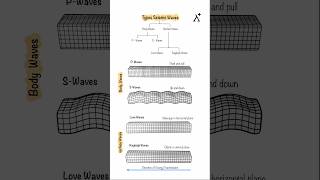
Types of Seismograms
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Analog Seismograms
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're exploring analog seismograms. Does anyone know what they are?

Aren't they the old-fashioned way of recording earthquakes?

Exactly! They record ground motion on smoked or photographic paper. Can anyone tell me one limitation of this method?

I think it's hard to digitize those records?

Right again! This limitation makes it difficult to analyze them with modern tools. Remember: Analog = Aging Technology. A good mnemonic to remember!
Exploring Digital Seismograms
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let’s shift our focus to digital seismograms. Who can explain how they differ from analog?

I think they use computers to record seismic activity, right?

Correct! Digital seismograms digitize signals at high resolution. This allows for easier computation and interpretation. It’s like comparing a vintage film camera with a high-resolution digital camera – the difference in clarity is huge!

So, they're just better overall for analysis?

Precisely! Digital recordings are stored as time-series data, which can be analyzed quickly, aiding engineers immensely in designing structures to withstand earthquakes.
Importance in Earthquake Engineering
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Why do you think understanding seismograms, both analog and digital, is vital for earthquake engineers?

They need to know how the ground moves during an earthquake!

Exactly! Engineers analyze these records to predict impacts on structures. Can someone give me an example of how this knowledge is applied?

They can design buildings that don't fall during earthquakes!

Right! They apply these insights to enhance seismic resilience, ensuring structures can endure tremors. Key takeaway: Seismograms guide many construction principles.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
This section discusses two main types of seismograms: analog seismograms, which are older and use traditional paper methods for recording seismic activity, and digital seismograms, which employ modern digital technology for enhanced precision and ease of analysis, playing a essential role in earthquake engineering.
Detailed
Types of Seismograms
Seismograms serve as critical tools for capturing and analyzing ground motion during earthquakes. This section dives into two distinguished types of seismograms—analog and digital—which are fundamentally different in both their technology and application:
Analog Seismograms
- Historically used, analog seismograms record seismic data on smoked or photographic paper. While effective for their time, these older instruments present challenges in digitization and modern analysis, limiting their utility in contemporary seismic research.
Digital Seismograms
- In contrast, digital seismograms utilize advanced technology to digitize seismic signals at high resolution, making them more manageable for computational analysis. They allow for the storage of data in a time-series format, enabling swift interpretation and application in engineering contexts.
Both types of seismograms play significant roles in earthquake engineering, helping professionals understand seismic activity and apply this knowledge toward designing resilient infrastructure.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Analog Seismograms
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Older instruments recorded motion on smoked paper or photographic paper.
- Difficult to digitize or analyze with modern tools.
Detailed Explanation
Analog seismograms represent the earlier technology used in seismology to document and visualize earthquake motions. These devices worked by creating a physical recording of ground vibrations on materials such as smoked or photographic paper. The mechanism involved a pendulum that moved in response to ground motion, leaving a trace on the paper. Though they were essential for early studies, the analog format made it challenging to apply modern analytical techniques, as digitization required conversion of physical records into digital data.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine writing down notes with a pen on paper. If you need to share your notes digitally, you'd have to find a way to scan or convert them into a text file. This is similar to how analog seismograms need to be converted into digital formats to use modern analysis tools effectively.
Digital Seismograms
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Modern instruments digitize signals at high resolution.
- Stored as time-series data, enabling easier computation and interpretation.
Detailed Explanation
Digital seismograms have revolutionized the way seismic data is collected and analyzed. Modern seismographs convert ground motion into digital signals at a high resolution. This means that each vibration is captured as distinct numerical measurements over time, allowing for sophisticated computational analysis. These digital records can easily be manipulated, allowing engineers and seismologists to apply complex algorithms for examining seismic waveforms and predicting potential impacts on structures.
Examples & Analogies
Think of it like taking a photograph versus a video. An analog recording is like a single snapshot, limited in what it can convey, while a digital seismogram is akin to a video that captures motion over time in detail. This advantage allows scientists to analyze seismic events with much greater accuracy and depth, ultimately leading to better earthquake preparedness and response.
Key Concepts
-
Analog Seismograms: Use traditional paper methods and have limitations in modern analysis.
-
Digital Seismograms: Modern technology allows for precise recording and easier analysis.
Examples & Applications
An analog seismogram could show a jagged trace on paper indicating a major earthquake, while a digital seismogram will display a refined graph that shows smoother and clearer waves.
An earthquake engineer reviewing digital seismogram data can quickly run simulations on expected structural responses using real-time data.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Analog's on paper, so long ago, Digital's on screens, now it's the show!
Stories
Imagine an old seismologist trying to read fuzzy lines on a paper, but a tech-savvy intern shows him clean lines on a screen with quick results!
Memory Tools
A.D. = Analog Difficulty; D.A. = Digital Advantage.
Acronyms
D.A.P.E. – Digital is Analyzed Promptly and Easily.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Seismogram
A graphical output or digital record capturing ground motion during an earthquake.
- Analog Seismograms
Older seismograms that record seismic activity on smoked or photographic paper.
- Digital Seismograms
Modern seismograms that digitize seismic signals for easier analysis and interpretation.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
