Practical Applications of CMOS Logic Families
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Static CMOS Logic Applications
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're diving into static CMOS logic and its applications. Static CMOS logic is widely used in digital circuits, especially in microprocessors and memory devices. Can anyone tell me why this might be?

Maybe because it uses less power compared to other types of logic?

Exactly! Static CMOS has low power consumption and high noise immunity. These features are crucial in ensuring reliability in circuits. Can someone summarize what we just learned about its characteristics?

It's low power, high noise immunity, and can drive large capacitive loads.

Great, that's a perfect recap! Let's remember 'SPL-H' for 'Static Power Low - High drive capability' to remind us of these traits.
Dynamic CMOS Logic Applications
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's discuss dynamic CMOS logic. It’s commonly found in areas that require quick processing, like in high-performance processors. Why do you think that is?

Because it can switch faster than static CMOS?

That's absolutely correct! Dynamic logic can achieve greater speeds due to its design, although it does consume more power. Who can list some applications of dynamic logic?

It’s used in memory circuits and pipelined architectures.

Excellent! For our memory aids, think of 'DYMO' for Dynamic Memory in Organization as a way to remember these applications.
Transmission Gate Logic Applications
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's shift our focus to transmission gate logic. It's known for fast switching and low power. Where might we see this implemented?

In multiplexers or analog-to-digital converters?

Yes, precisely! Transmission gates allow signals to pass through with minimal loss. Remember 'T-GATE' for 'Transmission Gate Applications for Timing Efficiency.' So, why do you think low power is advantageous in these applications?

It helps in reducing heat and extending battery life!

Exactly right! Let’s keep that insight in our notes.
Pass-Transistor Logic Applications
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, we’ll explore pass-transistor logic. PTL is preferred in low-power scenarios. Can anyone explain why it might be suitable for portable electronics?

Because it has fewer transistors, which means less power usage?

Exactly, fewer transistors equate to less power! What are some applications where you think this would be beneficial?

Maybe like mobile devices and sensors that need to conserve battery?

Spot on! For memory aid, use 'PTL-PAD' for Pass-Transistor Logic in Power-Aware Devices.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section highlights how different CMOS logic families such as static CMOS, dynamic CMOS, transmission gate logic, and pass-transistor logic are utilized in various applications ranging from microprocessors to low-power electronics. Each family is executed based on specific needs like speed, power consumption, and functional complexity.
Detailed
Practical Applications of CMOS Logic Families
In the realm of digital design, CMOS logic families play a crucial role due to their diverse applications across various technology sectors. This section delves into the practical uses of several CMOS logic families:
- Static CMOS Logic: As the most widely employed logic family, static CMOS logic is integral to almost all digital integrated circuits (ICs). It’s utilized in devices including microprocessors, memory devices, and digital signal processing to benefit from its low power consumption and high noise immunity.
- Dynamic CMOS Logic: This family is predominantly found in high-performance circuits where speed is essential. Applications include processors and memory architectures that require rapid data processing capabilities, demonstrating the dynamic logic's efficient performance in demanding environments.
- Transmission Gate Logic: Known for its simplicity and low power usage, transmission gate logic is commonly applied in analog switches, multiplexers, demultiplexers, and signal routing circuits. Its advantages include quick signal transmission with minimal loss, making it effective for various switching tasks.
- Pass-Transistor Logic (PTL): PTL is particularly advantageous for low-power scenarios, ideal for portable electronics and low-power logic applications given its efficiency in power consumption. By using fewer transistors, it simplifies the circuit design compared to traditional static logic families.
Overall, these various CMOS families respond to specific application requirements, providing a framework for designing digital circuits that balance speed, power efficiency, complexity, and performance.
Youtube Videos


