Seismogram Databases and Resources
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Seismogram Databases
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today we're diving into seismogram databases, which are critical for analyzing earthquakes. Can anyone tell me why access to seismogram records is so important?

I think it helps engineers design buildings that can withstand earthquakes.

That's right! Having accurate data allows engineers to analyze structural responses to seismic waves. Now, let's talk about specific databases. Who has heard of PEER?

I've heard of it! It's related to the Pacific Earthquake Engineering Research Center.

Exactly! The PEER Database is an excellent resource. It provides extensive ground motion records. Can someone explain why these records are essential for earthquake engineering?

They help in understanding what types of ground motion can occur in different conditions.

Absolutely. They allow for better predictions and improved building designs.
Overview of Key Databases
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we have a grasp on why seismogram databases are important, let’s dive into the main sources of this data. Who can tell me about the USGS Earthquake Archive?

It's a resource by the United States Geological Survey that keeps track of earthquakes.

Exactly! It's a vital archive for researchers. What do you think are the benefits of having access to such archives?

It must help scientists monitor seismic activity over time and contributes to our understanding of tectonic activities.

Correct! Continuous monitoring and historical data are crucial for predicting future seismic events. Can anyone tell me about IRIS?

IRIS collects seismic data for educational purposes, right?

Correct again! IRIS plays a significant role in making seismic data accessible. Together, these databases reinforce our ability to analyze and prepare for seismic events.
Uses of Seismogram Data in Engineering
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

We've discussed where to find seismogram data, but how exactly is this data used in engineering? Let's brainstorm.

I think it's used for creating better building codes and standards for construction.

Yes, and also for assessing the potential impacts of earthquakes on structures! Does anyone know specific example cases where this data was notably impactful?

The Northridge earthquake led to changes in building codes, right?

Exactly. Historical data from past earthquakes informs current design standards, which helps us build safer structures.

So the past directly influences how we build today?

Precisely! By analyzing data from seismograms, engineers can enhance safety and durability for new buildings.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section highlights significant seismogram databases like the PEER Ground Motion Database, USGS Earthquake Archive, and IRIS, which provide access to thousands of earthquake records. These resources are crucial for earthquake engineering and research.
Detailed
Seismogram Databases and Resources
In the realm of earthquake engineering and seismology, having access to a breadth of seismogram data is critical for analysis and design. This section identifies three primary databases that serve as valuable resources for obtaining earthquake records:
- PEER Ground Motion Database (Pacific Earthquake Engineering Research Center): A key platform that offers various ground motion records essential for empirical studies and design methodologies in earthquake engineering.
- USGS Earthquake Archive: Operated by the United States Geological Survey, this archive provides comprehensive data on seismic activities and is a reliable source for researchers and engineers.
- IRIS (Incorporated Research Institutions for Seismology): This institution aggregates various seismic data, making it accessible for educational and research purposes.
These databases collectively provide access to thousands of earthquake records, facilitating detailed analysis of seismic events, which is fundamental to the development and application of earthquake-resistant designs.
Youtube Videos

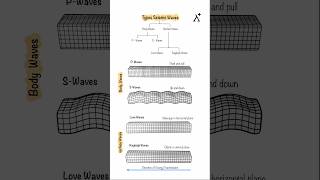


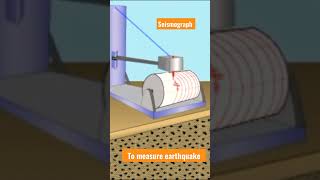



Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
PEER Ground Motion Database
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• PEER Ground Motion Database (Pacific Earthquake Engineering Research Center)
Detailed Explanation
The PEER Ground Motion Database is a comprehensive collection of seismic records provided by the Pacific Earthquake Engineering Research Center. It contains a wide variety of ground motion data that researchers and engineers can use for analyzing earthquakes and improving building design. By providing access to this database, users can study specific earthquake events and understand their impacts on structures.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the PEER Ground Motion Database like a large library of earthquake stories. Each record tells a unique story about how the ground shook during specific earthquakes, allowing engineers to learn from past events to build safer buildings in the future.
USGS Earthquake Archive
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• USGS Earthquake Archive
Detailed Explanation
The USGS Earthquake Archive is a crucial resource maintained by the United States Geological Survey. This archive contains extensive records of earthquakes that have occurred in the U.S. and around the world. The data can include information on the location, magnitude, depth, and timing of events. This archive helps scientists and engineers to analyze patterns in seismic activity and allows for improved predictions and risk assessments.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine the USGS Earthquake Archive as a digital map of every significant earthquake that has ever happened. Just like historians study ancient maps to understand past societies, engineers and scientists analyze this archive to learn about the patterns of earthquakes over time.
IRIS Resources
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
• IRIS (Incorporated Research Institutions for Seismology)
Detailed Explanation
IRIS, or the Incorporated Research Institutions for Seismology, is another vital resource offering access to numerous seismic data sets. IRIS provides educational resources, data from research projects, and opportunities for collaboration among those studying seismology. These resources are essential for advancing the field of earthquake research and ensuring that the most accurate and current information is available for analysis.
Examples & Analogies
Think of IRIS as a collaborative kitchen where chefs (researchers) come together to share their recipes (data) about earthquakes. Each chef contributes their expertise to create a vast menu (database) of knowledge that everyone can taste and learn from.
Importance of Access to Seismogram Data
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
These platforms provide access to thousands of earthquake records for analysis and design.
Detailed Explanation
Access to seismogram data through these platforms is essential for engineers and researchers. The thousands of records available allow for detailed analyses of seismic events, helping to develop better building codes and safety measures. By understanding how structures respond to past earthquakes, engineers can predict future risks and design buildings that can better withstand seismic forces.
Examples & Analogies
Consider the work of civil engineers who design buildings like architects designing houses. Just like a builder needs detailed blueprints to construct a home that can withstand weather conditions, engineers need accurate seismogram data to create buildings that can handle earthquakes effectively.
Key Concepts
-
Seismogram Databases: Resources like PEER, USGS, and IRIS hold extensive seismic data vital for analysis.
-
Importance of Seismogram Data: Historical and continuous monitoring data is essential for understanding seismic behavior and improving engineering practices.
Examples & Applications
The PEER Ground Motion Database provides records of significant earthquakes that can help researchers understand seismic risks associated with construction projects.
Data from the USGS Earthquake Archive aids in evaluating the long-term trends in seismic activity, influencing earthquake preparedness strategies.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Seismograms show wave where ground does shake, secure structures we will make!
Stories
Imagine a tiny earthquake detective who collects records from the PEER database to help engineers build safer buildings in cities prone to seismic waves.
Memory Tools
Remember 'PUI' for seismic databases: PEER, USGS, IRIS.
Acronyms
For the key databases
P-U-I (PEER
USGS
IRIS).
Flash Cards
Glossary
- PEER Ground Motion Database
A resource providing extensive ground motion records for earthquake analysis associated with the Pacific Earthquake Engineering Research Center.
- USGS Earthquake Archive
The United States Geological Survey repository of seismic event data and historical earthquake records.
- IRIS
The Incorporated Research Institutions for Seismology, which provides access to seismic data for educational and research purposes.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
