Duty, Delta, and Base Period
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Duty
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Good afternoon, class! Today, we'll discuss Duty in irrigation. Can anyone tell me what they think Duty refers to in terms of irrigation?

Isn't Duty the amount of water that crops need?

Good question! Duty actually refers to the area that can be irrigated per unit discharge of water. It helps us understand how much land we can water with a given amount of water flow. The formula is D = A / Q, where A is the area and Q is the discharge. Remember, D is about area, not just water needs.

So, if I have a certain amount of water, how do I know how much area I can irrigate?

Exactly! By knowing your discharge rate, you can find the irrigable area using the Duty formula. It's essential for efficient resource management.

Quick recap: Duty helps us calculate the area we can irrigate based on water discharge.
Understanding Delta
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let’s move to Delta, denoted as Δ. Who can explain what Delta means in the context of crop irrigation?

I think Delta is about the amount of water crops need, right?

Yes, that's correct! Delta represents the total depth of water a crop requires during its growing period. The calculation involves the formula Δ = (8.64 × B) / D, where B is the base period. Can anyone tell me what the base period refers to?

Is it the time from planting to harvesting?

Exactly! The base period indicates the duration of water application required for crops from the first watering to just before harvest. Understanding Delta helps us ensure that crops receive adequate water throughout their growth phases.

To summarize, Delta is crucial for determining how much water is needed during a crop's growth, and its calculation depends on both the base period and duty.
Base Period Importance
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let’s talk about the Base Period. Can anyone recall why the Base Period is significant in irrigation management?

It seems like the timing of watering is really important, right?

Absolutely! The Base Period defines when we start watering and when we stop before harvest. It affects how effectively we can use our water resources. A well-planned base period can optimize water allocation, avoiding both stress and waste.

So, does this mean farmers should monitor this period closely?

Exactly! Monitoring the base period allows farmers to schedule irrigation effectively and ensure that crops are properly hydrated, leading to better yields.

To wrap up, remember that Duty, Delta, and Base Period are interlinked concepts that help in optimal irrigation planning.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, we explore the definitions and calculations of duty (D), delta (Δ), and base period (B), highlighting their significance in determining the area that can be irrigated with a given discharge, the total water depth required by crops, and the timing of irrigation for optimal crop yields.
Detailed
Duty, Delta, and Base Period
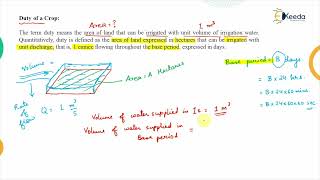
In irrigation management, three important terms are used to optimize water usage for crops: Duty (D), Delta (Δ), and Base Period (B). Duty refers to the area that can be irrigated per unit discharge of water, which is calculated as D = A / Q, where A is the area in hectares and Q is the discharge in cumecs. Delta represents the total depth of water required by a crop over its growing period, calculated using the formula Δ = (8.64 × B) / D, where B is the base period in days.
The Base Period defines the time span from the first watering to the last watering before harvest, influencing the irrigation schedule. Understanding these concepts aids farmers in efficient water resource management, ensuring crops receive sufficient moisture for optimal growth while minimizing water waste.
Youtube Videos









Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Duty (D)
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Duty (D)
The area irrigated per unit discharge of water. D = A / Q (in hectares/cumec)
Detailed Explanation
Duty refers to the efficiency of how water is used for irrigation. It is calculated by dividing the area that can be irrigated (A) by the discharge of water (Q) used for irrigation. It’s measured in hectares per cubic meter per second (hectares/cumec). A higher duty value means that more area can be irrigated with the same amount of water, which indicates more efficient water use.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a garden hose watering a garden. If you can water a larger area of the garden using a smaller flow of water from the hose, you have a higher 'duty.' Conversely, if you can only water a small patch with the same hose, your duty is low. Efficient usage leads to better water conservation.
Delta (Δ)
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Delta (Δ)
The total depth of water required by a crop during its base period. Δ = (8.64 × B) / D Where B = Base period (days)
Detailed Explanation
Delta measures how much water a crop needs in total during a specific period, known as the 'base period.' The formula to calculate delta includes factoring in both the base period duration in days (B) and the duty (D). Essentially, it tells you how deep a layer of water is needed over the area being irrigated, helping determine how much water needs to be supplied over time.
Examples & Analogies
Think of delta as a swimming pool. If the pool holds a certain amount of water (based on its area and depth), delta helps to understand how much water needs to be added or how deep the water will be after a specific watering period. Knowing how deep the pool will get ensures you don’t overfill it, preventing waste.
Base Period (B)
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- Base Period (B)
The time between the first watering to the last watering before harvest.
Detailed Explanation
The base period is the total time span from when a crop receives its first watering until it gets its last watering before it is harvested. This period is essential in understanding irrigation needs because it helps farmers plan how much water to supply and when. The efficiency of water usage during this period can significantly impact crop yield.
Examples & Analogies
Consider baking a cake. The base period is like the time from when you start mixing ingredients (the first watering) to when you take the cake out of the oven (the last watering before harvest). If you understand this timing well, you can get the best results from your baking, just like proper irrigation ensures a good crop yield.
Key Concepts
-
Duty: The area that can be irrigated per cumec of water, reflecting the efficiency of irrigation.
-
Delta: The total amount of water a crop needs over its base period, crucial for planning irrigation.
-
Base Period: The duration from the start of watering to the last watering before harvest, impacting crop water management.
Examples & Applications
If a farmer has a discharge rate of 10 cumecs, and the duty is 20 hectares/cumec, the farmer can irrigate 200 hectares.
For a crop with a base period of 30 days and a duty of 15 hectares/cumec, the total water required can be calculated as Δ = (8.64 × 30) / 15, giving Δ = 17.28 mm.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Duty on land, with water so grand, helps crops to stand in fertilized land.
Stories
Imagine a farmer named Sam, who uses Duty to plan how much land he can irrigate with his water. He learns from his mistakes, understanding Delta and Base Period as he prepares for harvest.
Memory Tools
Remember: D = Duty, Δ = Delta, B = Base (Duty, Delta, Base) - think of them in sequence!
Acronyms
DDB - Duty, Delta, Base (helps in irrigation planning).
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Duty (D)
The area irrigated per unit discharge of water, calculated as D = A / Q.
- Delta (Δ)
The total depth of water required by a crop during its base period, calculated using Δ = (8.64 × B) / D.
- Base Period (B)
The time interval from the first watering to the last watering before the harvest of a crop.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
