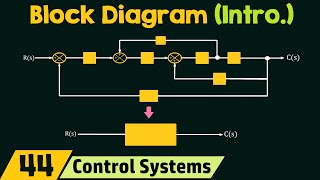
Summing Points
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Summing Points
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll explore summing points in block diagrams. Can anyone explain what a summing point does?

I think it combines different input signals.

Exactly! Summing points allow us to add or subtract signals, providing a clear representation of how inputs affect the output. Can anyone think of an example?

In a feedback system, the error signal is the difference between the desired input and the actual output, right?

Exactly! That's a great example of a summing point in action. Remember the acronym 'SUM' to recall 'Signals Unite at the Merging point'.
Mathematical Representation of Summing Points
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s delve into the mathematical representation of summing points. What do we usually express at these points?

We express the equation that shows how the inputs relate to the output.

Correct! Typically, we can represent outputs as Y = R - Y_feedback. Anyone want to elaborate on what Y_feedback is?

It’s the output from the feedback loop, right? It goes back into the summing point to help calculate the error.

That's right! The feedback mechanism is crucial for maintaining system stability. Let's remember to visualize summing points as places where calculations happen!
Practical Application of Summing Points
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

To wrap up, let's connect summing points to real-world systems. Can anyone provide an application?

In a temperature control system, the thermostat compares the set temperature with the actual temperature.

Exactly! That difference becomes the error signal at the summing point. How affects the heating system?

It helps to adjust the heat output to reach the desired temperature more quickly.

Great insights! Just remember, summing points simplify the path from input to output, making analysis clearer. 'WISER' can help remember – 'Where Inputs Sum to Explain Result.'
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Summing points in block diagrams are critical for combining multiple input signals which influence the system's output. Understanding these points enables better analysis and design of feedback systems.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
Summing points are essential components in block diagrams used in control systems. These points serve as junctions where multiple signals can be mathematically combined, typically involving addition or subtraction. The significance of summing points lies in their ability to clarify how different inputs, including feedback loops, are processed to produce a coherent output. For instance, in a feedback control system, the error signal at a summing point is calculated by comparing a reference input against the system output. Understanding summing points allows engineers to set up and analyze control systems effectively, ensuring accurate signal processing and system stability.
Youtube Videos



Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Summing Points
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Summing Points: Where signals are added or subtracted. These points allow us to combine multiple inputs into a single output.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk introduces the concept of summing points within block diagrams. Summing points are critical because they provide a location where multiple signals (inputs) can be combined to produce a single output. By allowing the addition or subtraction of signals, they enable engineers to represent complex systems more clearly. In a control system, for instance, summing points often facilitate the calculation of error signals, which is crucial for feedback control.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a summing point like a mixer in a kitchen. When you bake a cake, you combine various ingredients such as flour, sugar, and eggs into a bowl. Each ingredient represents a different signal, and the bowl is the summing point where these signals mix to create the cake batter. Similarly, in a control system, different input signals are mixed at the summing point to produce an error signal that helps the system maintain its desired performance.
Application of Summing Points in Feedback Systems
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Example: In a feedback system, the error signal is the difference between the reference input and the system output.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk discusses how summing points are applied specifically in feedback systems. In such systems, the summing point takes in a reference input, which is the desired value, and the output from the system, then computes the error by subtracting the output from the reference input. This error signal is crucial because it indicates how far the system output is from the desired value and informs necessary adjustments.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you are driving a car using a GPS. The GPS provides a reference route (the desired location), while your car's current position is the actual output. The difference between these two positions (reference and actual) is like the error signal. If you find that you are off track (the output does not match the reference), you would need to adjust your route accordingly. In a control system, the summing point helps make similar adjustments to ensure the system behaves as intended.
Key Concepts
-
Summing Points: Key components in block diagrams that combine inputs.
-
Error Signal: The calculated difference for feedback adjustments.
Examples & Applications
In a speed control system, the summing point compares the set speed with the actual speed to produce an error signal.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When inputs meet at the summing gate, the errors change, and outputs equate.
Stories
Picture a restaurant where orders (inputs) are taken to the kitchen (summing point), here they mix to create the final dish (output), but if an order is wrong (error), the chef (feedback) adjusts for correction.
Memory Tools
SUM: Signals Unite at the Merging point.
Acronyms
WISER
Where Inputs Sum to Explain Result.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Summing Points
Locations in a block diagram where multiple input signals are mathematically combined, typically by addition or subtraction.
- Error Signal
The difference between a reference input and the output of a system that is used to adjust the input to achieve a desired outcome.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
