HOOKE'S LAW
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Hooke's Law
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we're diving into Hooke's Law. Can anyone tell me what it says about the relationship between stress and strain?

It means that stress is proportional to strain, right?

Exactly! We can express this relationship mathematically. It's often written as: Stress = k × Strain, where k is the modulus of elasticity.

What is modulus of elasticity used for?

Great question! The modulus of elasticity tells us how stiff or flexible a material is. The higher the modulus, the stiffer the material. Remember: 'High K—less play!'

So, materials like rubber have a low modulus and can stretch a lot, right?

That's right! Remember, materials like rubber do not accurately follow Hooke's Law for larger strains.

Does this mean that Hooke's Law doesn't apply to all materials?

Yes! While it applies to most materials in their elastic range, there are exceptions, particularly in elastomers and some biological tissues.
Applications of Hooke's Law
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Can anyone think of an application where Hooke’s Law is important?

I think it’s important in buildings. They need to be strong but also flexible.

Right on! Engineers must consider the elastic properties of materials when designing structures to ensure they can withstand loads without permanently deforming.

What about in everyday objects, like springs?

Exactly! Springs follow Hooke’s Law, allowing us to predict how much they will stretch under a load, which is crucial in mechanisms like mattresses and vehicle suspension.

And in tools? Like clamping tools that need to hold things tightly?

Yes! The utilization of materials that obey Hooke’s Law ensures that tools perform effectively without failing.

Can we use this understanding for future technologies, like materials that can 'remember' their shape?

Absolutely! Understanding these fundamental principles allows us to innovate in material science.
Mathematical Representation and Limitations
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's break down the equation: Stress = k × Strain. Can anyone recite what that means in practical terms?

It means that if stress increases, strain increases proportionally up to the elastic limit.

Absolutely! But what happens if we exceed that limit?

The material may deform permanently!

Correct! That's the yield point. For materials exhibiting plastic deformation, Hooke’s Law no longer applies. Remember: 'Past the yield, shape is sealed!'

What if a material stretches too much? Does it regain its shape?

It depends! If within elasticity, it will return. If beyond, it won't. So understanding these limits is essential for safe design!

Sounds like Hooke's law is both crucial and limited in its scope of application!

Exactly! It gives us valuable insights but knowing its boundaries keeps us safe.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section discusses Hooke's Law, explaining how stress and strain are related through the modulus of elasticity, highlighting its empirical nature and the exceptions that exist for certain materials. Understanding Hooke's Law is important in analyzing elastic behavior and designing materials in engineering.
Detailed
Hooke's Law Overview
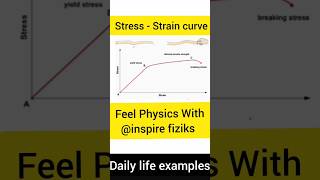
Hooke's Law is a fundamental principle in material science that describes the linear relationship between stress and strain for elastic materials. It states that the stress applied to a material is directly proportional to the strain produced, as long as the material remains within its elastic limit. Mathematically, this can be expressed as:
Stress = k × Strain
where k is known as the modulus of elasticity.
Key Points:
- Elastic Limit: Hooke's Law applies only within the elastic limit of a material. Beyond this limit, materials may exhibit plastic deformation or fracture.
- Modulus of Elasticity (k): The constant of proportionality (
k), seen in the equation, varies between materials and signifies how stiff or flexible a material is. Common forms of elasticity include Young’s modulus, shear modulus, and bulk modulus, each describing different responses to stress. - Exceptions: Certain materials, especially rubber and biological tissues, do not strictly follow Hooke's Law due to their non-linear characteristics in the elastic region.
- Relevance in Engineering: Understanding how materials behave when stressed is crucial in fields like mechanical engineering, civil engineering, and materials science for applications ranging from construction to aerospace design.
In summary, Hooke's Law is essential for predicting how materials deform under load, facilitating the design and utilization of various materials in engineering applications.
Youtube Videos





Key Concepts
-
Stress: The restoring force per unit area.
-
Strain: The ratio of change in dimension to the original dimension.
-
Elastic Limit: The threshold beyond which material deformation becomes plastic.
-
Modulus of Elasticity: Indicates how much stress is needed to produce a specific strain.
-
Proportionality: The relationship maintained under Hooke's Law between stress and strain.
Examples & Applications
A rubber band stretching when pulled, demonstrating Hooke's Law within the elastic limit.
A steel beam supporting a load in a building, showcasing the importance of stress and strain in construction.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Stretch and squish, not too far, stay within the limit of a good material star!
Stories
Imagine a rubber band; it can stretch so far, but if pulled too hard, it won't return, leaving a lasting scar.
Memory Tools
Remember 'Silly Stretchy', referring to how materials can either stretch back or break—keep the limits in check!
Acronyms
SEEL
Stress Equals Elasticity Limits - a reminder about Hooke's Law!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Hooke's Law
The principle that states stress is directly proportional to strain in elastic materials.
- Modulus of Elasticity
The constant of proportionality in Hooke's Law, indicating the stiffness of the material.
- Elastic Limit
The maximum extent to which a material can be deformed without undergoing permanent deformation.
- Stress
Restoring force per unit area within materials.
- Strain
The change in dimension of a material relative to its original dimension.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
