Crop Coefficient (Kc)
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Crop Coefficient (Kc)
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

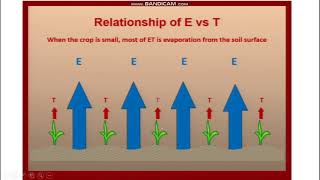
Today we are going to talk about the crop coefficient, represented as Kc. It's a dimensionless factor that helps us understand how much water a specific crop needs compared to a reference crop under similar environmental conditions.

Why is Kc important for crops?

Good question! Kc allows farmers to schedule irrigation more effectively. By knowing the Kc for a specific crop, we can calculate how much water it needs during different growth stages.

So, does Kc change for different crops?

Exactly! The value of Kc varies depending on the type of crop and its growth stage. For example, a growing crop typically has a higher Kc than a fully mature one.
Applying the Kc Formula
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

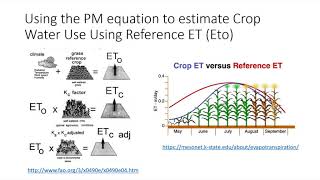
Now, let’s look at the formula for calculating the evapotranspiration of a crop: ETcrop = Kc × ETo. Can someone explain what each term means?

Sure! ETcrop is the evapotranspiration for the crop, Kc is the crop coefficient, and ETo is the reference evapotranspiration.

Correct! This means that if we have the Kc for a crop and the ETo value, we can determine how much water the crop needs.

Can we use this in different climates as well?

Absolutely! However, local conditions will influence ETo, and therefore, the Kc value will help adjust irrigation schedules to specific climatic conditions.
Factors Influencing Kc Values
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Kc values can change based on several factors including crop type, growth stages, and environmental conditions. Let's break these down.

What are some examples of crop types with different Kc values?

Great question! For instance, paddy typically has a higher Kc than wheat because it requires more water due to its persistent need for standing water.

Does the growth stage affect Kc too?

Yes! Young crops have lower Kc values, while they increase as the crops mature. Understanding this helps in scheduling irrigation correctly.
Kc and Water Management
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Understanding Kc is instrumental in water management. How do you think using Kc can improve irrigation efficiency?

It helps in providing the right amount of water at the right time!

Exactly! Efficient water management means we can reduce waste and improve crop yield. The use of Kc aligns irrigation practices with crop requirements.

So, could it also conserve water in drought conditions?

Absolutely! By applying water based on Kc, we can conserve resources, especially during periods of water scarcity. And that wraps up our discussion on the crop coefficient!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Understanding the crop coefficient (Kc) is vital for estimating the water requirements of crops by quantifying how much water a crop uses relative to reference evapotranspiration (ETo). Kc varies with different crops and growth stages, allowing for more accurate irrigation planning.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
In this section, we discuss the crop coefficient (Kc) as an essential tool for determining the water needs of crops. The crop coefficient is a dimensionless factor that describes the relationship between the evapotranspiration (ET) of a specific crop and a standard reference evapotranspiration (ETo). This relationship is crucial because it allows farmers and agronomists to assess irrigation requirements accurately.
The formula for estimating the crop's ET is:
ETcrop = Kc × ETo
Where:
- ETcrop: Evapotranspiration of the crop
- Kc: Crop coefficient, which varies with crop type and growth stage
- ETo: Reference evapotranspiration, a measure of the evaporation of water from a reference surface.
Kc is an important parameter in irrigation planning, enabling the adjustment of irrigation scheduling based on the crop's specific growth stage, climatic conditions, and soil moisture availability. This understanding of Kc aids in optimizing water use efficiency and supporting sustainable agricultural practices.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Crop Coefficient (Kc)
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
A dimensionless factor representing the relationship between ET of a particular crop and reference ET.
Detailed Explanation
The crop coefficient (Kc) is an important concept in irrigation management. It is a dimensionless number that helps relate the actual evapotranspiration (ETcrop) of a specific crop to the reference evapotranspiration (ETo), which serves as a standard for comparing water use by different crops. This relationship is essential for understanding how much water a crop needs during its growth stages.
Examples & Analogies
Think of Kc as a conversion factor similar to how you would convert kilometers to miles. Just like you multiply kilometers by a conversion constant to get miles, you multiply the reference evapotranspiration by Kc to find out how much water a specific crop requires.
Evapotranspiration Relationship
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
ETcrop = Kc × ETo
Detailed Explanation
This formula illustrates the relationship between the actual evapotranspiration of a crop (ETcrop) and the reference evapotranspiration (ETo). Here, ETcrop represents the actual water lost from the crop through both evaporation from the soil and transpiration from the leaves, while ETo is a baseline measurement of evapotranspiration under ideal conditions. By using Kc, we can adjust ETo based on the crop type and its growth stage to determine how much water the crop will need.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you're baking a cake and have a standard recipe. The Kc represents adjustments you might make based on your ingredient quality or altitude. Similarly, Kc adjusts the standard ET based on specific crop characteristics, helping farmers 'bake' the right amount of water into their irrigation plans.
Variability of Kc
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Where: Kc = Varies with crop type and growth stage
Detailed Explanation
The value of Kc changes depending on two main factors: the type of crop and the growth stage of that crop. Different crops have distinct water needs, and as they grow, these needs change. For instance, a young crop may require less water than a mature one, and thus the Kc value at different stages of growth will vary.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a plant like a child. When young, children might need smaller portions of food compared to when they grow into teenagers. Similarly, as plants grow, their Kc values increase, reflecting their increasing water needs during different growth stages.
Key Concepts
-
Crop Coefficient (Kc): A crucial factor for determining how much water a crop needs compared to a reference crop. It varies with crop type and growth stage.
-
Evapotranspiration (ET): The total water lost through evaporation and plant transpiration, essential for calculating irrigation needs.
-
Reference Evapotranspiration (ETo): A baseline measure of evaporation used to establish Kc values for various crops.
Examples & Applications
A Kc of 0.8 for a wheat crop means it uses 80% of the water of the reference evapotranspiration.
Paddy has a higher Kc value of about 1.2, which reflects its need for more water due to its growth conditions.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Crop coefficient, don't forget, helps us know the water we must get!
Stories
Imagine a farmer using Kc as his guiding star, setting irrigation timings and saving water from afar.
Memory Tools
Kc = K (Crops) x ETo (Evapotranspiration Reference): Remember to multiply Kc to ETo for crop needs.
Acronyms
Kc
Keep Control on Crop water needs!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Crop Coefficient (Kc)
A dimensionless factor representing the relationship between the evapotranspiration of a specific crop and the reference evapotranspiration.
- Evapotranspiration (ET)
The sum of evaporation from soil and transpiration from plants.
- Reference Evapotranspiration (ETo)
The rate of evaporation from a reference surface, typically a well-watered grass surface.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
