Ball Grid Array (BGA)
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to BGA
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we'll explore Ball Grid Array, or BGA, an advanced packaging technique. Can anyone tell me what they think makes BGA unique among packaging types?

I think it's the way it uses solder balls instead of pins, right?

Exactly! BGA utilizes an array of solder balls as connection points, which improves the performance and thermal management of the package. Let’s remember that ‘BGAs Bring Great Attachments’ for soldering! Now, can anyone think of why the design allows for such a high pin count?

Because the balls can be positioned more closely together compared to leads or pins?

Right! This compact arrangement enables a greater number of connections, crucial for modern ICs. Now, let's delve a bit deeper into some advantages.
Advantages of BGA Packaging
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

What are some advantages of using BGA over other packaging types, do you think?

I believe it offers better thermal performance because of the larger surface area?

That's correct! The surface area allows for improved heat dissipation, which is key in high-speed applications. Can anyone name another advantage?

It's smaller, so it helps with the design of compact devices!

Excellent point! Smaller footprints are integral for modern electronics. Remember the phrase, 'BGA’s more means performance galore!' for future reference.
Disadvantages of BGA Packaging
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Despite the advantages, BGA has its drawbacks. What might be a challenge with BGA?

The solder balls aren't visible after assembly, making it hard to check if they were soldered correctly.

Spot on! This invisibility means inspection becomes challenging and often requires X-ray technology. Can anyone think of why assembly might be complex?

I guess aligning them precisely has to be very specific?

Exactly! Precision during assembly is crucial, increasing the cost and complexity of manufacturing. Remember, 'BGA's complexities can be a manufacturing perplexity!'
Applications of BGA
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s look at where BGA packaging is commonly used. Can anyone name an area where high-performance processors might be found?

In computers and servers, especially for gaming designs!

Correct! High-performance processors are a significant use case for BGA. What about in consumer devices?

Smartphones! They need compact designs.

Exactly, BGA excels in miniaturized electronics. A good mnemonic here is 'In BGA's grasp, speed & size clasp!' for remembering its application. Let's summarize today.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
BGA, or Ball Grid Array, is a modern packaging method characterized by an array of solder balls as connection points, offering advantages in performance, thermal management, and compact design. Despite its higher pin density and improved electrical performance, BGA presents challenges related to inspection and assembly complexity.
Detailed
In-Depth Analysis of Ball Grid Array (BGA)
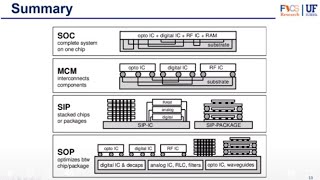
Ball Grid Array (BGA) is a key packaging technology used in modern electronic devices, allowing for effective interconnection of integrated circuits (ICs) to printed circuit boards (PCBs). BGA packages are distinguished by their use of solder balls strategically arranged beneath the package, offering various advantages such as:
-
Design Features:
- Solder Balls: These are the primary connection points that are reflowed to attach the IC to the PCB, making assembly efficient.
- High Pin Count: BGA packages support complex IC designs thanks to the compact nature of the solder ball layout, accommodating a greater number of connections in less space.
- Low Profile: Compared to other packaging methods, BGA components are thinner, which is beneficial for high-density electronics.
-
Advantages:
- Higher Pin Density: BGA allows for intricate circuit designs, supporting modern processors and memory devices effectively.
- Better Thermal Performance: The design enhances heat dissipation, which is crucial for performance in high-speed applications.
- Improved Electrical Performance: BGA's shorter interconnect paths decrease inductance and resistance, thus enhancing signal integrity.
- Smaller Footprint: The compact design aligns with trends toward miniaturization in electronics.
-
Disadvantages:
- Inspection and Rework: The solder balls are concealed post-assembly, complicating quality checks, often necessitating X-ray technology for evaluation.
- Complex Assembly: Precision is vital during assembly, incurring higher manufacturing costs and enhancing the risk of defects.
-
Applications:
- BGAs are prevalent in sectors demanding high-performance solutions, including:
- High-Performance Processors: Essential for demanding applications in computing.
- Mobile Devices and Consumer Electronics: Ensuring compact size and high functionality in devices like smartphones.
- Networking Equipment: Optimized for handling numerous high-speed connections efficiently.
Understanding BGA is essential for engineers involved in PCB design, enhancing their ability to select appropriate packaging solutions while considering trade-offs in performance, cost, and reliability.
Youtube Videos



Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Applications of Ball Grid Array Packaging
Chapter 1 of 1
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● High-Performance Processors: BGAs are commonly used in microprocessors, memory ICs, and GPUs, where high pin count and thermal management are essential.
● Mobile Devices and Consumer Electronics: BGAs are widely used in smartphones, tablets, and gaming consoles where small size, high performance, and efficient heat dissipation are required.
● Networking Equipment: BGAs are often found in routers, switches, and networking ICs due to their ability to handle high-speed signals and high-density connections.
Detailed Explanation
BGA packages are utilized in fields demanding advanced technology and small sizes. They are essential in high-performance processors and memory devices where efficient thermal management and higher pin counts are required. In consumer electronics like smartphones and gaming consoles, their compact nature supports the high functionality needed in these devices. Moreover, networking equipment benefits from BGA's capability to manage high-speed signals efficiently.
Examples & Analogies
Think of a high-performance sports car: just as this car design maximizes aerodynamics and power in a compact space, BGA packaging maximizes electronic performance while minimizing physical space, making it the smart choice for advanced technology like mobile devices and networking hardware.
Key Concepts
-
BGA: A packaging style that maximizes pin density and minimizes circuit size.
-
Solder Balls: Essential for connecting ICs to PCBs, aiding in thermal and electrical performance.
-
Thermal Management: BGA's design improves heat dissipation.
-
Inspection Challenges: BGA's design complicates quality control post-assembly.
Examples & Applications
BGA is commonly used in microprocessors for computers, facilitating efficient performance.
Smartphones incorporate BGA technology for miniaturization and effective heat management.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In a grid where balls hold sway, connections last to save the day!
Stories
Imagine a tiny castle where solder balls are the brave knights connecting the kingdom of circuits, making everything run smoothly without overheating.
Memory Tools
BGA: 'Bringing Great Attachments'.
Acronyms
BGA
Ball Grid Array stands for 'Better Graphics Always' in processors.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Ball Grid Array (BGA)
A packaging technology that uses an array of solder balls as connection points for integrated circuits.
- Solder Balls
Small spherical metal connections used to attach the packaging to the PCB in BGA technology.
- Pin Count
The number of connection points available for an integrated circuit.
- Thermal Management
The process of controlling the temperature of a system to enhance performance and reliability.
- Inspection
The process of checking the quality and correctness of assembled components.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
