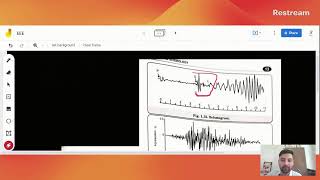
Components of a Seismogram
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Seismograms
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to talk about seismograms, which are crucial for understanding how the ground moves during earthquakes. Can anyone tell me what a seismogram is?

Isn't it a type of graph that shows earthquake activity?

Exactly! A seismogram records the motion of the ground, helping engineers design safer structures. Now, how many components do you think a seismogram has?

I think it has three components?

That's right! We have vertical, North-South, and East-West components. Let's discuss each one.
Vertical Component of a Seismogram
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

First, let's look at the vertical component of a seismogram, which captures up-and-down movement. What do you think primarily affects this component?

I think it's influenced by P-waves!

Exactly! P-waves are the fastest seismic waves and cause significant vertical motion. This can affect buildings during an earthquake. What might happen if engineers don't consider this?

They might design buildings that collapse under vertical stress!

Correct! It shows why understanding the vertical component is vital for earthquake-resistant design.
Horizontal Components of a Seismogram
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's examine the horizontal components. Can anyone tell me what the North-South component measures?

It measures lateral motion in the North-South direction, right?

Yes! It captures motions influenced by S-waves and surface waves. And what about the East-West component?

That one captures lateral motion in the East-West direction!

Absolutely! Together, these components provide a comprehensive view of seismic activity. Can you see how this information is crucial for engineers?

Definitely! They need to know how structures will react in different directions.
Interpreting Seismograms
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Each of these three components provides independent but complementary information. Why might it be important to analyze all three?

It gives a complete understanding of how the ground moves overall!

Precisely! By analyzing the different directions and motions, engineers can better plan and design structures. How might having incomplete data affect our designs?

We could miss key factors that could cause buildings to fail during an earthquake.

Exactly! That's why understanding every component of a seismogram is critical.
Summary of Components
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s summarize what we’ve learned about the components of a seismogram. Can anyone name the three components?

Vertical, North-South, and East-West!

Great! And why do we need to analyze these components together?

To understand the complete motion of the ground during an earthquake!

Exactly! This understanding helps engineers design safer buildings. Remember, each component gives us vital information for earthquake preparedness.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The seismogram captures the motion of the Earth's surface through three components: vertical (Z-axis) for up-and-down motion, horizontal North-South for lateral motion in that direction, and horizontal East-West for motion in the opposite direction. Each component plays a vital role in analyzing ground motion during seismic events.
Detailed
Components of a Seismogram
A seismogram is an essential tool for understanding earthquake dynamics, recording the Earth's movement during seismic events. It consists of three main components:
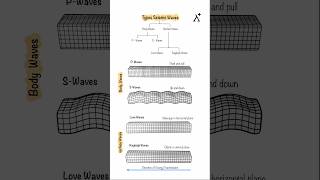
- Vertical (Z-axis): This component captures up-and-down movements, predominantly influenced by P-waves (primary waves), the fastest seismic waves.
- Horizontal - North-South (N-S): This captures the lateral ground motion in the North-South direction and is sensitive to both S-waves and surface waves, providing crucial information about horizontal movement.
- Horizontal - East-West (E-W): Similar to the N-S component, this captures lateral ground motion but in the East-West direction, also responding to S-waves and surface waves.
Each of these components provides independent yet complementary data, allowing engineers and seismologists to analyze the direction and magnitude of seismic activity effectively. Understanding these components is crucial for interpreting seismograms, helping in the design of earthquake-resistant structures.
Youtube Videos





Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Vertical (Z-axis) Motion
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Captures up-and-down motion.
• Usually affected by P-waves (primary waves).
Detailed Explanation
The vertical component of a seismogram records how much the ground moves up and down during an earthquake. This motion is primarily influenced by P-waves, which are the first seismic waves to arrive after an earthquake occurs. These waves compress and expand the material they pass through, causing a vertical displacement of the earth's surface.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a slinky being pushed up and down at one end. The movement at the other end mimics how P-waves push the ground vertically during an earthquake. Just like the slinky responds quickly, P-waves do too, being the fastest of the seismic waves.
Horizontal - North-South (N-S) Motion
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Captures lateral ground motion in the N-S direction.
• Sensitive to both S-waves and surface waves.
Detailed Explanation
The north-south horizontal component records side-to-side movements of the ground in the north-south direction during seismic activity. This component is particularly responsive to S-waves, which arrive after P-waves and are responsible for lateral ground displacement. Surface waves, which travel along the earth's surface, also contribute to this motion, often leading to more extensive damage.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a rowing boat being rocked by waves: the boat shifts side to side. This is similar to the ground moving horizontally as S-waves pass through, causing a back-and-forth motion.
Horizontal - East-West (E-W) Motion
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• Captures lateral ground motion in the E-W direction.
• Also responsive to S-waves and surface waves.
Detailed Explanation
Similar to the north-south motion, the east-west horizontal component of a seismogram captures the lateral ground movement, but in the east-west direction. This motion is similarly influenced by S-waves and surface waves, each contributing to the overall shaking felt during an earthquake. Understanding this component is critical for assessing how different parts of a structure will respond to lateral forces.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a swing being pushed at both ends. As it sways to the left and right, it illustrates how the ground moves east and west during seismic events, giving us insight into the ground's lateral movement.
Importance of Seismogram Components
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Each component provides independent but complementary information about the direction and magnitude of seismic motion.
Detailed Explanation
The three components of a seismogram—vertical, north-south, and east-west—work together to provide a comprehensive picture of the seismic activity during an earthquake. Each component offers unique insights into how the ground behaves, which is essential for engineers and seismologists in assessing the earthquake's impact and designing structures that can withstand such forces.
Examples & Analogies
Consider piecing together a puzzle. Each puzzle piece provides specific information to create a complete picture. In the same way, the information from each seismograph component combines to help engineers understand the complex effects of an earthquake on the surface.
Key Concepts
-
Seismogram: A recording that provides vital information during earthquakes.
-
Vertical Component: Measures up-and-down motion primarily caused by P-waves.
-
Horizontal Components (N-S and E-W): Measure lateral movements affected by S-waves and surface waves.
Examples & Applications
A seismogram recorded during the 2011 Japan earthquake shows significant vertical and horizontal components indicative of seismic motion.
Engineers interpret seismograms from past earthquakes to design buildings capable of withstanding similar seismic events.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In the ground, motions play, vertical up and down sway. North-South ledge, East-West best, seismograms help us pass the test.
Stories
Imagine the seismogram as a performer on stage. The vertical component is the ballet dancer, soaring up and down, while the North-South and East-West performers twirl side to side, creating a complete performance during an earthquake.
Memory Tools
Remember the three components of seismograms: 'V-N-E' for Vertical, North-South, and East-West.
Acronyms
The acronym 'VEN' stands for Vertical, East-West, North-South to help memorize the seismogram components.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Seismogram
A graphical output or digital record that captures the motion of the ground during an earthquake.
- Seismograph
An instrument used to produce a seismogram by recording ground motions.
- Pwave
Primary waves, the fastest seismic waves that usually cause vertical motion.
- Swave
Secondary waves that arrive after P-waves, causing lateral motion.
- Surface Waves
Waves that travel along the surface of the ground, causing significant damage.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
