Understanding Product Design
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Product Design
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will dive into what product design is. Can anyone tell me what they believe product design involves?

I think it’s about making things look nice.

That's part of it! Product design also involves solving problems. It combines creativity with practical solutions. This is often referred to as 'blending aesthetics with functionality.' To remember this, think of the acronym **C-FP**: Creativity & Functionality in Product design.

So, it’s not just how it looks?

Exactly! It's also about how well it performs. Let’s talk about user-centered design next.
User-Centered Design
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

User-centered design focuses on understanding the users' needs and behaviors. Why do you think this is important?

If we don’t understand users, we might make something they don’t like.

Exactly! The goal is to enhance usability by incorporating user feedback. Remember the mnemonic **U-C-F**: Users Come First, to keep this principle in mind.

What happens if we don’t ask for feedback?

We risk creating a product that no one wants. Iteration allows for continuous improvements based on that feedback.
Balance of Form and Function
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Next, let’s talk about the balance between form and function. Can you think of a product that excels in both?

How about the iPhone?

Great example! The iPhone is visually appealing and highly functional. Remember, **F-F**: Form Follows Function—this can help you in your design decisions.

But can it be too focused on function and not look good?

Yes, that's known as 'function over form.' A good designer needs to strike a balance to appeal to users.
Sustainability in Product Design
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's discuss sustainability. Why should designers care about the environment?

Because it helps reduce waste and pollution?

Exactly! Designers must consider how their products impact the environment. A memory aid to remember this could be the acronym **ESM**: Eco-Friendly Sustainable Materials.

Can you give an example of sustainable materials?

Sure! Bamboo and recycled plastics are two examples.
The Iterative Design Process
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Lastly, let's discuss iteration. What does it mean to iterate a design?

To keep changing it until it's right?

Correct! Iteration means applying user feedback to refine a product. The mantra to remember is **R-T**: Refine and Test continuously.

Why is it important to do that?

It ensures the product meets the users' needs and improves their experience.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Understanding Product Design covers the essential elements of product design, including user-centered design, the balance of aesthetics and functionality, sustainability practices, and the importance of iteration. These components are crucial for creating effective and environmentally friendly products.
Detailed
Understanding Product Design
Overview
Product design is an interdisciplinary process that focuses on creating solutions to specific problems through innovative products. It incorporates creativity and practical problem-solving to meet user needs.
Key Elements of Product Design:
- User-Centered Design (UCD): This approach places the user at the forefront of the design process, emphasizing their needs and feedback throughout development.
- Form vs. Function: Designers must find a balance between the aesthetic appeal of a product and its functional capabilities. This duality is essential for creating successful products.
- Sustainability: Modern product design prioritizes environmental impact by using recyclable materials and efficient manufacturing processes, aiming for minimal waste.
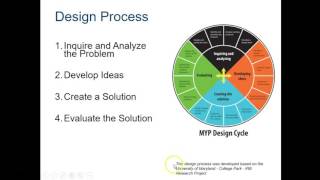
- Iteration: Continuous improvement is achieved by using feedback from testing and user interactions to refine and optimize designs.
Significance
Product design is foundational within the technology and innovation sectors, driving advancements in engineering, robotics, and prototyping. It cultivates an engaging and relevant exploration of real-world problems for students.
Youtube Videos

Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
What is Product Design?
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Product design is the process of imagining and creating products that solve specific problems or meet certain needs. It blends aesthetics, functionality, usability, and manufacturability.
Detailed Explanation
Product design is a systematic approach where designers conceptualize and create items that address particular issues or fulfill specific demands. It is essential to consider several aspects, including how the product looks (aesthetics), how well it works (functionality), how easy it is for people to use it (usability), and how feasible it is to produce (manufacturability). This means a good product must not only be visually appealing but also practical, user-friendly, and economical to manufacture.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a smartphone. It not only needs to look good but also has to function well, be easy for people to use, and be cost-effective for the company to produce. If a smartphone is beautiful but difficult to operate, or too expensive to make, it might not succeed in the market.
Key Elements of Product Design
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
- User-Centered Design (UCD): Focuses on the needs, behaviors, and feedback of end-users.
- Form vs. Function: Balancing how a product looks with how well it performs.
- Sustainability: Designing with minimal environmental impact, using recyclable materials and efficient manufacturing.
- Iteration: Using feedback to continuously improve the product.
Detailed Explanation
There are several key elements crucial for effective product design:
1. User-Centered Design (UCD) emphasizes designing products around the user’s needs and incorporating their feedback throughout the process.
2. Form vs. Function is the challenge of making products not only visually appealing but also high-performing. Designers must find the right balance.
3. Sustainability ensures that products are made responsibly, minimizing environmental effects by using eco-friendly materials and production methods.
4. Iteration refers to the ongoing process of refining the product based on testing and feedback, leading to continuous improvement.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine designing a backpack. If you're using UCD, you'd gather input from students about what they need in a backpack—like space, pockets, and comfort. While designing it, you need to ensure it looks appealing (form) but also can hold books comfortably (function). For sustainability, you might choose recycled materials, and you'd create several prototypes to test and refine it based on real user experiences (iteration).
Key Concepts
-
User-Centered Design: an approach that focuses on user feedback and needs.
-
Aesthetics vs. Functionality: the balance between how a product looks and how well it works.
-
Sustainability: designing with minimal environmental impact.
-
Iteration: refining designs based on testing and feedback.
Examples & Applications
A stylish ergonomic chair that provides comfort while enhancing workspace aesthetics.
A reusable water bottle made from recycled materials that encourages sustainability.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In design, aim to shine, make it pleasing and fine; but don't forget to show, that it works, just so.
Stories
Imagine a young knight who must build a castle. If he only cares about how it looks, the dragons will knock it down! He learns that balance is crucial for a safe and beautiful stronghold.
Memory Tools
Remember C-FP for Creativity & Functionality in Product design.
Acronyms
Use **U-C-F** for Users Come First in design discussions.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- UserCentered Design (UCD)
A design philosophy focused on understanding and addressing users' needs and feedback.
- Aesthetics
The visual appeal or beauty of a product.
- Functionality
How well a product performs its intended purpose.
- Sustainability
The practice of designing products with attention to reducing environmental impact.
- Iteration
The process of refining a product based on user feedback and testing.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
