Hotspots and Intraplate Volcanism
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Hotspots
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will learn about hotspots, which are extraordinary features in geology. Can anyone explain what a hotspot is?

Is it some kind of volcano?

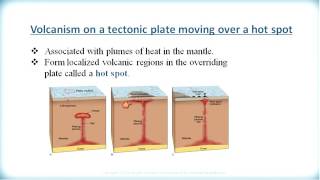
That's right! Hotspots are stationary plumes of hot magma that originate from deep within the Earth's mantle. They are significant because they can create volcanism away from plate boundaries.

So like the Hawaiian Islands? They formed from a hotspot?

Exactly! The Hawaiian Islands were created as the Pacific Plate moved over the Hawaiian hotspot. This shows how hotspots can form chains of islands.

How do we know the direction that the plate moved?

Great question! The age of the islands provides clues. The youngest island, Hawaii, is over the hotspot, while the older islands are farther away, indicating the plate's movement.

What else can hotspots tell us?

They help track tectonic plate movement and can also give insights into volcanic activity patterns. Let’s recap: hotspots are stationary magma sources and important for understanding plate tectonics.
Intraplate Volcanism and Earthquakes
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, we will talk about intraplate volcanism and its relation to earthquakes. Can anyone define intraplate earthquakes?

Are they earthquakes that happen inside tectonic plates?

That's correct! Intraplate earthquakes occur away from plate boundaries and can be tied to hotspot activity or reactivation of old faults.

Why are they so significant if they are less common?

Although rare, they can still cause significant damage. Knowing where they might occur helps in risk assessment and preparedness.

Can you give an example of intraplate earthquake activity?

Certainly! Some earthquakes in the central United States, like the 1811–1812 New Madrid earthquakes, are believed to be intraplate events.

This makes me think about how we can prepare for such events!

Absolutely! Understanding these concepts is crucial for disaster preparedness. Let’s summarize: intraplate earthquakes can occur due to hotspots or reactivated faults, and they are important to study for geological safety.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Hotspots are stationary plumes of magma that originate deep in the Earth’s mantle, contributing to the formation of unique volcanic structures, such as the Hawaiian Islands and Yellowstone. The section highlights the tectonic implications of these hotspots and notes the occurrence of intraplate earthquakes linked to hotspot activity or ancient fault reactivations.
Detailed
Hotspots and Intraplate Volcanism
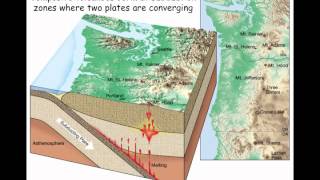
This section covers the concept of hotspots, which are stationary plumes of hot magma from deep within the Earth's mantle. Unlike volcanic activity associated with tectonic plate boundaries, hotspots can cause volcanism within tectonic plates themselves. A prominent example is the Hawaiian Islands, which formed as the Pacific Plate moves over a hotspot. Other notable hotspots include Yellowstone, known for its geothermal activity.
Tectonic Implications
The movement of tectonic plates over these hotspots leads to the formation of chains of volcanic islands, providing valuable information about the direction and velocity of plate movement. This allows geologists to track tectonic shifts over geological timescales.
Intraplate Earthquakes
Additionally, the section discusses intraplate earthquakes which occur away from plate boundaries, often due to the effects of hotspot activity or reactivation of ancient geological faults. Although intraplate earthquakes are less common than those at plate boundaries, they can have significant geological impacts.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Understanding Hotspots
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Hotspots: Stationary plumes of hot magma originating deep in the mantle.
Detailed Explanation
Hotspots are areas where magma from deep within the Earth's mantle rises to the surface. Unlike volcanic activity that generally occurs at tectonic plate boundaries, hotspots can cause volcanism in the middle of tectonic plates. This happens because the magma plume remains stationary while the tectonic plates move over it, which can create a series of volcanoes.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a hotspot like a candle under a piece of wax. As the heat rises from the candle (the hotspot), it melts the wax (the Earth's crust) above it. If you were to move the wax across the flame, you’d eventually see multiple melted spots where the wax had been heated, similar to how a moving tectonic plate can create a chain of volcanic islands over a stationary hotspot.
Examples of Hotspots
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Examples: Hawaiian Islands, Yellowstone.
Detailed Explanation
The Hawaiian Islands are a prime example of hotspot volcanism. As the Pacific Plate moves northwestward over the stationary hotspot, it creates a chain of volcanic islands. These islands become progressively older as you move away from the hotspot, illustrating the plate's motion. Yellowstone National Park is another notable hotspot, featuring a large caldera formed by massive volcanic activity over millions of years.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine dragging a finger across a melting ice cream cone. As you move your finger (the plate) across the surface, you'll leave a trail where the ice cream has melted, representing the series of volcanic islands formed as the plate moves over a hotspot.
Tectonic Implications of Hotspots
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Tectonic Implications: Plates move over hotspots, forming chains of volcanic islands; useful in tracking plate direction and velocity.
Detailed Explanation
As plates drift over hotspots, they leave behind a trail of volcanic activity, which can be mapped out. By studying the age and position of these volcanic islands, scientists can determine the rate and direction of tectonic plate movement. This provides valuable information about Earth's dynamic processes.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a slow-moving conveyor belt with a stationary printer on it. The printer (the hotspot) prints out labels (volcanic islands) as the belt (the tectonic plate) moves past it. By examining the order and placement of labels on the conveyor belt, you can determine how fast and in which direction the belt is moving.
Intraplate Earthquakes
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Intraplate Earthquakes: Though rare, they can occur away from plate boundaries due to hotspot activity or ancient fault reactivation.
Detailed Explanation
Intraplate earthquakes are seismic events that occur within a tectonic plate rather than at its boundaries. These earthquakes are less common but can arise from tectonic stresses or from ancient faults that are reactivated by new stresses, including those from nearby hotspot activity.
Examples & Analogies
It’s like when you have a water balloon (the tectonic plate) and press down on it in the middle (the hotspot). Even though you aren’t applying pressure at the edges, the balloon can still pop in the middle if the pressure becomes too great (similar to an intraplate earthquake).
Key Concepts
-
Hotspot: A source of magma that leads to volcanic activity away from the edges of tectonic plates.
-
Intraplate Earthquake: An earthquake that occurs within a tectonic plate, often due to factors unrelated to plate boundaries.
Examples & Applications
The Hawaiian Islands are formed by a hotspot in the middle of the Pacific Plate, illustrating how hotspots can create volcanic islands.
The Yellowstone National Park is built over a hotspot that has caused significant geothermal activity and eruptions.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Hotspots make islands, oh what a treat, as magma lays under, it’s quite the feat!
Stories
Imagine a hidden campfire deep inside the Earth. As the tectonic plates drift, they keep stopping over this campfire, cooking up delicious islands like Hawaii, each bite telling the story of a hotspot.
Memory Tools
H.I.P: Hotspots, Intraplate earthquakes, and Plate movement. This reminds us of the terms we learned today.
Acronyms
HIVE
Hotspots Involve Volcanism Everywhere
capturing the essence of what hotspots do.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Hotspot
A stationary plume of hot magma originating from deep in the Earth's mantle, leading to volcanic activity.
- Intraplate Earthquake
An earthquake that occurs within a tectonic plate, away from plate boundaries, often related to hotspot activity or ancient fault lines.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
