Irrigation Requirement (IR)
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Irrigation Requirement
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will explore Irrigation Requirement, or IR. Can anyone tell me what IR is?

Isn't IR how much water we need to supply to crops?

Exactly! IR is the quantity of water we must provide to meet the total water needs of a crop. It’s a critical factor in irrigation planning. Now, how do we calculate it?

Is it IR equals WR minus ER?

Correct! We subtract Effective Rainfall from Crop Water Requirement to find IR. Let's remember this with the acronym 'I-R-W-E': Irrigation Requirement = Water Requirement - Effective Rainfall.
Effective Rainfall (ER)
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's dive deeper into Effective Rainfall, or ER. Why do you think not all rainfall is effective?

Because some might run off or not reach the roots!

Exactly! Runoff and deep percolation mean that some water doesn't reach the plants’ root zones, which we account for in our IR calculations. Who knows how we might estimate ER?

I think there are methods like the USDA method or soil moisture balance method!

Great points! These methods help us understand the effective portion of rainfall and play a vital role in irrigation management. Remember, ER directly influences our IR calculations.
Significance of IR in Agriculture
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Why do we think understanding IR is crucial for farmers?

So they know how much water to supply?

Correct! It helps farmers avoid over or under-irrigation, which can lead to water wastage or stress on crops. Can anyone think of what might happen with under-irrigation?

Crops could become stressed and yield would reduce!

Right! Proper calculation of IR ensures optimal water use, contributing to sustainable farming practices. Always remember the equation and its components!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The section on Irrigation Requirement (IR) discusses how to determine the amount of water necessary for crop irrigation, factoring in effective rainfall. Understanding these calculations is crucial for efficient agricultural practices.
Detailed
Irrigation Requirement (IR)
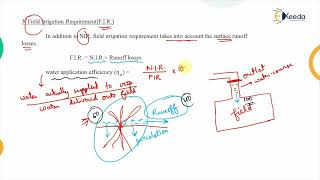
The Irrigation Requirement (IR) represents the quantity of water that must be supplied via irrigation to meet the Crop Water Requirement (WR). It is calculated as:
IR = WR - ER
where ER is the Effective Rainfall, defined as the portion of rainfall that is actually usable by crops.
Understanding IR is essential for efficient irrigation practices, ensuring that crops receive the necessary water without wastage. This plays a critical role in agricultural sustainability and productivity, particularly in water-scarce regions.
Youtube Videos








Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Irrigation Requirement
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
The quantity of water that must be supplied through irrigation to meet the WR.
Detailed Explanation
Irrigation Requirement (IR) refers to the amount of additional water needed through irrigation systems to fulfill the overall water requirement (WR) of crops. WR includes all types of water needed for crops to grow, while IR specifically focuses on irrigation water, excluding any rainfall that can support crop growth. Thus, IR helps farmers and agricultural planners estimate how much irrigation water they need to apply in addition to what they get from rain.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a plant in your garden during a sunny week. If it receives enough rain, it may only need a little extra watering to thrive. However, if there's a drought, you would need to provide more water through your hose or watering can to keep it healthy. In agricultural terms, that extra watering is what we consider the Irrigation Requirement.
Formula for Calculating IR
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
IR = WR – ER
Where ER is Effective Rainfall (portion of rainfall usable by crops).
Detailed Explanation
To calculate the Irrigation Requirement (IR), you use the formula IR = WR – ER. Here, WR represents the total water need of the crops throughout their growth period, while ER denotes the effective rainfall, meaning only the portion of the rainfall that is actually beneficial for the crops (usable by plants). This formula allows agriculturalists to determine how much extra irrigation is necessary after accounting for rainfall.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you're trying to fill a glass with water using both a jug and some rainwater that has collected in a bucket. The total amount of water you need to fill the glass represents WR. The amount of rainwater you can actually pour into the glass, which won't spill or evaporate, is ER. The amount you must still pour from the jug to fill the glass completely is your IR.
Key Concepts
-
Irrigation Requirement (IR): The amount of water supplied through irrigation to meet crop needs.
-
Effective Rainfall (ER): The usable portion of rainfall impacting irrigation plans.
-
Water Requirement (WR): Total water needed by crops over their growth cycle.
Examples & Applications
A farmer calculates that their crop requires 500 mm of water over the growing season and receives 200 mm of rain; thus, their IR would be 500 mm - 200 mm = 300 mm.
If another crop needs 700 mm in total but effective rainfall accounts for 100 mm, the irrigation requirement would be 700 mm - 100 mm = 600 mm.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
IR tells us what we lack, WR is what we track, ER's the rain that we can stack!
Stories
Once, a farmer named Sam forgot to calculate his irrigation needs properly. He watched his crops suffer from stress due to lack of water, remembering he should compare his Water Requirement with any Effective Rainfall!
Memory Tools
Think of "I-R-E" where I is for Irrigation, R stands for Requirement, and E is for Effective Rainfall to remember the calculation process.
Acronyms
Use the acronym 'IR-WE' - Irrigation Requirement = Water Requirement - Effective Rainfall.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Irrigation Requirement (IR)
The total amount of water that needs to be supplied through irrigation to meet the crop's water requirement.
- Crop Water Requirement (WR)
The total quantity of water required by a crop during its entire growth period.
- Effective Rainfall (ER)
The portion of total rainfall that is usable by crops, accounting for losses due to runoff and deep percolation.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
