Case Studies on Magnitude and Intensity Application
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Case Studies
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we'll discuss two crucial earthquakes: the 2001 Bhuj Earthquake and the 2015 Nepal Earthquake. These cases will help us understand how magnitude and intensity apply in real scenarios.

Why do we need to study these specific earthquakes?

Great question! They exemplify how different magnitudes and intensities can impact areas differently. The Bhuj earthquake, for instance, had severe impacts despite its high magnitude.

So, the effects of earthquakes can vary based on magnitude?

Exactly! But there’s more. Intensity can vary based on local geological conditions and building types. Let's dive into the details.
2001 Bhuj Earthquake Analysis
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

The Bhuj Earthquake had a magnitude of Mw 7.7 and experienced MMIs of IX to X in epicentral areas. This severe ground shaking caused extensive damage.

What does MMI IX-X mean exactly?

MMI levels denote perceived shaking and damage. Level IX indicates considerable damage, while level X signifies total destruction. This helps engineers assess safety and planning.

So, it’s critical we consider both magnitude and intensity in design?

Absolutely! We need to improve zoning based on these factors. Past earthquakes teach us vital lessons.
2015 Nepal Earthquake Overview
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Moving to the 2015 Nepal Earthquake, which had a magnitude of Mw 7.8. Despite this high magnitude, the intensity in urban areas was moderate due to the earthquake's depth and fault type.

Does that mean not all high-magnitude earthquakes cause severe damage?

Correct! Structural vulnerability can affect how intensities manifest in populated areas. Engineers must consider these factors to prevent disasters.

So, depth matters significantly?

Yes, depth plays a critical role in the shaking felt at the surface. A deeper focus often results in less intense shaking.
Lessons Learned from Case Studies
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

From these case studies, what lessons can we take into account for future earthquake preparedness?

We need better building codes and zoning regulations!

Exactly. Understanding both magnitude and intensity is crucial in disaster planning and risk mitigation.

It seems like structural vulnerability is a key point!

Definitely! The interaction of structural design with seismic characteristics determines overall safety during earthquakes.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, we analyze two major earthquakes—the 2001 Bhuj earthquake in India and the 2015 Nepal earthquake—focusing on their magnitude and observed intensity. These case studies exemplify the importance of understanding both magnitude and intensity for effective seismic hazard assessment and engineering practices.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
This section examines two critical case studies to elucidate the application of magnitude and intensity in real-world earthquake scenarios. The first case study focuses on the 2001 Bhuj Earthquake in India, which had a magnitude of Mw 7.7 and resulted in severe ground shaking that reached Modified Mercalli Intensity (MMI) levels of IX-X in epicentral regions. The aftermath underscored the imperative for better zoning practices that consider both the magnitudes and observed intensities in earthquake-prone areas.
The second case study, the 2015 Nepal Earthquake (Mw 7.8), highlights the complex interaction of depth and fault type influencing observed intensity levels, demonstrating that a high magnitude does not always correlate with high intensity in urban areas. This indicates structural vulnerability significantly impacts the observed effects of seismic events. Overall, both case studies illustrate key engineering implications, showing how understanding these concepts can improve seismic hazard assessments and building resilience.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
2015 Nepal Earthquake
Chapter 1 of 1
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
29.12.2 2015 Nepal Earthquake (Mw 7.8)
• High Mw but moderate intensity in urban zones due to depth and fault type.
• Demonstrated importance of structural vulnerability in determining intensity impact.
Detailed Explanation
The 2015 Nepal Earthquake had a moment magnitude of 7.8, indicating a very strong earthquake. However, the intensity observed in urban areas was moderate. This discrepancy can be attributed to the earthquake's depth and the characteristics of the fault that caused it. Moreover, the structural vulnerability of buildings played a significant role in how intense the shaking was perceived to be and the resulting damage. This case emphasizes how critical it is to assess building safety and suitability relative to anticipated seismic activity.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a crowded dance floor at a party. The music can be very loud (the earthquake's magnitude), but if the floor is solid and well-constructed (like strong buildings), people can dance without much trouble. However, if the floor is weak and unstable, even if the music isn't very loud, people might feel uncomfortable or even unsteady. The Nepal earthquake illustrates this idea: even strong quakes can have mild noticeable effects in certain settings, and the readiness of buildings to withstand those effects is vital.
Key Concepts
-
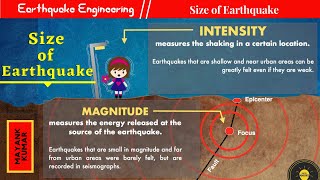
Magnitude vs Intensity: Understanding the difference between the energy release of an earthquake and its effects.
-
MMI Scale: An important measure of earthquake effects experienced by people and structures.
Examples & Applications
The 2001 Bhuj earthquake had significant damage due to its high magnitude and intensity in populated areas.
The 2015 Nepal earthquake, despite its high magnitude, resulted in moderate intensity effects due to the earthquake's depth and geological conditions.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Magnitude is the energy release, Intensity shows the damage at a piece.
Stories
Imagine an earthquake shaking a town—Magnitude tells how hard it hit, while Intensity reveals the destruction found.
Memory Tools
M/I: Magnitude for energy, Intensity for impacts.
Acronyms
MI
Magnitude Intensity—one measures the quake's heart
the other its effects like art.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Magnitude
A measure of the total energy released at the source of the earthquake.
- Intensity
A measure of the effects of an earthquake at specific locations.
- Modified Mercalli Intensity (MMI)
A qualitative scale that measures the intensity of shaking and damage from I (not felt) to XII (total destruction).
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
