General Characteristics of p-Block Elements
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Variable Oxidation States
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're examining the variable oxidation states of p-block elements. Who can tell me what oxidation states are?

Are oxidation states the different charges an atom can have?

Exactly! They occur due to the loss or gain of electrons. p-Block elements can exhibit several oxidation states. Can anyone think of an example?

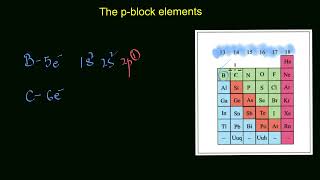
Carbon can have oxidation states of -4, 0, and +4.

Great example! Remember, the more oxidation states an element has, the more versatile it is in compounds. We can keep this in mind with the acronym 'VAR' for 'Variable oxidation state, Atom versatility, Reactivity'.

So, does that mean they can react with various elements?

Spot on! It really enhances their reactivity and the types of compounds they can form. To summarize, p-block elements show various oxidation states, aiding in diverse chemical reactions.
Metallic vs Non-metals
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Let's talk about the metallic and non-metallic properties found in p-block elements. Who can distinguish between these two types?

Metallic elements are shiny and conductive, while non-metals are dull and not conductive.

Correct! Now, can you name an example of a metalloid?

Silicon is a metalloid!

Excellent! Metalloids, like silicon, exhibit properties in between metals and non-metals, which can be very useful. Remember the mnemonic 'M-NM-M' for 'Metal, Non-metal, Metalloid' to keep them organized in your mind.

Can these properties impact their uses in real life?

Absolutely! Metals are often used in wires for conductivity, while non-metals like nitrogen are crucial for fertilizers. Let's sum it up: p-block elements range from metals to metalloids, affecting their utility greatly.
Importance of p-Block Elements
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let’s discuss why p-block elements are essential in biology. Can anyone state a vital p-block element?

Oxygen is vital for respiration!

That's right! Oxygen is essential for breathing and many chemical processes. What other p-block elements come to mind?

Carbon is essential too, especially in organic chemistry!

Well said! Carbon's ability to form numerous compounds underpins all of organic chemistry. Think of the acronym 'COLENS'– 'Carbon, Oxygen, Life Elements Needed for Survival.'

What about nitrogen? It’s in the atmosphere.

Exactly! Nitrogen is crucial for plant growth, found in amino acids, and is a key component of fertilizers. To recap, p-block elements like O, C, and N are indispensable for life.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
The p-block elements, located in Groups 13 to 18 of the periodic table, showcase a range of oxidation states and can display both metallic and non-metallic characteristics. They are vital for various biological processes and are commonly found in Earth's atmosphere, water, and crust.
Detailed
General Characteristics of p-Block Elements
p-Block elements encompass groups 13 to 18 of the periodic table and are defined by the filling of their outermost p-orbitals. They exhibit a remarkable variety of behaviors and characteristics.
Key features include:
1. Variable Oxidation States: p-Block elements can have multiple oxidation states, making them versatile in chemical reactions.
2. Metallic and Non-Metallic Properties: This group includes metals, non-metals, and metalloids, each showing different properties based on their position and electronic configuration.
3. Biological Significance: Elements such as oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), and carbon (C) are essential for life forms.
4. Prevalence in Nature: Their compounds can be found throughout the environment— in the air, water, and Earth's crust, indicating their importance in ecological and geological processes.
In essence, p-block elements play pivotal roles in both chemical reactiveness and biological functions.
Youtube Videos





Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Variable Oxidation States
Chapter 1 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Show variable oxidation states.
Detailed Explanation
p-Block elements can have more than one oxidation state, which means that they can lose different numbers of electrons when they form compounds. For instance, carbon can have oxidation states of -4, +2, and +4, allowing it to participate in various chemical reactions and to form a wide variety of compounds.
Examples & Analogies
Think of oxidation states like the different roles a person can play in their life. Just as someone can be a student, a friend, or a worker at different times, elements can 'change roles' depending on the chemical reactions they're involved in.
Metallic and Non-Metallic Properties
Chapter 2 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Exhibit both metallic and non-metallic properties.
Detailed Explanation
p-Block elements display a range of properties that can be metallic, non-metallic, or in between (such as metalloids). For example, metals like aluminum are shiny and conductive, while non-metals like sulfur are dull and insulative. This combination of properties allows p-block elements to be versatile in their applications.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a toolbox where some tools are great for cutting (non-metals), while others are really good for hammering (metals). Each tool has its use depending on the job, just like how p-block elements can be used in varying scenarios based on their properties.
Essential Elements for Life
Chapter 3 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Many are essential to life (e.g., Oxygen, Nitrogen, Carbon).
Detailed Explanation
Several p-block elements are crucial for living organisms. For instance, oxygen is vital for respiration, nitrogen is a key component of amino acids, and carbon is the backbone of all organic molecules. Their presence in biological systems highlights their importance in sustaining life.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a recipe for a salad; just like you need specific ingredients to make it delicious—lettuce, tomatoes, and dressing—life requires essential elements like carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen to thrive. Without these, just like the salad would be incomplete, living organisms would struggle to exist.
Common Compounds in Nature
Chapter 4 of 4
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
● Their compounds are commonly found in air, water, and the Earth's crust.
Detailed Explanation
p-block elements form a variety of compounds that are prevalent in our environment. For example, carbon dioxide (CO₂) is found in the air, while water (H₂O) includes oxygen and hydrogen. Compounds like these are integral to various natural processes such as photosynthesis and respiration.
Examples & Analogies
Think of the Earth as a giant kitchen where ingredients are used in multiple recipes. Just as you might find salt (sodium chloride) in various dishes, compounds from p-block elements are essential ingredients for Earth’s processes, making them key players in the 'kitchen' of our planet.
Key Concepts
-
Variable Oxidation States: p-block elements can have multiple oxidation states, enhancing their chemical versatility.
-
Metallic and Non-Metallic Properties: p-block elements exhibit a range of physical and chemical properties.
-
Biological Significance: Elements such as C, O, and N are crucial for life processes and organic compounds.
Examples & Applications
Carbon's oxidation states are -4, 0, and +4, allowing it to form many compounds.
Oxygen is vital for respiration, making it essential for life.
Sulfur can exist in several oxidation states, affecting its compounds and reactions.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
In the p-block group, watch them shine, with variable states, they define, life’s process sure, they intertwine!
Stories
Once in a land of elements, the p-block rulers ruled with their powers, from the wise Carbon building life forms, to Nitrogen nourishing the flowers.
Memory Tools
Remember C.O.N. for Carbon, Oxygen, Nitrogen – the life essentials from the p-block.
Acronyms
Use VAMP
Variable states
All types (metals
non-metals)
Metallic and non-metal properties
P-block existence.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Oxidation State
The charge of an atom in a compound, indicating the loss or gain of electrons.
- Metalloid
An element with properties intermediate between metals and non-metals.
- pBlock Elements
Elements in Groups 13-18 of the periodic table, characterized by their p-orbital electron filling.
- Variety
A range of different forms or types.
- Biological Significance
The importance of an element in biological processes and life.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