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Static CMOS Logic Applications
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Static CMOS Logic: The most widely used family, suitable for most digital ICs, including microprocessors, memory devices, and digital signal processing.
Detailed Explanation
Static CMOS logic is a fundamental technology used to create integrated circuits in various applications. Its most significant traits—low power consumption, high noise immunity, and scalabiity—make it suitable for nearly all digital Integrated Circuits (ICs). This family is the go-to choice for critical components such as microprocessors and memory devices, which form the backbone of modern computing systems.
Examples & Analogies
Think of static CMOS logic like the foundations of a skyscraper. Just as a strong, reliable foundation is essential for supporting a large structure, static CMOS logic provides the necessary stability and efficiency for digital circuits, enabling everything from everyday personal computers to complex data centers.
Dynamic CMOS Logic Applications
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Dynamic CMOS Logic: Commonly used in high-performance circuits where speed is critical, such as processors, memory, and pipelined architectures.
Detailed Explanation
Dynamic CMOS logic is characterized by its ability to perform operations at high speeds, making it ideal for applications demanding quick processing times. This logic family relies on temporary charge storage for operation, which is highly effective in modern processors and memory systems that strive for high performance. Designers often favor dynamic CMOS for applications where throughput is prioritized over power consumption.
Examples & Analogies
You can think of dynamic CMOS logic like a race car. In racing, speed is essential; every millisecond counts. Dynamic CMOS logic is like the advanced technology in those race cars, designed to maximize speed and efficiency, thereby helping your computer or device perform tasks swiftly and efficiently.
Transmission Gate Logic Applications
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Transmission Gate Logic: Used in analog switches, multiplexers, de-mux, and signal routing circuits.
Detailed Explanation
Transmission gate logic stands out for its simple operation and effectiveness in signal transmission. This logic family is extensively used in circuits that require switching between multiple signals without distortion, such as multiplexers and analog switches. The ability to transmit signals efficiently and with low power consumption makes transmission gates valuable in both digital and mixed-signal environments.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine using a traffic signal at a busy intersection. Just as traffic lights efficiently manage the flow of vehicles and pedestrians, transmission gates act as switches that control the direction of signal flows in circuits, ensuring that information gets to its destination safely and quickly.
Pass-Transistor Logic Applications
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Pass-Transistor Logic: Ideal for low-power applications where power consumption is a key consideration, such as portable electronics and low-power logic.
Detailed Explanation
Pass-transistor logic (PTL) is specifically designed to optimize power efficiency by utilizing fewer transistors. This capability makes PTL particularly well-suited for devices that rely on battery power, like smartphones and portable gadgets. Despite some challenges with voltage loss, the low-power demands of PTL circuits provide vast benefits in extending the lifespan of electronic devices.
Examples & Analogies
Think about a hybrid car that uses less fuel to travel long distances. Just like a hybrid car prioritizes fuel efficiency to reduce costs and emissions, pass-transistor logic optimizes power consumption in electronic devices, allowing them to run longer on less energy.
Key Concepts
-
Static CMOS Logic: Used in most digital ICs for its low power and high noise immunity.
-
Dynamic CMOS Logic: Important in high-speed circuits, consuming more power and requiring a clock signal.
-
Transmission Gate Logic: Employed in switches and multiplexers for its fast performance and low power.
-
Pass-Transistor Logic: Suitable for low-power applications while maintaining simplicity.
Examples & Applications
Static CMOS logic is found in computer processors, where reliability and power efficiency are crucial.
Dynamic CMOS logic is used in advanced smartphones for faster processing speeds.
Transmission gate logic connects different circuit paths in multiplexers with minimal signal loss.
Pass-Transistor Logic is applied in battery-operated devices to conserve power.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Static will sit, dynamic will run, for high-speed tasks, it’s the one!
Stories
Imagine building a house with different types of builders: static is steady and reliable, dynamic is quick and speedy, transmission gate is the efficient courier, while PTL is the clever minimalist saving energy!
Memory Tools
Remember 'ST-DTP' for Static, Dynamic, Transmission, Pass-Transistor Logic.
Acronyms
For static CMOS remember 'SPL-H' for Static Power Low - High drive capability.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Static CMOS Logic
A type of CMOS logic that maintains logic states without requiring a clock signal, known for its low power consumption and high noise immunity.
- Dynamic CMOS Logic
A CMOS logic family that uses a clock signal to determine output states, allowing for faster operational speeds but at a higher power consumption.
- Transmission Gate Logic
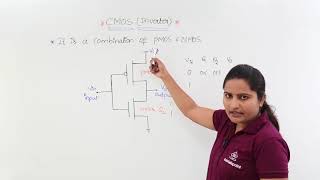
A configuration made of NMOS and PMOS transistors that allows signals to pass through with low power usage and fast performance.
- PassTransistor Logic (PTL)
A type of logic that utilizes NMOS or PMOS transistors to pass voltage levels directly, offering simplicity and low power consumption.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
