Root Zone Depth and Soil Moisture Depletion
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Root Zone Depth
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we are going to discuss root zone depth and its importance in crop irrigation. Can anyone tell me what they think root zone depth means?

Is it how deep the roots of a plant grow?

Exactly! The root zone depth refers to how deep the plant's roots can access water and nutrients in the soil. Different crops have different depths. For example, paddy typically has a root zone depth of 0.2 to 0.3 meters.

What about other crops, like wheat?

Great question! Wheat can have a root zone depth ranging from 0.6 to 1.2 meters. The deeper the roots, the more water they can access, which leads us to our next topic: managing soil moisture.

How can we tell when to water the crops?

We need to monitor soil moisture depletion! We should apply water when the depletion reaches the allowable limit to avoid stress on the crops. Let’s recap: root zone depth varies by crop, and we must manage soil moisture to optimize growth.
Soil Moisture Depletion Importance
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we’ve discussed root zone depth, why do you think managing soil moisture depletion is important?

If the soil dries out too much, plants might not grow well, right?

Correct! Crop stress due to improper watering can reduce yield and quality. Monitoring allows us to apply just the right amount of water. Can anyone think of the risks of overwatering?

Maybe it leads to waterlogging or root diseases?

Yes, good point! Overwatering can create a poor environment for roots. Let's summarize: proper moisture management ensures healthy crops and efficient water use.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The root zone depth of crops influences their water needs significantly. It is crucial to monitor soil moisture levels and apply water only when depletion hits a threshold to ensure optimal growth and yield while avoiding unnecessary water usage.
Detailed
Root Zone Depth and Soil Moisture Depletion
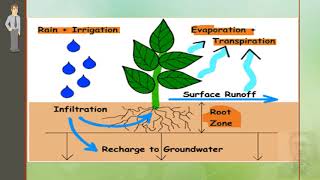
Understanding the relationship between root zone depth and soil moisture depletion is critical for effective irrigation management in agriculture. Each crop has a unique root zone depth that dictates how much water it can access and use during its growth period. The table below illustrates the typical root zone depths for various major crops:
| Crop | Root Zone Depth (m) |
|---|---|
| Paddy | 0.2 – 0.3 |
| Wheat | 0.6 – 1.2 |
| Cotton | 1.2 – 1.5 |
| Sugarcane | 1.5 – 2.0 |
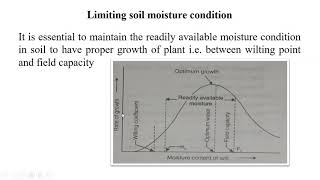
It is essential to apply water only when the soil moisture depletion reaches the allowable limit for each crop. This approach helps prevent plant stress, which can lead to diminished yield and quality. Monitoring soil moisture levels effectively ensures that crops receive the right amount of water at the right time, contributing to sustainable agricultural practices.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Introduction to Root Zone Depth
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Different crops have different root zone depths.
Detailed Explanation
Root zone depth refers to the area of soil where the roots of the plant can absorb water and nutrients. Each crop species has its own root zone depth depending on its growth requirements and adaptation to the soil types. Knowing the root zone depth is important for optimal irrigation planning to ensure that water reaches the roots effectively.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the root zone depth like the height of a well that supplies water to a plant. If the water level in the well is too low, the roots cannot access it properly. Similarly, if the root zone is shallow, crops cannot reach deep moisture, which is essential for their growth.
Allowed Depletion Before Irrigation
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Water should be applied when depletion reaches the allowable limit to avoid stress.
Detailed Explanation
Allowable depletion refers to the specific level of soil moisture depletion that can occur before applying irrigation without stressing the plant. Understanding this limit helps farmers schedule their irrigation effectively. If plants experience water stress, it can affect their growth, yield, and overall health.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you are waiting for a bus, and you have a limited amount of water in your bottle. You wouldn't drink it all immediately; instead, you would sip it slowly to make it last until the bus arrives. Similarly, plants need careful management of water to avoid reaching a point of stress where they cannot function properly.
Root Zone Depth for Various Crops
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Crop Root Zone Depth (m)
- Paddy 0.2 – 0.3
- Wheat 0.6 – 1.2
- Cotton 1.2 – 1.5
- Sugarcane 1.5 – 2.0
Detailed Explanation
Different crops have varying root zone depths. For example, paddy, which is grown in flooded conditions, has a root zone depth of 0.2 to 0.3 meters, while crops like sugarcane may extend to 1.5 to 2.0 meters deep. These differences affect how much water these crops can access and their irrigation needs. Farmers must take these depths into account when planning how much water to apply.
Examples & Analogies
Consider planting flowers in a garden bed of varying depths. Flowers with shallow roots need less water because they can only reach the moisture at the surface, while deeper-rooted plants can access water deeper in the ground. This is similar to how different crops are adapted to various root zone depths, affecting their water consumption.
Key Concepts
-
Root Zone Depth: Varies per crop, determines accessibility of water and nutrients.
-
Soil Moisture Depletion: Needs regular monitoring to optimize irrigation.
-
Irrigation Timing: Critical to apply water based on allowable limits to avoid crop stress.
Examples & Applications
Paddy requires frequent water applications due to its shallow root zone depth (0.2 – 0.3 m), while sugarcane, with a depth of 1.5 – 2.0 m, may utilize water less frequently yet in greater quantities.
Managing soil moisture for wheat is crucial as its root zone can reach a depth of up to 1.2 meters, meaning it can access deeper water but still needs monitoring to avoid stress.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
When roots go deep, the crops will thrive, / But if the soil dries, our plants won’t survive.
Stories
Once in a garden, there were crops of every type. The wise gardener knew that the tall cotton needed deep waters, while the delicate paddy only needed shallow puddles to bloom. He always checked the soil before watering, ensuring each plant had just what it needed.
Memory Tools
Use the acronym 'D.A.P' - Depletion, Allowable limit, and Plants to remember what to monitor for healthy crops.
Acronyms
RWS – Root zone, Water needs, Soil moisture as a guide to remember the basics of irrigation management.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Root Zone Depth
The depth in soil from which a plant's roots can extract water and nutrients.
- Soil Moisture Depletion
The reduction in soil moisture levels that occurs as plants use water during growth.
- Allowable Limit
The threshold of soil moisture depletion that is acceptable before irrigation is required.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
