Recombination of Spectrum
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Understanding Recombination
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we will discuss how we can take the colors produced by light passing through a prism and combine them back into white light using another prism. Does anyone remember what the colors are when white light is dispersed?

Yes! They are violet, indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange, and red!

Great! We can remember them with the acronym VIBGYOR. Now, if we put a second prism upside down after the first prism, what do you think will happen?

The colors will come together again to form white light!

Exactly! This process of combining colors back to create white light is called recombination. Let’s explore this further!
The Science Behind Recombination
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Can someone explain why the second prism can recombine the colors into white light, based on what we've learned?

I think it's because the angles at which the colors emerge can be adjusted by the second prism.

Yes! Each color bends at different angles, but with the right orientation of the second prism, they can meet at the same point and recombine into white light.

So, it effectively reverses the process of dispersion?

Precisely! By reversing the dispersion, we demonstrate the composite nature of white light. This is a crucial principle in optoelectronics.
Newton's Experiment Connection
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, can anyone tell me how this concept correlates with Newton's famous experiment with prisms?

He used sunlight and a prism to create a spectrum and then recombined it with another prism!

Correct! Newton's experiment laid the foundation for understanding light's nature. He showed that white light could be split into colors and then recombined, confirming his findings about light.

And that proved that white light is made up of multiple colors!

Exactly! This is significant because it helped to advance our understanding of optics and light in science.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
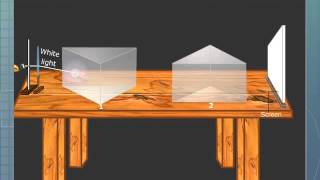
In this section, we explore the phenomenon of recombination of the spectrum using a second prism. This process demonstrates that when the seven colors produced by the dispersion of white light are passed through an inverted prism, they come together to form white light again, evidencing that white light consists of various colored components.
Detailed
Recombination of Spectrum
Recombination of the spectrum involves taking the seven colors produced from the dispersion of white light and using a second prism to recombine them into white light again. This illustrates the idea that white light is not simply a single color, but a combination of multiple colors. When light passes through the first prism, it is split into its constituent colors: violet, indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange, and red (VIBGYOR). By placing a second prism in an inverted position to the first, these colors can be recombined accurately, thus creating white light once again. This process serves as a conclusive demonstration of light's composite nature and reinforces key concepts from earlier sections regarding dispersion and the behavior of light through different mediums.
Youtube Videos







Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Recombination Using a Second Prism
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
A second prism, placed in an inverted position after the first prism, can recombine the seven colors to form white light again.
Detailed Explanation
This process involves using a second prism that is positioned upside down, after the first one that created the spectrum. When light passes through this second prism, the different colors come back together to form white light. This shows how all the individual colors blend back into the single color of white light that we originally started with.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine mixing different paints together. If you have seven different colors of paint (representing the seven colors of the spectrum), and you mix them all together, you will get a new color, like brown. In the case of light, the second prism acts like a mixing bowl that brings the colored light together again to recreate the original white light.
White Light as a Combination of Colors
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
This shows that white light is a combination of all seven colors.
Detailed Explanation
The ability to recombine the colors back into white light proves that white light is not a single, uniform color, but rather a mixture of many colors. Each of these colors contributes to the final appearance of white light. Without the individual colors, white light would not exist. This concept is important in understanding how light behaves and how we perceive different colors.
Examples & Analogies
Think of white light as a colorful salad made with various ingredients. Just like each ingredient adds its unique flavor and texture to the salad, each color of light adds its unique contribution when combined to form white light.
The Process of Recombination
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
This process is called recombination.
Detailed Explanation
Recombination is the term used to describe the action of mixing the seven colors again to create white light. This concept not only reinforces the idea of color blending but also highlights how scientific experiments, like those conducted by Newton, confirm our understanding of light. The process is essential in optics and helps in practical applications such as photography and color printing.
Examples & Analogies
Recombination can be likened to baking a cake. You have all the ingredients (the colors), and once you mix and bake them, you end up with a delicious cake (the white light). Each ingredient is essential for the final product to be complete and tasty.
Key Concepts
-
Recombination: The process of using a second prism to bring back separated colors into white light.
-
Prism: An optical tool used to refract light and create a spectrum of colors.
-
Dispersion: The separation of white light into its constituent colors based on different wavelengths.
Examples & Applications
An example of recombination is when after viewing a rainbow through a prism, you place another prism in front to see the colors merge back to form white light.
To visualize, think of a painter mixing various colors on a palette; the combined colors can yield white or gray depending on the proportions.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In the prism, colors blend, once again white light they'll send.
Stories
Imagine two friends with a glow stick; they first separate its colors and mix them back to form light again. This teaches us how prisms work with light!
Memory Tools
Think of 'Recombination' as 'Re-combining' the colors again!
Acronyms
Remember Recombination = Reverse of VIBGYOR.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Recombination
The process of combining previously separated colors back into white light using a prism.
- Prism
A transparent optical element that refracts light, splitting it into a spectrum of colors.
- Dispersion
The phenomenon where white light is separated into different colors based on their wavelengths.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
