Seismic Intensity Scales
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Seismic Intensity
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we’re diving into seismic intensity scales. Who can tell me what seismic intensity refers to?

Is it about how strong an earthquake feels?

Exactly! It's about the perceived shaking and damage at specific locations. It varies based on distance and local conditions. Can someone provide an example of how this might vary?

Maybe it would feel stronger in a city compared to an open area?

Great point! The intensity indeed varies due to factors like building type and soil composition. Remember, intensity is all about effects—think 'damage and perception'!

So, how do we measure this intensity?

Good question! Let's move on to specific scales, starting with the Modified Mercalli Intensity scale.
Modified Mercalli Intensity (MMI) Scale
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

The MMI scale measures intensity from I to XII. What does level I mean?

It means the earthquake wasn't felt at all!

Correct! And what about level XII?

Total destruction and people can see ground waves!

Exactly! The MMI is qualitative and uses human experiences and damage reports. This makes it very useful for post-event assessments. Can you think of how MMI helps engineers?

It helps them understand which buildings need to be stronger!

Right! Understanding intensity data helps in zoning for future building safety.
Other Intensity Scales
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

While the MMI scale is popular, we also have the European Macroseismic Scale and the MSK scale. What might make these useful?

They might provide more specific information for different regions or building types!

Exactly! The EMS-98 considers European architecture and post-earthquake conditions. And what about MSK? Why was that significant?

It was used in countries like India and focused on human reactions!

Spot on! Understanding these scales contributes to better risk assessment and overall seismic preparedness.
Practical Applications of Intensity Scales
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s illustrate how we can use these intensity scales in practice. How do you think intensity assessment is applied in urban planning?

They can determine where to build or reinforce structures!

Great insight! It aids in zoning regulations and helps ensure that buildings can withstand expected shaking levels. Given this context, how does understanding intensity help insurance companies?

They can estimate potential losses after an earthquake!

