Summary
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
The Importance of Product Design
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will explore why product design is so crucial in our daily lives. Can someone share any products they believe were well-designed?

I think smartphones are very well-designed because they are user-friendly and have all the features we need.

Great example! Smartphones indeed blend functionality with aesthetics. This shows the concept of User-Centered Design (UCD), where we focus on user needs.

Why is UCD so important in product design?

UCD ensures that the product meets the user's requirements, enhancing usability and satisfaction. Remember the acronym UCD: Understand, Create, and Deliver.

What other principles should we consider during design?

Excellent question! Along with UCD, we also consider aspects like sustainability, the balance between form and function, and the importance of iteration in improving the design.

Iteration sounds like a process. Can you explain how that works?

Iteration is the practice of refining the product based on user feedback. You want to produce a better version each time you test it.

To sum up, product design is about solving problems through a structured approach that includes understanding user needs, sustainability, and continual improvement.
Engineering and Product Design
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let’s delve into engineering principles in product design. What are some key principles we should know?

I think things like statics and mechanics are important for making sure structures aren’t going to collapse.

Absolutely! Statics and mechanics help us understand how forces act on objects. This ensures our designs, like bridges or even furniture, are safe.

What role does material selection play?

Choosing the right materials is critical. They affect durability and cost. In fact, knowing properties such as weight and environmental impact is part of responsible design.

How does technology like CAD fit into all this?

CAD software helps visualize and simulate designs before they’re built. It’s a powerful tool for engineers to prototype effectively, helping save resources.

In summary, engineering plays a pivotal role in ensuring our designs are not only creative but also feasible, sustainable, and safe.
Robotics in Product Design
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s talk about robotics and its contribution to product design. Why do you think robotics is essential?

Robotics can automate tasks, right? It makes designing things like robots really exciting!

Exactly! Robotics helps create machines that can perform tasks autonomously. What do you think are key components of a robotic system?

Um, maybe the sensors and actuators?

Correct! Sensors gather data from the environment, while actuators control the movements. Together, they allow the robot to interact with its surroundings.

How do we go from an idea to a functional robot?

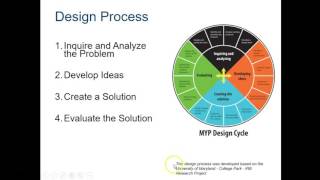
By following the design process: defining the problem, planning the design, building, programming, and testing. It’s an iterative cycle!

In summary, robotics enhances product design by enabling automation and smart interactions, which make products more efficient and user-friendly.
Prototyping in Product Design
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s shift our focus to prototyping. Can anyone explain what prototyping means?

It's about making a model to test a product idea, right?

Exactly! Prototyping helps us test form, function, and usability before mass production. Why do you think this is important?

So that we can identify issues early and improve the design?

Spot on! Early feedback allows for significant improvements in design. Can anyone tell me the difference between low-fidelity and high-fidelity prototypes?

Low-fidelity is like cardboard models, and high-fidelity uses advanced tools like 3D printing, right?

Yes! Each type of prototype serves its purpose in the design cycle. In summary, prototyping is a crucial step that allows designers to visualize and test their ideas, paving the way for functional products.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, we interpret the significance of product design in the 21st century as an interdisciplinary endeavor that integrates creativity, technical knowledge, and empathy. It highlights how MYP Design students learn through a structured approach involving engineering principles, robotics, and physical prototyping.
Detailed
Summary
Product design in the 21st century represents a fusion of philosophy, creativity, and technical execution aimed at solving real-world problems. It is an interdisciplinary process that connects engineering principles, robotics, and physical prototyping. This section emphasizes the importance of empathy for the user while engaging in the design cycle, outlining how MYP Design students leverage their learnings to innovate and create functional solutions that resonate with the needs of today’s world. Through the practice of user-centered design, iteration, and an emphasis on sustainability, young designers not only work on theoretical projects but also create tangible products that can impact their communities positively.
Youtube Videos

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Interdisciplinary Nature of Product Design
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Product design in the 21st century is a rich, interdisciplinary process that brings together creativity, technical skill, and empathy for the user.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk emphasizes the interconnected fields involved in product design today. It highlights that effective product design integrates creativity—which involves imagination and artistry—with technical skills that are grounded in science and engineering. Additionally, understanding user needs and perspectives is essential, hence the importance of empathy. In this context, students not only learn technical aspects but also how to think creatively and consider the user's experiences and challenges when designing products.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine designing a smartphone. A creative person might suggest a sleek design or unique features, while an engineer would think about how to make it lightweight yet durable. A good product designer combines these ideas, ensuring the smartphone is not only appealing but also works well and meets the needs of users.
Engagement in Real-World Problem Solving
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
From conceptual sketches to working robotic systems, students in the MYP Design program engage in meaningful problem-solving that reflects real-world innovation.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk underlines the practical aspect of the learning experience in product design. It conveys that students transition from mere ideas (conceptual sketches) to real products (working robotic systems). Through this hands-on process, they are able to tackle actual problems faced by society or specific user groups, thus applying their knowledge to create innovative solutions that have the potential to make a difference in the world.
Examples & Analogies
Think about students designing a water-saving faucet for schools. They start with sketches on paper, discussing how it would look and function. After brainstorming, they create a prototype that uses sensors to conserve water. This project not only teaches them design principles but also addresses an important issue—wasting water—and can lead to actual changes in their community.
Integration of Engineering Principles
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
By integrating engineering principles, robotic systems, and hands-on prototyping, young designers not only build products—they shape the future.
Detailed Explanation
This chunk stresses the importance of combining various disciplines to facilitate effective product design. Engineering principles provide the foundational knowledge necessary for building efficient systems, robotics introduces automation and functionality, while prototyping allows ideas to become tangible. Collectively, these elements empower young designers to not just create individual products, but to innovate and envision future technologies and solutions that can influence tomorrow's world.
Examples & Analogies
Consider how self-driving cars are being designed. Engineers apply physics to ensure safety during crashes, robotic systems allow the car to navigate autonomously, and prototypes are tested in real-world conditions. Each part of the design process is crucial in developing a vehicle that could transform transportation in the future.
Key Concepts
-
Interdisciplinary nature of product design: It integrates creativity and technical skills.
-
User-Centered Design: A design approach focused on user needs and behaviors.
-
Sustainability in design: Creating products with minimal environmental impact.
-
Iterative process: Repeatedly improving a design based on feedback.
-
Prototyping: Creating models to test ideas before final production.
Examples & Applications
Designing a smartphone that balances usability with technical specifications.
Creating a collapsible bike helmet that incorporates both safety and comfort in its design.
Building a household robot capable of completing daily chores autonomously.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Design with care, it must fit right, user needs should be in sight!
Stories
Imagine a student designing a smart water bottle. They consider what users need, test their ideas on friends, and improve their design, showcasing the iterative process!
Memory Tools
UCD: Understand, Create, Deliver - Keep users in mind and they'll deliver!
Acronyms
FAST
Functional
Aesthetic
Sustainable
Tested - Remember these four pillars of good design!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- UserCentered Design (UCD)
Design methodology that prioritizes the needs and feedback of users.
- Iteration
The process of repeatedly improving a design based on feedback.
- Sustainability
The practice of creating products with minimal environmental impact.
- CAD (ComputerAided Design)
Digital software to create precise drawings and models.
- Robotics
Field combining mechanical, electrical engineering, and computer science to design autonomous machines.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
