Static CMOS Logic
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Static CMOS Logic
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to explore Static CMOS Logic, which is essential in digital circuit design due to its ability to maintain stable logic states without requiring a clock. Can anyone tell me what CMOS stands for?

Is it Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor?

Exactly! CMOS allows the creation of both PMOS and NMOS transistors which are essential in building logic gates. Now, what do you think 'static' indicates in this context, Student_2?

Does it mean the logic levels don't change unless there's an input switch?

Great observation! The static nature means the circuit does not need any external clock signal to maintain its state. Student_3, can you recall one of the primary advantages of static CMOS logic?

I think it's low power consumption because it only uses power when switching!

Spot on! This low power consumption is crucial for modern devices. Let’s summarize: static CMOS logic maintains logic without a clock, leverages low power consumption, and offers strong noise immunity.
Operational Principle of Static CMOS Logic
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's now discuss how static CMOS logic functions at a transistor level. In a static CMOS circuit, PMOS is connected to Vdd and NMOS to ground. Can someone explain why this is significant?

It's to create a complementary output where one type of transistor conducts while the other is off!

Exactly! This complementary operation allows the output to reflect either a high or low state efficiently. Now, Student_1, why is high noise immunity important in these circuits?

Because it ensures that the output isn't affected by small fluctuations in voltage, right?

Correct! High noise immunity preserves signal integrity, especially in complex digital systems. To recap, static CMOS logic's combination of PMOS and NMOS fosters efficient operation with excellent noise resistance.
Applications of Static CMOS Logic
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's look at applications. Why do you think static CMOS logic is used extensively in microprocessors and memory devices?

Because they need to manage complex operations while consuming minimal power!

That's right! Static CMOS's benefits extend to scalability as well, allowing compact circuit designs. Student_3, what are some other applications where you might find static CMOS?

In virtually all digital devices like smartphones and computers!

Great point! So, as we finish up, remember that static CMOS logic not only serves a critical role in digital circuitry but also continues to evolve within advanced applications. Let's close with a summary of its core characteristics: low power, high noise immunity, and versatility.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Static CMOS logic represents a fundamental category of CMOS digital logic that is characterized by stability in logic levels (high or low) without needing a clock signal. This section discusses its operational principles, key characteristics such as low power consumption and high noise immunity, and its extensive applications in digital integrated circuits.
Detailed
Detailed Summary of Static CMOS Logic
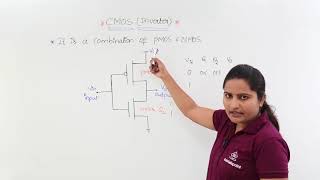
Static CMOS logic is the dominant form of CMOS digital logic used in electronic circuits. The 'static' in its name indicates that the circuit maintains its logic levels either high (1) or low (0) indefinitely in the absence of any clock signal or external control. This is primarily achieved through its structure, where PMOS transistors are linked to the positive supply voltage (Vdd) and NMOS transistors are linked to ground, with the output sourced from the junction of these transistors.
Key Characteristics
- Low Power Consumption: Static CMOS logic consumes negligible static power since no current flows when the circuit is idle (not switching).
- High Noise Immunity: Its complementary transistor arrangement reinforces a robust distinction between logic levels, which improves noise immunity and reduces the chance of misinterpretation of signals.
- High Drive Capability: These circuits possess strong drive capabilities, allowing them to effectively manage larger capacitive loads, beneficial in complex digital applications.
Applications
Due to these advantages, static CMOS logic is broadly applied across almost all digital ICs, especially in microprocessors, memory devices, and various digital systems. Its reliability and efficiency make it essential in the advancement of modern digital technology.
Youtube Videos


