Summary of Key Concepts
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to CMOS Logic Families
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

CMOS stands for Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor. Who can tell me what logic families are?

Are they groups of different types of logic gates or circuits?

Exactly! And CMOS logic families are specifically based on that technology. They include static CMOS, dynamic CMOS, and others. Can anyone tell me why it's important to understand these families?

Because different families can have different characteristics like speed and power consumption?

Right! Now let’s explore each type in detail.
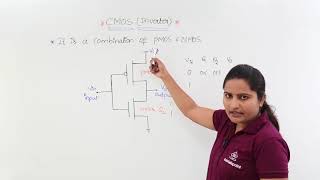
Static CMOS Logic
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Static CMOS logic is widely used because it has low power consumption and high noise immunity. Can anyone share what this means?

Low power consumption means it doesn’t waste energy when it’s not working, right?

That's correct! And high noise immunity means it can differentiate better between high and low signals. Why is that beneficial?

It helps prevent errors in data processing.

Exactly! That’s why it’s used in many digital circuits, including microprocessors.
Dynamic CMOS Logic
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Dynamic CMOS logic uses a clock signal for operation. Who can explain what that means?

It can be faster because it doesn't need both types of transistors on at the same time.

Exactly! However, it also consumes more power, especially when charging and discharging capacitors. Why do you think that's a drawback?

It can lead to energy inefficiency in certain applications.

Correct! So, dynamic CMOS logic is better for high-speed applications, whereas static logic is preferred for low-power designs.
Comparisons of Logic Families
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's compare the key families of CMOS logic. What are the main considerations for choosing a logic family?

You have to think about speed, power consumption, and how complex the design is.

Exactly! Each family has its advantages: static CMOS is low in power, dynamic CMOS is fast, and transmission gate logic is effective in terms of simplicity. Can anyone give an example of when you might choose each type?

Use static for chips like memory where power saving is crucial, dynamic for quick processors, and transmission gates in multiplexers!

Great examples! Remembering the trade-offs will help you make informed decisions in your designs.
Design Considerations in CMOS Logic
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

When designing digital circuits, we need to weigh factors like speed and power against complexity. Why do you think that’s challenging?

Because you want to balance everything perfectly for the specific application!

Exactly! Choosing the wrong family could lead to inefficiencies or poor performance. This highlights the importance of deep understanding in logic design.

So, proper evaluation is key to avoid making inefficient designs, right?

Absolutely! Great observation. Always consider your application's requirements first!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The summary provides an overview of various CMOS digital logic families, including their specific characteristics, trade-offs, and applications. Key design considerations for selecting an appropriate logic family for digital circuits are also highlighted.
Detailed
In this section, we encapsulate the critical components of CMOS digital logic families, including static CMOS, dynamic CMOS, transmission gate logic, and pass-transistor logic. Each family exhibits distinct advantages and disadvantages in areas such as speed, power consumption, noise immunity, and complexity. Selecting an appropriate logic family for a particular application requires a careful assessment of these factors, as well as the specific requirements of the desired application.
Youtube Videos


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of CMOS Digital Logic Families
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● CMOS Digital Logic Families: Various CMOS logic families such as static CMOS, dynamic CMOS, transmission gate logic, and pass-transistor logic are used for digital circuits based on specific design requirements.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk introduces the concept of CMOS digital logic families. It states that there are different types of CMOS logic families, including static CMOS, dynamic CMOS, transmission gate logic, and pass-transistor logic. Each of these families is suited to different design requirements, indicating that there's no one-size-fits-all solution. Understanding the characteristics of each family is crucial for engineers when designing digital circuits.
Examples & Analogies
Think of CMOS digital logic families like different types of vehicles. Just as you have cars, trucks, motorcycles, and buses, each serving different purposes, you have different CMOS families designed for specific tasks in electronics.
Understanding Trade-offs in Logic Families
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Trade-offs: Each logic family has trade-offs in terms of speed, power consumption, complexity, and noise immunity, and the choice depends on the specific application.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk highlights that selecting a CMOS logic family involves making trade-offs. For instance, some families might be faster but consume more power; others may have low power consumption but can be complex to design. Understanding these trade-offs helps engineers choose the right logic family based on the specific needs and constraints of their project.
Examples & Analogies
Consider the choice between a sports car and an electric car. The sports car is fast but consumes a lot of fuel, while the electric car is environmentally friendly and economizes on fuel but may not have the same speed. Engineers face similar choices when selecting a logic family.
Key Design Considerations
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Design Considerations: When designing CMOS circuits, careful consideration of power, speed, complexity, and application requirements is necessary to select the appropriate logic family.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk emphasizes the importance of considering various factors during the design of CMOS circuits. Factors such as power and speed need to be balanced with the complexity of design and the specific application for which the circuit is intended. These considerations help in ensuring that the final product meets performance expectations while being efficient and reliable.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine planning a party. You need to think about the venue size (capacity), the type of entertainment (speed of fun), the food you can prepare (complexity), and the theme (application). Just like you would balance these factors for a successful party, engineers balance power, speed, complexity, and application requirements for successful circuit designs.
Key Concepts
-
CMOS Digital Logic Families: Different families such as static CMOS, dynamic CMOS, transmission gate logic, and pass-transistor logic based on specific design requirements.
-
Trade-offs: Various factors such as speed, power consumption, complexity, and noise immunity that influence the choice of logic family.
-
Design Considerations: Essential factors to evaluate when developing CMOS circuits for specific applications.
Examples & Applications
Static CMOS logic is commonly used in digital ICs like microprocessors, while dynamic CMOS logic is preferred for high-speed applications such as pipeline processors.
Transmission gate logic is effectively used in multiplexers and ADCs, whereas pass-transistor logic is applied in low-power digital circuits.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Static is low power, keeps its state, while Dynamic must charge, to operate great!
Stories
Imagine a relay race where static runners maintain their pace without needing a baton pass. Dynamic runners rush, but they must regroup at intervals, wasting energy as they dodge obstacles.
Memory Tools
Remember 'SSSDP' for Static, Speedy, Static, Dynamic, and Pass-Transistor - to recall the main logic types!
Acronyms
Think of 'DCP' for Dynamic, Clocked, Pre-charge to remember dynamic CMOS's features!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- CMOS
Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor, a technology for constructing integrated circuits.
- Static CMOS
A type of CMOS logic that does not require a clock signal to maintain logic levels indefinitely.
- Dynamic CMOS
A CMOS logic type that requires a clock signal for evaluation and precharging.
- Noise Immunity
The ability of a circuit to resist interference from external signals that can lead to errors.
- Power Consumption
The amount of power used by a circuit during operation.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
