Advantages of CMOS Logic
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Low Power Consumption
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's start with one of the major advantages of CMOS logic, which is low power consumption. Can anyone tell me what they think contributes to this low power?

Is it because transistors don't consume power when they're off?

Exactly! In CMOS logic, when the transistors are in the off state, no current flows, leading to very low static power consumption. This is crucial for battery-operated devices!

How does this compare to other logic types?

Great question! Other logic types may still draw power even when idle, which can drain batteries quickly. CMOS logic's efficiency is a significant advantage.

So, CMOS is better for mobile devices then?

Absolutely! Devices like smartphones rely heavily on CMOS technology to conserve battery life while maintaining performance.

In summary, CMOS logic's 'no current flow' when off feature is a key point for low power consumption.
High Noise Immunity
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's delve into high noise immunity. Can anyone explain why CMOS logic is considered to have high noise immunity?

Is it because the signals are clear? Like there's a big difference between high and low levels?

Exactly! The design of CMOS with PMOS and NMOS transistors results in clear voltage levels. This helps the circuit distinguish between a logical '1' and '0' even in noisy environments.

What happens if there's a lot of noise?

In many instances, CMOS can still function correctly, whereas other logic families might misinterpret the noise as valid signals, leading to errors.

To wrap it up, high noise immunity allows CMOS logic to perform reliably in various situations, especially in high-speed applications where noise interference can be problematic.
Scalability of CMOS Technology
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let's go over scalability. Why do you think scalability is essential for CMOS technology?

Is it about making smaller and more efficient circuits?

Exactly! As technology progresses, manufacturers can create smaller transistors, allowing for more complex circuits within the same area, enhancing performance without increasing power consumption.

What if transistors get too small?

That's a good point! There are physical limits, but ongoing innovations in materials and designs aim to push those boundaries further.

So, scalability is vital in keeping up with growing demand for more powerful devices?

Absolutely! Higher scalability equals higher performance in electronics, which is crucial as we see rising demand for faster and more efficient devices.

In summary, scalability allows CMOS circuits to meet modern performance requirements without the drawbacks of increased power consumption.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The advantages of CMOS logic lie in its design, which results in low static power consumption, high noise immunity due to clear logic levels, and excellent scalability as transistor sizes shrink. These features make CMOS logic essential in contemporary digital circuit applications.
Detailed
Advantages of CMOS Logic
In this section, we highlight the benefits of CMOS logic circuits, which play a vital role in digital logic design. The three primary advantages include:
- Low Power Consumption: CMOS logic circuits are designed to consume minimal static power. This is because, when the transistors are turned off, there is no current flowing through the circuit, which maintains efficiency and prolongs battery life in portable devices.
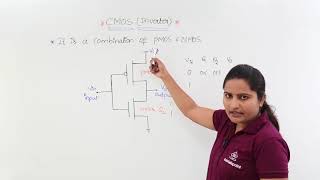
- High Noise Immunity: The complementary nature of PMOS and NMOS transistors creates well-defined voltage levels for logical states (high representing '1' and low representing '0'). This clear distinction enhances the circuit's ability to function correctly in the presence of electrical noise, which can interfere with signal integrity.
- Scalability: CMOS technology scales effectively with the advancement of semiconductor manufacturing processes. As transistor sizes shrink, manufacturers can create more complex and higher-performing circuits without significantly increasing power consumption.
These advantages contribute significantly to the widespread adoption of CMOS logic in various applications, including microprocessors, memory, and various digital circuits.
Youtube Videos


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Low Power Consumption
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Low Power Consumption: CMOS logic consumes very little static power because no current flows when transistors are off.
Detailed Explanation
CMOS logic is known for its remarkably low power consumption. This is because when the transistors in a CMOS circuit are in the 'off' state, they do not allow any current to flow through. Essentially, this means that when a CMOS circuit is not actively switching states (from high to low or vice versa), it doesn't draw power, leading to very minimal energy usage during idle times.
Examples & Analogies
Think of CMOS logic like a light switch in your home. When the switch is off, the light doesn’t consume any electricity at all. Similarly, when CMOS transistors are off, there is no power drawn, making them very efficient, especially in devices that need to conserve battery life.
High Noise Immunity
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● High Noise Immunity: The clear distinction between high and low logic levels results in higher noise immunity.
Detailed Explanation
One of the key advantages of CMOS logic is its strong noise immunity. This means that the circuits can effectively distinguish between high (logic 1) and low (logic 0) signals, even in the presence of noise or interference. The complementary nature of PMOS and NMOS transistors helps create a robust output that is less likely to misinterpret a noisy signal as a legitimate logic state change.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine trying to hear a quiet conversation at a loud party. If your hearing is very good (high noise immunity), you can pick out the conversation without being interrupted by the noise. Similarly, CMOS logic can maintain clarity in its signals amidst electrical interference, ensuring reliable operation.
Scalability
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Scalability: CMOS technology scales well with shrinking transistor sizes, enabling more complex circuits and higher performance.
Detailed Explanation
CMOS technology is highly scalable, which means that as technology advances and we can make transistors smaller, we can fit more of them onto a single chip. This scaling allows for the development of more complex circuits and systems without a significant increase in power consumption. The ability to increase density and performance makes CMOS a preferred choice in modern applications, including smartphones and computers.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a city planning to accommodate more residents. By building smaller yet efficient apartments, more people can live in a smaller area without losing quality of life. Similarly, shrinking CMOS transistors allows more computational capabilities within the same physical space on a chip.
Key Concepts
-
Low Power Consumption: CMOS circuits consume minimal power when transistors are off, essential for battery life.
-
High Noise Immunity: Clear distinctions between logic levels enhance resistance to electrical interference.
-
Scalability: CMOS technology allows for smaller transistors which lead to increased circuit complexity and performance.
Examples & Applications
CMOS is extensively used in modern smartphones and laptops for efficient power management.
Microprocessors utilizing CMOS technology can operate at high frequencies without overheating due to low power consumption.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
CMOS is the way; low power every day.
Stories
Imagine a battery that lasts longer because it wastes no power when using CMOS tech, it’s like a car that only goes when you press the gas, saving energy on every trip.
Memory Tools
L-N-S: Low Power, Noise immunity, Scalability helps us remember CMOS advantages.
Acronyms
LPS
Low Power & Scalability – key advantages of CMOS.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- CMOS
Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor, a technology for constructing integrated circuits.
- Static Power Consumption
Power consumed by a circuit when it is not switching states.
- Noise Immunity
The ability of a circuit to operate correctly in the presence of electrical noise.
- Scalability
The capability of a technology to efficiently adapt to larger scale circuit designs without performance loss.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
