Design Features of Surface-Mount Packaging
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Surface-Mount Technology
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will discuss surface-mount technology, commonly known as SMT. Can anyone explain what SMT is?

Isn’t it a method where components are directly mounted on the PCB surface?

Correct! SMT allows for higher component density and eliminates the need for holes in PCBs. What do you think the implications of this are?

It probably makes PCB designs smaller and lighter!

Exactly! Smaller designs lead to more compact devices. Remember, SMT stands for 'Surface-Mount Technology' which focuses on the mounting on the surface—use the acronym SMT to recall this key concept!
Key Features of Surface-Mount Packaging
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s dive deeper into the design features of SMT. What can anyone tell me about the lead configuration of SMT components?

They have flat leads, right?

Yes! These flat leads are soldered directly to the PCB without the need for holes. This leads to which major advantage in manufacturing?

It allows for faster automated assembly!

Exactly. Automation is a huge benefit of SMT. The components being smaller and having a low profile also contributes significantly. Can someone tell me why low profiles matter?

It helps in making devices slimmer!

Great! So, remember the features of SMT: Flat leads, smaller size, and low profile. Use the mnemonic 'F-S-L' for Flat, Small, and Low to remember these key features!
Advantages and Disadvantages of SMT
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now that we know the features, let’s talk about the advantages of SMT. What advantages do you think come from SMT's compact size?

It makes the devices cheaper to produce in bulk!

Correct! The automation and smaller component sizes lead to lower costs in high-volume production. On the flip side, what’s a disadvantage of SMT?

They can be harder to repair, right? Because they're smaller and might need special tools?

Absolutely! SMT can present challenges for repair due to their smaller size and assembly methods. Always consider both the advantages, such as compactness and automated assembly, and the disadvantages like repairability.
Applications of Surface-Mount Packaging
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let’s explore the applications of SMT. Where do you think we would find SMT being utilized most frequently?

In consumer electronics, like smartphones and tablets!

Exactly! SMT is predominant in consumer electronics due to the need for compactness. What other fields can SMT be found in?

What about in automotive systems?

Correct! It's also widely used in automotive and industrial electronics. Remember, SMT's advantages make it a favorite choice in high-performance circuits.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Surface-mount packaging (SMT) is a prevalent method in IC packaging that facilitates higher component density on PCBs through its unique design features. This section elaborates on the characteristics of SMT, its benefits for automated assembly, challenges in mechanical strength and repairability, and its wide range of applications in consumer electronics and high-performance circuits.
Detailed
Design Features of Surface-Mount Packaging
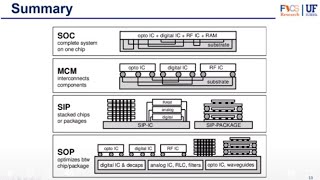
Surface-mount technology (SMT) is a modern and widely used packaging method in the semiconductor industry. This section outlines the crucial design features of SMT:
- Flat Leads: SMT components utilize flat leads or solder pads that are directly soldered onto the PCB's surface, eliminating the need for drilled holes in the PCB. This feature promotes a more streamlined assembly process.
- Smaller Size: The components used in SMT are typically more compact than through-hole components, allowing for a denser and more efficient layout on the PCB. This miniaturization plays a critical role in meeting the demands of modern electronics which require hefty packing densities.
- Low Profile: SMT components usually feature a lower profile compared to their through-hole counterparts, which is advantageous in designs that prioritize space and weight.
The significance of these design features extends beyond mere physical dimensions; they contribute to the ability of SMT to accommodate more complex circuitry and higher performance needs in various applications.
Youtube Videos



Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Flat Leads
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Flat Leads: SMT components have flat leads or pads that are soldered directly onto the PCB.
Detailed Explanation
In surface-mount packaging, the components are designed with flat leads rather than long pins. These flat leads are attached directly onto the surface of the printed circuit board (PCB) without needing to go through holes. This design allows for more efficient use of space and simplifies the mounting process.
Examples & Analogies
Think of flat leads like stickers that you attach to a wall instead of nails. Stickers can be placed quickly and neatly on the surface, just as flat leads are soldered directly onto the PCB.
Smaller Size
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Smaller Size: SMT components are typically smaller than through-hole components, allowing for higher-density packing on the PCB.
Detailed Explanation
Surface-mount components are generally much smaller than their through-hole counterparts. This smaller size enables designers to pack more components into a given area of the PCB, which is increasingly important for modern electronic devices that require compact designs.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine packing your suitcase for travel. If you use smaller items, you can fit many more into the same space, just like how smaller SMT components allow more to be fitted onto a circuit board.
Low Profile
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Low Profile: These components generally have a lower profile compared to through-hole components.
Detailed Explanation
The low profile of SMT components means that they are much flatter compared to through-hole components, which can be taller due to their extended leads. This feature contributes to a sleeker overall design for electronic devices, making them more aesthetically pleasing and easier to integrate into smaller enclosures.
Examples & Analogies
It’s similar to how a modern sports car is designed with a low profile to improve aerodynamics. The flatter a component is, the less space it takes, allowing for more flexibility in the device's design.
Key Concepts
-
Flat Leads: Flat leads on SMT components allow them to be soldered directly to the PCB surface, enhancing assembly speed.
-
Compact Size: SMT components are smaller than through-hole components, enabling increased component density on PCBs.
-
Low Profile: A low profile design allows for slimmer devices, crucial in modern electronics.
Examples & Applications
Smartphones utilize SMT for their compact circuit boards, allowing for numerous features in a limited space.
Automotive systems leverage SMT for efficient mass production and ensuring reliability in critical components.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Flat leads and compact size, Surface-mount makes devices wise.
Stories
Imagine a tiny gadget that does a lot. It uses surface-mount technology to fit components tightly, just like fitting clothes into a small suitcase efficiently.
Memory Tools
Remember ‘F-S-L’ for Flat, Small, Low profile of SMT components!
Acronyms
SMT - ‘Soldered on the Mounting Top’ to recall the concept of surface mounting.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- SurfaceMount Technology (SMT)
A method of mounting electronic components directly onto the surface of a PCB, allowing for higher component density and smaller footprint.
- PCB
Printed Circuit Board, a board used for connecting electronic components.
- Automated Assembly
The use of machines to assemble components onto PCBs, increasing efficiency and consistency.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
