Cause of Dispersion
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Dispersion
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Good morning class! Today, we will explore why different colors of light split apart when they pass through a prism. This fascinating phenomenon is called dispersion. Can anyone tell me why light travels differently depending on its color?

I think it has to do with the wavelength of the colors.

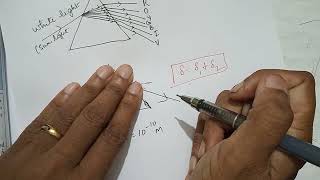
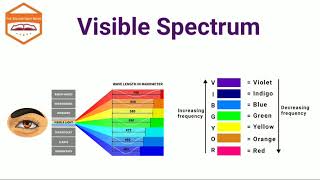
Exactly! Each color has a different wavelength. The short wavelengths bend more than the long wavelengths. Let's remember this with the mnemonic 'VIBGYOR' for the colors: Violet, Indigo, Blue, Green, Yellow, Orange, and Red.

So, violet bends the most, and red bends the least?

That's correct! This is why we see a vibrant spectrum when light passes through a prism. Great observation!
Refractive Index
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's discuss the refractive index. Does anyone know what refractive index means?

Isn't it how much light bends when it enters a new medium?

Exactly! And it's different for each color of light. The refractive index is higher for violet light than for red light, which contributes to the bending we observe. Can anyone guess why this is important?

It helps us understand why we see different colors when light disperses!

Correct! The separation of light colors through dispersion not only shows us the beauty of the spectrum but is also critical for many optical applications.
Practical Implications of Dispersion
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

In real life, dispersion affects technologies such as cameras and optical fibers. How do you think this information relates to these technologies?

Maybe in sharpening images or data transmission?

Absolutely! Understanding how light disperses allows engineers and scientists to create better optical devices. It ensures clear images and effective data transfer.

So, if we use different colors correctly, we can improve technology?

That's exactly right! Harnessing the science of dispersion can lead to remarkable innovations.
Review and Reinforcement
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

To wrap up, can anyone summarize why dispersion occurs in terms of speed and wavelength?

Different colors travel at different speeds, and this is why they bend at different angles!

Correct! Remember, violet bends the most, while red bends the least. This differentiation is crucial for understanding the full spectrum of light. Great job today, everyone!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
Dispersion occurs when light of varying wavelengths travels at different speeds within a medium like glass. This phenomenon causes violet light to bend the most, while red light bends the least, leading to the separation of colors.
Detailed
Cause of Dispersion
Dispersion refers to the phenomenon where light is separated into its constituent colors when it passes through a medium such as glass. The key reason behind this dispersion is that light of different colors (or wavelengths) travels at varying speeds in the medium. This results in different refractive indices for each color, causing them to bend at different angles during refraction. Specifically, violet light has the shortest wavelength, bends the most, and thus travels slower in glass, while red light has the longest wavelength and bends the least. Understanding the cause of dispersion not only explains the spectrum of colors but also aids in a deeper comprehension of optical phenomena.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Speed of Light in Different Colors
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Light of different colors (wavelengths) travels at different speeds in a medium like glass.
Detailed Explanation
When light passes through a medium such as glass, each color of light does not travel at the same speed. This is because different wavelengths of light, which correspond to different colors, interact with the material of the glass differently. For example, violet light (the color with the shortest wavelength) travels slower through the glass compared to red light (the color with the longest wavelength). This variation in speed is fundamental to understanding dispersion.
Examples & Analogies
Think of it like a group of people running through a crowded room. The shorter people (representing violet light) may struggle more to navigate through the crowd than the taller people (representing red light). As a result, the shorter people might take longer to get to the other side, just like violet light takes longer to travel through glass.
Refractive Index Variation
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Due to this, the refractive index of the medium is different for each color.
Detailed Explanation
The refractive index of a medium is a measure of how much the speed of light is reduced inside that medium compared to its speed in a vacuum. Since different colors of light travel at different speeds in glass, they also have different refractive indices. Violet light has a higher refractive index than red light, meaning it bends more when entering or exiting the prism, while red light bends less.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a group of friends walking through a hallway where the floor is slippery in some places and rough in others. The friends that have easy shoes to run in (like red light) can move quickly through the rough parts, while the ones in heavy boots (like violet light) struggle. This difference in ease of movement represents how different refractive indices affect the bending of light.
Bending of Colors
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Violet light bends the most and red bends the least.
Detailed Explanation
As light passes through a prism, each color is bent by a different amount due to the differences in their refractive indices. Violet light, which travels the slowest in glass, is bent the most as it enters and exits the prism, while red light, which travels the fastest, is bent the least. This bending is what creates the visible separation of colors called dispersion.
Examples & Analogies
Consider how a rainbow forms after rain: it’s as if light enters the prism of water droplets, bending and spreading out into a fan of colors. Just like this, when light passes through a prism, violet, being the most bent, will appear at one end, and red, being the least bent, will showcase at the opposite end.
The Separation of Colors
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
This separation of colors is the cause of dispersion.
Detailed Explanation
The process where the different colors of light are separated due to their varying speeds and bending angles is known as dispersion. Essentially, because of the changes in speed and refractive direction of each color as they pass through the prism, we can see a spectrum instead of just a white light. This phenomenon is responsible for creating the beautiful range of colors we can observe.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine having a set of crayons where each crayon represents a color of light. If you were to spill water on them, it might mix them up. But if you use a tool like a ruler or a stick to separate them based on size, you see each crayon clearly again. Just like this, a prism acts as a separator that allows us to see individual colors instead of just white light.
Key Concepts
-
Dispersion: The process of splitting light into its constituent colors.
-
Refractive Index: Different wavelengths of light have different refractive indices in the same medium.
-
Wavelength: Determines how much light bends; violet has a shorter wavelength, red has a longer wavelength.
Examples & Applications
When white light passes through a prism, it spreads out to form a rainbow of colors.
Violet light is refracted at a higher angle than red light when passing through glass.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
Light bends like a rainbow's friend, Red on the edge, Violet at the end.
Stories
Once there was a beam of light that loved to dance through a prism. It split into seven colorful friends, each bending differently, dancing joyfully as they went.
Memory Tools
Remember the order of colors using the phrase 'Vann's Invisible Ball Grows Yellow, Orange, Red'.
Acronyms
VIBGYOR helps us remember the colors
Violet
Indigo
Blue
Green
Yellow
Orange
Red.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Dispersion
The separation of light into its constituent colors when passing through a medium.
- Refractive Index
A measure of how much the speed of light is reduced within a medium.
- Wavelength
The distance between successive peaks of a wave, determining the color of light.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
