Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Introduction to Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're going to explore unsaturated hydrocarbons. Unsaturated hydrocarbons are unique because of their double or triple bonds, unlike saturated hydrocarbons which contain only single bonds.

What are the types of unsaturated hydrocarbons?

Great question! There are two main types: alkenes, which have a double bond, and alkynes, which have a triple bond. Can you think of an example of each?

Ethene for alkenes and Ethyne for alkynes?

Exactly! Alkenes, like Ethene, follow the formula CₙH₂ₙ, while alkynes, like Ethyne, follow CₙH₂ₙ₋₂.
Properties and Reactions of Alkenes
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's dive deeper into alkenes. They are quite reactive due to the double bond. Can anyone tell me why this makes them different from alkanes?

Because double bonds can participate in reactions like addition?

Exactly, well done! In fact, alkenes can undergo reactions such as hydrogenation where hydrogen is added across the double bond.

What about their physical properties?

Alkenes typically have lower boiling points compared to their alkane counterparts because they are less saturated. Remember that the structures dictate their boiling points!
Properties and Reactions of Alkynes
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now let's talk about alkynes. Who can remind me of the general formula for alkynes?

CₙH₂ₙ₋₂.

Correct! Alkynes are even more reactive than alkenes due to the triple bond. They can also undergo similar addition reactions, sometimes resulting in different products.

Are there any uses for alkynes in real life?

Absolutely! Acetylene, a simple alkyne, is used in welding due to its high flame temperature. It's fascinating how chemistry plays a role in our daily lives!
Comparison and Summary of Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

To wrap up, let’s summarize the main points about unsaturated hydrocarbons. What differentiates alkenes and alkynes?

Alkenes have double bonds while alkynes have triple bonds.

Correct! And can anyone share the implications of these differences in terms of reactivity?

Alkynes are more reactive due to the triple bond.

Exactly! Understanding these properties helps us predict how these compounds will react in a variety of situations. Well done, everyone!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Unsaturated hydrocarbons, including alkenes and alkynes, differ from saturated hydrocarbons by having double or triple bonds, respectively. Their general formulas, significance in organic chemistry, and examples help illustrate their role in chemical reactions and structures.
Detailed
Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
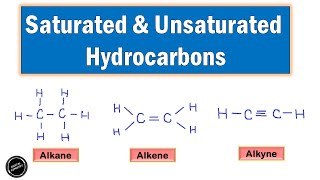
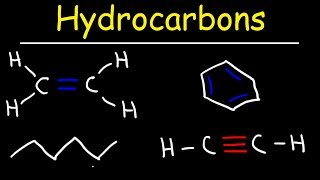
Unsaturated hydrocarbons are a significant class of organic compounds characterized by the presence of one or more double or triple bonds between carbon atoms. Unlike saturated hydrocarbons, which only consist of single C–C bonds and follow the general formula CₙH₂ₙ₊₂ (like alkanes), unsaturated hydrocarbons can be categorized into two main types: alkenes and alkynes.
Types of Unsaturated Hydrocarbons:
- Alkenes: These compounds contain one double bond and follow the general formula CₙH₂ₙ. An example is Ethene (C₂H₄).
- Alkynes: These compounds feature one triple bond and follow the general formula CₙH₂ₙ₋₂. An example is Ethyne (C₂H₂).
The presence of these multiple bonds enables unsaturated hydrocarbons to engage in various chemical reactions, making them essential in the field of organic chemistry and industrial applications. Understanding these compounds is crucial for students studying organic chemistry as they lay the groundwork for learning about more complex molecules.
Youtube Videos






Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Definition of Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Unsaturated Hydrocarbons:
○ One or more double/triple bonds
Detailed Explanation
Unsaturated hydrocarbons are types of hydrocarbons that contain at least one double bond (alkenes) or one triple bond (alkynes) between carbon atoms. These double or triple bonds create a difference in the chemical properties compared to saturated hydrocarbons, which only contain single bonds.
Examples & Analogies
Think of unsaturated hydrocarbons as a stretchy rubber band. When the rubber band is not stretched (like saturated compounds), it can only connect in one way. But when you pull on it (creating double or triple bonds), it can change shape and connect in more complex ways, just like how unsaturated hydrocarbons can combine with other elements in more varied chemical reactions.
Types of Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Alkenes: One double bond; general formula CₙH₂ₙ
- e.g., Ethene (C₂H₄)
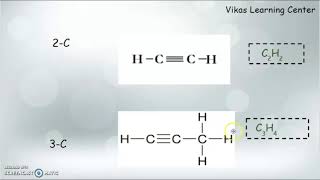
Alkynes: One triple bond; general formula CₙH₂ₙ₋₂
- e.g., Ethyne (C₂H₂)
Detailed Explanation
There are two primary types of unsaturated hydrocarbons: alkenes and alkynes. Alkenes contain one double bond and have a general formula of CₙH₂ₙ. An example of an alkene is Ethene (C₂H₄). Alkynes, on the other hand, contain one triple bond with a general formula of CₙH₂ₙ₋₂. Ethyne (C₂H₂) is a well-known example of an alkyne.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine alkenes and alkynes as different types of vehicles. Alkenes are like cars that can take you on one straight road (double bond), whereas alkynes are like sports cars that can go off-road and handle tricky terrains (triple bond). Both vehicles provide different capabilities, just like the different types of unsaturated hydrocarbons participate in various reactions in organic chemistry.
Key Concepts
-
Alkenes: Unsaturated hydrocarbons with double bonds, formula CₙH₂ₙ.
-
Alkynes: Unsaturated hydrocarbons with triple bonds, formula CₙH₂ₙ₋₂.
-
Reactivity: Unsaturated hydrocarbons are generally more reactive than saturated hydrocarbons.
Examples & Applications
Ethene (C₂H₄) as an example of an alkene.
Ethyne (C₂H₂) as an example of an alkyne.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Alkenes come in pairs, with double bond flares; Alkynes like to explore, with triple bonds in store.
Stories
In a chemistry town, there lived Alkenes who loved to dance together with their partners (double bonds) while Alkynes preferred to stand alone, showcasing their triple bonds.
Memory Tools
A for Alkene and A for Additive reactions; T for Alkyne and T for Triple bonds.
Acronyms
U.H. for Unsaturated Hydrocarbons - U for Unstable (reactive) characteristics.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Hydrocarbon
A compound consisting of only carbon and hydrogen atoms.
- Alkene
A type of unsaturated hydrocarbon with at least one double bond.
- Alkyne
A type of unsaturated hydrocarbon with at least one triple bond.
- Saturated Hydrocarbon
A hydrocarbon with only single C–C bonds.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
