earth's geological features.
Continental Margins and Their Features
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let's dissect continental margins further. They include continental shelves, slopes, and trenches.

What’s the difference among them?

Good question! Shelves are shallow, slopes are steeper, and trenches are deep areas where tectonic plates converge.

Why does that matter?

Understanding these structures is vital for maritime navigation, resource exploration, and environmental conservation.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The ocean floor is divided into major segments based on depth and relief, including abyssal plains, mid-oceanic ridges, and continental margins. This section explains the significance of these features in understanding the distribution of continents and oceans.
Detailed
Ocean Floor Configuration
In this section, we explore the ocean floor's structure, dividing it into three main components that help us understand the geography of the Earth: 1) Continental Margins, which transition between land and sea; 2) Mid-Oceanic Ridges, the world's longest mountain chain located beneath ocean waters; 3) Deep-Sea Basins.
Key Features
Abyssal Plains
These are flat expanses located between the continental margins and mid-oceanic ridges, formed by sediments deposited over time.
Mid-Oceanic Ridges
Characterized by active volcanic areas, these ridges form an interconnected mountain range within the oceans, featuring a central rift that showcases significant geological activity.
Continental Margins
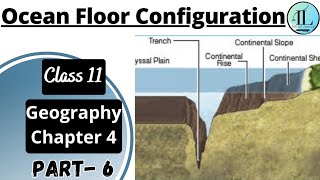
These include various features like continental shelves, slopes, rises, and deep-oceanic trenches—areas crucial to studying oceanic and continental distributions.
Understanding these features is vital for grasping how geological processes shape our planet and affect oceanic and continental movement.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of Ocean Floor Configuration
Chapter 1 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In this section we shall note a few things related to the ocean floor configuration that help us in the understanding of the distribution of continents and oceans. You will be studying the details of ocean floor relief in Chapter 13. The ocean floor may be segmented into three major divisions based on the depth as well as the forms of relief. These divisions are continental margins, deep-sea basins and mid-ocean ridges.
Detailed Explanation
The ocean floor can be divided into three main parts: continental margins, deep-sea basins, and mid-ocean ridges. This division is important for understanding how oceans and continents are positioned on Earth. Each of these parts has unique features and plays a crucial role in the ocean's overall structure.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the ocean floor like a cake that has different layers. The continental margins are like the edges where the cake meets the plate, deep-sea basins can be seen as the cavernous, fluffy middle of the cake, and mid-ocean ridges are like the raised areas on top, where the frosting is piled higher.
Abyssal Plains
Chapter 2 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
These are extensive plains that lie between the continental margins and mid-oceanic ridges. The abyssal plains are the areas where the continental sediments that move beyond the margins get deposited.
Detailed Explanation
Abyssal plains are broad, flat regions of the ocean floor found between the continental margins and the mid-ocean ridges. These plains are formed by sediments that have settled over time, creating a smooth, expansive area, much like how dust settles on a surface. They represent some of the deepest parts of the ocean and are crucial for marine ecosystems.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a large swimming pool. The abyssal plains are the bottom of the pool, where all the dirt and debris settle after a party - it's flat and smooth, unlike the shallow ends where there's more activity and disruption.
Mid-Oceanic Ridges
Chapter 3 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
This forms an interconnected chain of mountain system within the ocean. It is the longest mountain-chain on the surface of the earth though submerged under the oceanic waters. It is characterised by a central rift system at the crest, a fractionated plateau and flank zone all along its length. The rift system at the crest is the zone of intense volcanic activity.
Detailed Explanation
Mid-oceanic ridges are underwater mountain ranges that run through the oceans. They are formed by tectonic plates moving apart, which creates a rift where magma rises, leading to volcanic activity. This mountain chain is the longest on Earth, illustrating the dynamic nature of the ocean floor and how it is constantly reshaped by geological processes.
Examples & Analogies
Think of mid-oceanic ridges as a gigantic underwater zipper that opens up. As the zipper moves apart, magma seeps in, forming new material. Just like a zipper connects two sides of a jacket, these ridges connect different parts of the ocean floor.
Distribution of Earthquakes and Volcanoes
Chapter 4 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Study the maps showing the distribution of seismic activity and volcanoes given in Figure 4.2. You will notice a line of dots in the central parts of the Atlantic Ocean almost parallel to the coastlines. It further extends into the Indian Ocean. It bifurcates a little south of the Indian subcontinent with one branch moving into East Africa and the other meeting a similar line from Myanmar to New Guiana.
Detailed Explanation
By examining maps of earthquakes and volcanoes, one can see that there is a distinct pattern where these geological events tend to occur. Many earthquakes and volcanoes are located along the mid-oceanic ridges, as that is where tectonic plates are moving and where magma escapes from beneath the Earth's crust.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a busy highway where there are lots of traffic jams (earthquakes) and construction work (volcanoes) happening along certain areas. The highway represents the mid-ocean ridges – areas of intense activity because of the movement of cars (tectonic plates).
Continental Margins
Chapter 5 of 5
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
These form the transition between continental shores and deep-sea basins. They include continental shelf, continental slope, continental rise and deep-oceanic trenches.
Detailed Explanation
Continental margins serve as the transition zones between the land and the deep ocean. They have various features including the continental shelf (the sea floor that stretches out from the land), continental slope (a steep drop-off), continental rise (a sloping area at the bottom of the slope), and deep-oceanic trenches (very deep areas of the ocean). These features play key roles in marine ecosystems and ocean currents.
Examples & Analogies
Consider the continental margins as the beach area of a coastline where there's sand (shelf), then a steep drop into the water (slope), then a gradual incline as you go further out (rise), and finally a deep part of the ocean like an underwater canyon (trench).
Key Concepts
-
Continental Margins: Transitional zones from land to ocean featuring vital geological structures.
-
Abyssal Plains: Flat ocean floor regions where sediments accumulate, covering geological formations.
-
Mid-Oceanic Ridges: Underwater mountain ranges formed by volcanic activity and tectonic movements.
-
Deep-Sea Basins: Areas of low elevation on the ocean floor that collect sediments.
Examples & Applications
The Mid-Atlantic Ridge is an example of a mid-ocean ridge, showcasing volcanic activity and tectonic movement.
The abyssal plains between the Americas and Europe represent vast flat areas formed from sediment deposition over millions of years.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In the ocean way down low, Abyssal plains help sediments grow.
Stories
Imagine a deep ocean explorer discovering vast, flat abyssal plains that are home to unique creatures, showcasing the wonders hidden beneath.
Memory Tools
Remember as 'CMD' for Continental Margins, Abyssal plains, and Mid-oceanic ridges.
Acronyms
MACE for 'Mid-oceanic ridges, Abyssal plains, Continental Margins, and Earthquakes'.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Continental Margins
Zones where continents transition to ocean; includes shelves, slopes, rises, and trenches.
- Abyssal Plains
Flat regions on the ocean floor between continental margins and mid-ocean ridges.
- MidOceanic Ridges
Submerged mountain ranges in the ocean where tectonic activity, such as volcanic eruptions, occurs.
- DeepSea Basins
Low areas of the oceanic floor where sediments collect, found beneath the abyssal plains.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