Exactly! This connection between intensity and economic impact is crucial for effective risk management. Great discussion today!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section discusses various seismic intensity scales, such as the Modified Mercalli Intensity (MMI) scale, which quantitatively assesses earthquake impact based on observable effects. Understanding these scales is vital for assessing risk and planning for earthquake mitigation.
Detailed
Seismic Intensity Scales
Seismic intensity scales are essential for measuring the effects of earthquakes at specific locations. Unlike magnitude, which quantifies the energy released at the earthquake's source, intensity considers how that energy is perceived and the resulting damage in various areas. The intensity of an earthquake is influenced by factors such as distance from the epicenter, geology, and building structures. This section introduces several significant intensity scales used to evaluate earthquake impacts:
1. Modified Mercalli Intensity (MMI) Scale
- A qualitative scale from I (not felt) to XII (total destruction).
- Based on human perception, structural damage, and ground deformation.
- Example Levels:
- I: Not felt except by a few.
- V: Felt indoors; unstable objects disturbed.
- XII: Total destruction; ground surface waves seen.
2. European Macroseismic Scale (EMS-98)
- Tailored for European structures with detailed damage descriptions based on building types.
- Primarily used in post-earthquake analysis.
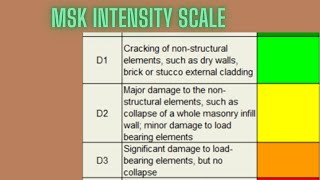
3. Medvedev–Sponheuer–Karnik (MSK) Scale
- Previously employed in India and the USSR, aligned similarly to the MMI scale with emphasis on human reactions and building damage.
Significance
Understanding these intensity scales is imperative for seismic hazard assessments and zoning, as they guide engineering practices and help mitigate damage during earthquakes.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Seismic Intensity
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Intensity refers to the perceived shaking and damage observed at a specific location due to an earthquake. It varies with distance from the epicenter, geology, and structural characteristics.
Detailed Explanation
Seismic intensity is a measure of how strong the shaking from an earthquake is, as observed by people and measured by the effects on buildings and structures in a specific location. Unlike magnitude, which quantifies the energy released by an earthquake at its source, intensity captures the impact felt at various distances from the epicenter. Factors like distance from the epicenter and the local ground conditions (such as rock or soil type) heavily influence intensity levels.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine throwing a stone into a pond. The point where the stone hits the water is like the epicenter of an earthquake. The ripples you see spread out from that point, and how strong those ripples feel will depend on how close you are to the splash (epicenter) and what kind of surface the ripples are traveling through (wet sand vs. concrete). This shows how intensity can vary based on location.
Modified Mercalli Intensity (MMI) Scale
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Qualitative scale ranging from I (not felt) to XII (total destruction).
• Based on:
- Human perception of shaking.
- Damage to structures.
- Ground deformation.
Detailed Explanation
The Modified Mercalli Intensity (MMI) scale is a descriptive scale used to assess the intensity of shaking during an earthquake. It does not use numerical values like other scales; instead, it describes what people felt and the damage observed. Ranging from I to XII, it starts with level I, indicating that the earthquake was not felt, to level XII, which denotes complete destruction. This helps convey not just the strength of the quake but the extent of damage in a more relatable way.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the MMI scale like a movie rating system. For instance, level I is like a 'G' rating where nothing happens, level V is something mild like a 'PG' movie that might scare some, and level XII is an 'R' rating where everything is chaotic and destructive. Just as people classify movies based on how they affect viewers, we classify shaking intensity based on how it affects people and structures.
Intensity Level Descriptions
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
MMI Level Description
I Not felt except by a few.
V Felt indoors; unstable objects disturbed.
VII Difficult to stand; slight structural damage.
IX General panic; considerable damage.
XII Total destruction; ground surface waves seen.
Detailed Explanation
Each level on the MMI scale is accompanied by descriptions that provide context for what people experience during an earthquake at that intensity. For instance, at level I, people may not even notice the earth shaking, whereas at level V, many inside a building might feel it and see objects wobbling. As the levels increase, the descriptions highlight the observable damage, panic among people, and the level of destruction that can occur, showcasing how devastating an earthquake can be.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a birthday party where you tell guests it's a surprise. At level I, it’s like no one realizes it’s a surprise yet, at level V, people start to murmur excitedly but there’s no chaos. At level IX, guests are running around, shouting with excitement and some decorations fall from the ceiling, and at level XII, everything has gone wild, with guests completely overwhelmed by the surprise party! Just like intensity levels describe the experience of an earthquake, this analogy shows how reactions can escalate in a situation.
Applications of Intensity Scales
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Widely used in seismic hazard zonation and vulnerability mapping.
Detailed Explanation
Intensity scales, particularly the MMI, are crucial for understanding potential damage areas in the event of an earthquake. By mapping out areas based on expected intensity, urban planners and engineers can assess where buildings might be at higher risk and how to implement solutions for disaster preparedness. This is essential for creating effective building codes and emergency response plans that cater to the specific needs of different regions.
Examples & Analogies
Think of this like a weather forecast. Just as a meteorologist predicts areas at higher risk for storms, using intensity scales helps predict where earthquakes will cause significant damage. Planners can then prepare safer designs and infrastructure to protect people, similar to how storm shelters are built in high-risk areas. This foresight helps save lives and minimize destruction.
Key Concepts
-
Seismic Intensity: Refers to shaking and damage effects experienced due to an earthquake, varying by location.
-
Modified Mercalli Intensity Scale: A qualitative measure of how an earthquake affects people and structures ranging from I (not felt) to XII (total destruction).
-
European Macroseismic Scale: Tailored for European contexts to record intensity and damage, focusing on specific building types.
-
Medvedev–Sponheuer–Karnik Scale: Affected similar to MMI but used in specific regions, focusing as much on human reaction.
Examples & Applications
In a city setting, a magnitude 6 earthquake may register as intensity V based on structural damage, while in a rural area, it may not be felt (intensity I).
During the 2011 earthquake in Japan, the MMI scale indicated high intensity in urban areas due to dense construction, leading to significant damage reports.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
If the earthquake's slight, MMI I's in sight, But when it's a fright, level XII takes flight.
Stories
Once upon a time, an earthquake shook a town. At first, the people felt nothing, so they rated it I. But soon, the ground trembled violently, and they saw devastation, marking it a full XII on the MMI scale!
Memory Tools
Remember 'MMC' for 'Magnitude is More Constant', helping recall that intensity measures effects, not just raw energy.
Acronyms
Use 'MICE' to remember Modified Mercalli, Intensity, and its Effects.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Seismic Intensity
A measure of the shaking and damage experienced at specific locations during an earthquake.
- Modified Mercalli Intensity (MMI) Scale
A scale that quantifies the effects of earthquakes based on human perception and structural damage, ranging from I (not felt) to XII (total destruction).
- European Macroseismic Scale (EMS98)
An intensity scale designed for European conditions, providing detailed descriptions of damage for various building types.
- Medvedev–Sponheuer–Karnik (MSK) Scale
An intensity scale similar to the MMI, used primarily in countries like India and the former USSR, focusing on human reactions and building damage.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
