Comparison of CMOS Logic Families
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Overview of CMOS Logic Families
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we'll compare various CMOS logic families. Can anyone remind me how many major families we discussed?

Four families: Static CMOS, Dynamic CMOS, Transmission Gate Logic, and Pass-Transistor Logic.

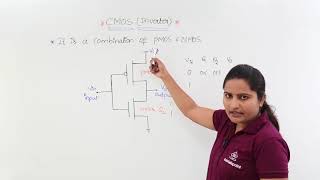
Correct! Each family has unique characteristics regarding power, speed, complexity, and more. Let's start with **Static CMOS Logic**.
Static CMOS Logic Characteristics
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Static CMOS is known for its low power consumption and high noise immunity. Can anyone explain why it consumes so little power?

I think it’s because no current flows when the circuit is not switching.

Exactly! When it’s not in operation, it has practically zero static power. Now, it can handle large capacitive loads, making it suitable for digital ICs.

What types of applications typically use Static CMOS Logic?

Great question! It’s widely used in microprocessors and memory devices due to its reliability.
Dynamic CMOS Logic
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let’s talk about Dynamic CMOS Logic. It boasts faster switching speeds but has higher power consumption. Why do you think that is?

Because it needs to charge and discharge output capacitance during operation.

Correct! It also requires clock signals to operate properly. So, where would we typically use Dynamic CMOS Logic?

In high-speed applications, like processors!

Exactly right! It's essential for applications where performance matters.
CMOS Transmission Gate Logic
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let’s discuss CMOS Transmission Gate Logic. Can anyone recall how it operates?

It uses NMOS and PMOS transistors to transmit signals when activated.

Exactly! And why is it favored in many applications?

It consumes low power and is fast.

Correct! It’s commonly found in multiplexers and ADCs.
Pass-Transistor Logic (PTL)
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let’s cover Pass-Transistor Logic. What can you tell me about its efficiency?

It’s more power-efficient but can suffer from voltage loss during transmission.

Exactly! That’s a trade-off we consider. Where might PTL be suitable?

In low-power applications, like portable electronics.

Great summary! Remember, each logic family has its distinct advantages and trade-offs for different applications.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, we compare four major CMOS logic families: Static CMOS, Dynamic CMOS, CMOS Transmission Gate, and Pass-Transistor Logic. Each family exhibits distinct characteristics regarding power consumption, speed, complexity, noise immunity, and their typical applications, aiding in the selection of the appropriate logic family for specific digital designs.
Detailed
Comparison of CMOS Logic Families
This section provides a comparative analysis of four primary CMOS logic families: Static CMOS Logic, Dynamic CMOS Logic, CMOS Transmission Gate Logic, and Pass-Transistor Logic (PTL). Each family is evaluated based on critical parameters, including:
- Power Consumption: Referring to the energy usage during the operation. Static CMOS Logic is characterized by low static power consumption, while Dynamic CMOS Logic has higher dynamic power consumption due to the need for periodic charging of nodes.
- Speed: The switching speed of each logic family varies, with Dynamic CMOS generally being higher due to its architecture that does not require both PMOS and NMOS to be on simultaneously.
- Complexity: Complexity pertains to design complexity and integration. Static CMOS Logic shows moderate complexity, whereas Dynamic and PTL can introduce more intricate design demands due to their operating principles.
- Noise Immunity: The ability to tolerate noise without affecting the output is a critical factor. Both Static and Dynamic CMOS Logic provide high noise immunity, while Transmission Gate Logic also exhibits robustness in this area.
- Applications: Each logic family has tailored applications, including: Static CMOS in digital ICs, Dynamic CMOS for high-speed processors, Transmission Gates in multiplexers and ADCs, and PTL for low-power circuits.
By assessing these parameters, designers can make informed choices about which CMOS logic family to adopt for their projects based on power, performance, and application requirements.
Youtube Videos


Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Overview of Logic Families Comparison
Chapter 1 of 1
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Logic Family Power Consumption Speed Complexity Noise Immunity Applications
Static CMOS Logic Low Static Power Moderate High High Digital ICs, Microprocessors, Memory
Dynamic CMOS Logic High Dynamic Power Very High Moderate Moderate High-speed processors, Memory
CMOS Transmission Gate Low Static Power High Low High Multiplexers, ADCs, Digital switches
CMOS PTL (Pass-Transistor Logic) Low Power Moderate Low Moderate Low-power digital circuits, Analog switches
Detailed Explanation
This chunk presents a comparative table summarizing the characteristics of different CMOS logic families: Static CMOS Logic, Dynamic CMOS Logic, CMOS Transmission Gate Logic, and CMOS Pass-Transistor Logic (PTL). Each logic family is evaluated based on four main criteria: Power Consumption, Speed, Complexity, and Noise Immunity. For example, Static CMOS Logic is characterized by low power consumption and high noise immunity, making it suitable for digital ICs and microprocessors. In contrast, Dynamic CMOS Logic tends to have higher power consumption but offers very high speed, which is ideal for high-speed processors.
Examples & Analogies
Think of these logic families like different types of vehicles. Static CMOS Logic is like a fuel-efficient sedan; it's reliable and economical for everyday use (like digital ICs). Dynamic CMOS Logic resembles a sports car; it's designed for speed and performance, but it consumes more fuel (like in high-speed applications). CMOS Transmission Gate Logic can be compared to a motorcycle; it has low power needs and is fast, but it’s simpler than a car. Finally, PTL is like a bicycle, offering low power and simplicity but is not as complex or fast as a car.
Key Concepts
-
Power Consumption: Refers to the energy consumed by the logic families during operation.
-
Switching Speed: The time required for a logic family to change from one state to another.
-
Complexity: Refers to the design intricacies involved in implementing different logic families.
-
Noise Immunity: The ability of a logic family to resist noise interference in electronic signals.
-
Applications: The specific domains or products where each logic family is commonly used.
Examples & Applications
Static CMOS Logic is used in most digital ICs, including processors and memory devices due to its high noise immunity.
Dynamic CMOS Logic is commonly found in high-speed computing applications like modern CPUs and GPUs.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Static CMOS is low and slow, Dynamic's fast, but needs to flow.
Stories
In a digital land, Static loved to rest, using little power it thought was the best. Dynamic rushed with speed and flair, but needed a clock—was that even fair?
Memory Tools
Remember 'STADPT' - Static, Dynamic, Transmission Gate, Pass-Transistor for CMOS families.
Acronyms
P.S. D.C.T.P - Power, Speed, Design, Complexity, Transmission, Pass-Transistor.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- CMOS
Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor, a technology used for constructing integrated circuits.
- Static CMOS Logic
A type of logic family that retains its output state indefinitely without a clock signal.
- Dynamic CMOS Logic
A CMOS logic family that relies on clock signals and dynamic behavior for operation, consuming more power.
- Transmission Gate
A CMOS switch that allows signals to pass through with low power losses.
- PassTransistor Logic (PTL)
A logic family using NMOS or PMOS transistors to pass voltage levels as logic states.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
