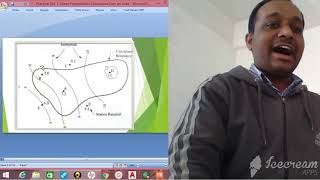
Use of Isopluvial Maps
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Isopluvial Maps
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll discuss isopluvial maps. Does anyone know what an isopluvial map is?

Is it a map that shows rainfall?

Exactly! Isopluvial maps show lines of equal rainfall depth or intensity. Why do you think these maps are important in hydrology?

They help in understanding rainfall distribution?

Yes, very good! They are particularly useful for estimating rainfall in areas without gauges. Remember this acronym SED: 'Systematic Estimation of Design storms.'

Can you give an example of how these maps are used?

Sure! Engineers use them to assess urban drainage needs and flood risks effectively. At the end of this discussion, you should remember the key role these maps play in flood management.
Applications of Isopluvial Maps in Design
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's dive deeper into how these maps are applied. Why do you think urban planners use isopluvial maps?

To figure out where flooding might happen?

Exactly! By analyzing rainfall patterns shown on isopluvial maps, they can design effective drainage systems. Can anyone think of how this might prevent issues downtown?

It could help prevent road flooding during heavy rain.

Great point! This is why isopluvial maps are crucial in urban planning. Always keep in mind the acronym UDF: 'Urban Drainage Forecasting.'

What happens in areas without enough data?

In such areas, isopluvial maps fill the gap by providing estimations. By the end of our lesson, I hope you all understand how crucial these maps are for stormwater management!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
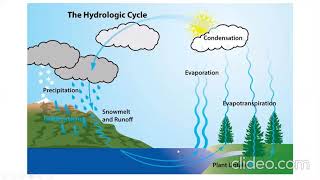
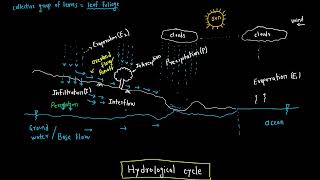
In this section, we explore isopluvial maps, which depict lines of equal rainfall depth or intensity over specific durations and frequencies. These maps serve hydrologists and engineers in estimating rainfall for ungauged areas, significantly enhancing urban drainage and flood modeling.
Detailed
Use of Isopluvial Maps in Hydrology
Isopluvial maps are essential tools in hydrology that illustrate areas with equal rainfall depth or intensity, particularly for specified durations and frequencies. These maps are pivotal for engineers and hydrologists when estimating design storms for ungauged sites, ensuring appropriate planning and infrastructure development in urban drainage and flood control systems.
Key Functions of Isopluvial Maps:
- Estimation of Design Storms:
- For ungauged locations, isopluvial maps provide a scientific basis for predicting potential stormwater runoff and flooding risks.
- Application in Urban Drainage:
- Helps design drainage systems that can effectively manage excess rainfall, which is crucial for disaster prevention and water resource management.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Isopluvial Maps
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Isopluvial maps show lines of equal rainfall depth or intensity for specific durations and frequencies.
Detailed Explanation
Isopluvial maps are graphical representations that display areas of equal rainfall depth or intensity. This means that if you were to look at such a map, you would see lines that connect points receiving the same amount of rainfall over a given time period. This is important because different areas might receive different amounts of rainfall during storms, and understanding how rainfall varies spatially can help in planning and design.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a weather map showing different temperatures across a country, with lines connecting places that have the same temperature. An isopluvial map works similarly, but instead of temperature, it shows rainfall depth or intensity. For example, if one section of a city receives more rain than another during a storm, the isopluvial map will visually represent that difference.
Applications of Isopluvial Maps
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Engineers and hydrologists use them for:
– Estimating design storms at ungauged locations.
– Urban drainage and flood modeling.
Detailed Explanation
Isopluvial maps are vital tools for engineers and hydrologists in several ways. Firstly, they can help estimate rainfall amounts in areas without rain gauges—referred to as ungauged locations. This is crucial for designing drainage systems to ensure they can handle potential floodwaters. Secondly, these maps assist in flood modeling by predicting how rainwater will behave in urban settings. With accurate rainfall intensity and depth information, engineers can better design infrastructure to manage storms effectively.
Examples & Analogies
Think of planning a party outside without a weather station nearby. You might have a friend check the weather in a nearby area and share the information, giving you an idea of how much it might rain. Similarly, isopluvial maps help give engineers guidance on how rainfall will vary by guiding them in designing necessary drainage and flood management systems in areas where direct measurements are unavailable.
Key Concepts
-
Isopluvial Map: Represents areas of equal rainfall depth or intensity.
-
Design Storm: A calculated event used in planning drainage systems.
-
Urban Drainage: The management of rainfall runoff in city areas.
Examples & Applications
An isopluvial map may be used to determine rainfall depths for a proposed park's drainage system, ensuring the area won't flood during heavy storms.
City planners utilize isopluvial maps to decide where to place new stormwater drains based on projected rainfall distribution.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Isopluvial maps are quite stunning, they show rainfall depth—it’s all about the flooding!
Stories
Imagine a town preparing for the spring floods. The planners make isopluvial maps to predict where water will pool, ensuring safe drainage and dry roads.
Memory Tools
Remember 'R.I.D.E' for understanding isopluvial maps: Rainfall Intensity Distribution Estimation.
Acronyms
I.M.P.A.C.T - Isopluvial Maps Predict Accurate Current Trends in rainfall.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Isopluvial Map
A map that shows lines of equal rainfall depth or intensity for specific durations and frequencies.
- Design Storm
A theoretical storm event with defined characteristics used for designing drainage systems and other water infrastructure.
- Urban Drainage Modeling
The simulation of how stormwater behaves in urban environments to manage runoff and prevent flooding.
- Ungauged Location
A geographical area where there are no rainfall measurement instruments installed.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