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Static CMOS Logic
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Static CMOS logic is the most widely used form of CMOS digital logic. It is called static because the logic states (high or low) are maintained indefinitely without requiring a clock signal or external control.
Detailed Explanation
Static CMOS logic represents a fundamental building block of digital circuits using CMOS technology. The term 'static' signifies that once a logic state is established (either high or low), it remains in that state until changed intentionally, without needing a continuous clock signal. This makes it very efficient for many applications, particularly because it simplifies the design and operation of circuits.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a light switch in your room. Once you flip it on (for a high state) or off (for a low state), the light stays in that position until you transform it again. Similarly, static CMOS logic holds its output state until it is changed by new input signals.
Operation of Static CMOS Logic
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
In static CMOS logic, a PMOS transistor is connected to the positive supply voltage (Vdd) and an NMOS transistor is connected to ground. The output is taken from the common node between the transistors.
Detailed Explanation
Static CMOS logic operates based on the complementary action of PMOS and NMOS transistors. When the input conditions are satisfied to trigger a 'high' output, the PMOS transistor turns on while the NMOS turns off, connecting the output to the positive voltage. Conversely, for a 'low' output, the NMOS turns on and the PMOS turns off, connecting the output to ground. This complementary action ensures that only one type of transistor conducts at any time, preventing unnecessary power consumption during steady states.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a seesaw in a playground. When one side goes up (the PMOS is on), the other side goes down (the NMOS is off), and vice versa. Just like you can have only one side of the seesaw raised at any time, in static CMOS logic, either the PMOS or the NMOS can conduct, keeping things balanced and avoiding waste.
Characteristics of Static CMOS Logic
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Characteristics:
- Low Power Consumption: Static CMOS logic has very low static power consumption because no current flows when the circuit is not switching.
- High Noise Immunity: The complementary nature of the transistors ensures a clear distinction between logic high (1) and logic low (0), which enhances noise immunity.
- High Drive Capability: Static CMOS gates can drive large capacitive loads efficiently.
Detailed Explanation
Static CMOS logic possesses several vital characteristics that make it desirable for use in various digital applications. Firstly, it is power-efficient; it consumes minimal power during static conditions because current is not drawn when the circuit isn't processing information. Secondly, due to the distinct operational boundary of high and low states maintained by PMOS and NMOS transistors, it provides high noise immunity, making circuits resilient to electrical interference. Lastly, it has high drive capability, meaning it can effectively control larger loads, essential for driving subsequent stages of circuits without any performance loss.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a water pipe system. A well-sealed pipe that only allows water through when there's a defined pressure (high state) prevents leaks and waste (low power consumption) while still being strong enough to move larger quantities of water (high drive capability) without breaking down. This is like how static CMOS logic effectively manages power, noise, and load handling.
Applications of Static CMOS Logic
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Applications: Static CMOS logic is used in almost all digital ICs, from microprocessors to memory devices, because of its high noise immunity, low static power consumption, and scalability.
Detailed Explanation
Due to its advantageous properties, static CMOS logic is a cornerstone in the design and fabrication of various digital integrated circuits (ICs). This includes microprocessors, which are the brains of computers, and memory devices that store data. As technology has advanced, the demand for circuits that consume less power while being capable of high performance has made static CMOS technology increasingly relevant.
Examples & Analogies
If we think of static CMOS logic as the foundation of a building, the entire structure (the various digital devices we use every day, like laptops and smartphones) relies on this strong and efficient base. Just like a strong foundation supports a tall, multi-story building, static CMOS logic supports various electronic devices by providing efficiency and reliability.
Key Concepts
-
Static CMOS Logic: A logic family that maintains output states without needing a clock, offering low power consumption and high noise immunity.
-
PMOS and NMOS Transistors: Essential components in CMOS technology, where PMOS connects to Vdd and NMOS connects to ground.
-
Low Power Consumption: The primary benefit of static CMOS logic, as there's little to no current flow when not switching.
-
Noise Immunity: The ability of static CMOS logic to resist voltage fluctuations, ensuring reliable outputs.
Examples & Applications
Static CMOS logic is employed in microprocessors that require careful power management while delivering high performance.
Memory devices such as RAM and flash storage utilize static CMOS for consistent data retention without continuous power.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
CMOS static, logic that's fantastic, low power's the goal, noise immunity's the role.
Stories
Imagine a busy librarian (static CMOS) who remembers every book's location without needing to check each time (the clock). This helps save energy while keeping shelves organized (representing low power and high noise immunity).
Memory Tools
Remember 'Penny Needs Chocolate' for PMOS and NMOS, highlighting the complementary relationship in a static setup.
Acronyms
LIN - Logic INtelligently
for understanding the stable inputs and outputs in Static CMOS Logic.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- CMOS
Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor, a technology used for constructing integrated circuits.
- Static Logic
A type of logic circuit that maintains its output state without an external clock signal.
- PMOS
A type of MOSFET transistor that uses positively doped material to conduct current.
- NMOS
A type of MOSFET transistor that uses negatively doped material to conduct current.
- Vdd
The positive supply voltage in a CMOS circuit.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
