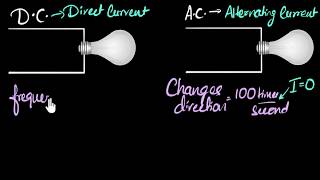
Advantages of AC Over DC
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
Easier Generation of AC
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Today, we're discussing the advantages of Alternating Current over Direct Current. Let's start with generation. Can anyone tell me why AC might be easier to generate than DC?

I think it's because AC can be created using a rotating coil in a magnetic field?

That's correct! This rotating coil approach is straightforward and doesn't require complex changes like in rectification for DC. Remember, AC stands for ‘Alternating Current’—change is part of its nature!

So, is that why generators are often used for AC?

Exactly! Generators exploit this simplicity of AC production, making it widespread in power plants.

Is there a memory aid to help us remember this benefit?

Sure! Think of the phrase ‘Rotating Coil = Reliable AC’ to remember how AC is generated.

That's a helpful way to remember it!

Great! Let's summarize. AC generation is simpler due to the mechanical motion of coils, making it efficient and reliable.
Efficient Transmission of AC
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Now, let's look at why AC is more efficient for transmission. Who can explain how voltage transformation helps in long-distance transmission?

AC can be transformed to high voltages using transformers, which reduces energy loss.

Exactly! High voltage means lower current for the same power, reducing resistive losses. This makes AC ideal for long-distance transmission.

Is this why we see high-voltage power lines?

Yes! Higher voltages in transmission lines prevent energy loss due to heating. Just remember, ‘High Voltage, Lower Loss’ to keep this in mind.

Got it! What’s the impact on energy costs?

Lower losses translate to less energy wasted and lower costs for consumers. Summarizing, AC's ability to transform voltage enhances its efficiency for long-distance transmission.
Convenient Usage of AC
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Finally, let's address the convenience of using AC. How does AC benefit motors and appliances?

AC allows motors to operate effectively because they can manage varying power needs!

Exactly! Many household appliances are designed for AC because it provides power that can easily adjust to different requirements. Remember the phrase ‘AC = Adaptable Current’ to capture this idea.

That makes sense! Is AC used in specific devices?

Yes! It powers everything from fans to refrigerators. So, in summary: AC is convenient due to its adaptability for different devices and appliances.

Thanks, this really clarifies it!
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
AC offers easier generation and efficient long-distance transmission capabilities due to its ability to be easily transformed to higher voltages, making it ideal for use in various applications, including household appliances and motors.
Detailed
Advantages of AC Over DC
Key Advantages of Alternating Current (AC)
- Easier Generation: AC is simpler to produce compared to DC because it can be generated by rotating a coil within a magnetic field, leading to the conversion of mechanical energy into electrical energy without the need for complex rectification processes.
- Efficient for Transmission: AC can be transformed to high voltages with the help of transformers, enabling efficient long-distance transmission. This characteristic significantly reduces energy loss due to resistive heating in the wires during transmission.
- Convenient for Use: Many electrical devices, especially motors, operate more effectively using AC because it can easily provide varying power levels, catering to the requirements of different appliances.
Overall, the benefits of AC over DC make it the preferred choice for power generation and distribution systems.
Youtube Videos



Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
Easier to Generate AC
Chapter 1 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
AC is easier to generate than DC because it can be produced by rotating a coil in a magnetic field.
Detailed Explanation
To generate alternating current (AC), we use a method that involves rotating a coil within a magnetic field. This rotation allows the coil to cut through magnetic lines of force, inducing an electric current. Unlike direct current (DC), which requires a constant flow in one direction, AC's reversal of current makes it inherently easier and more efficient to produce through this mechanical method.
Examples & Analogies
Think of how a windmill works. As the wind turns the blades, they generate energy. Similarly, in an AC generator, as the coil spins in a magnetic field, it generates electrical energy, making AC generation straightforward and efficient.
Efficient for Transmission
Chapter 2 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
AC can be easily transformed to high voltages for efficient long-distance transmission, reducing energy loss.
Detailed Explanation
When transmitting electricity over long distances, one of the biggest challenges is energy loss due to resistance in the wires. AC can be transformed into higher voltages using transformers before transmission. Higher voltage means lower current for the same power level, which significantly reduces heat loss in the wiring caused by the resistance. This feature allows electricity to travel long distances more efficiently.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine a highway where larger trucks can move heavier loads. If you could use larger trucks to carry the same amount of goods but at a lower frequency (fewer trips), you'd reduce wear and tear on the road (less energy loss). Similarly, transforming AC to high voltages reduces the 'wear' on transmission lines.
Convenient for Use
Chapter 3 of 3
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
AC is more suitable for running motors and other equipment that require varying power.
Detailed Explanation
Many household appliances and industrial machines use motors that function more efficiently with alternating current. AC motors can easily start and stop and can manage varying power loads better than DC motors. This versatility allows for more flexible design in machines and devices, catering to a wide range of applications from small household devices to large industrial equipment.
Examples & Analogies
Consider a dimmer switch for your lights. It allows you to adjust brightness as needed, similar to how AC can provide different levels of power to a motor, allowing it to run at various speeds depending on demand. This adaptability makes AC ideal for diverse electrical applications.
Key Concepts
-
Easier Generation: AC is simpler to generate as it requires mechanical motion.
-
Efficient Transmission: AC can be transformed to high voltages to reduce losses.
-
Convenient Usage: AC is adaptable for many applications, notably in household appliances.
Examples & Applications
An electric generator that uses rotating coils produces AC easily.
Transformers raise the voltage of AC for minimal energy loss during transmission.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
AC's easy to create, motors and power do relate!
Stories
Imagine a factory where workers are struggling to lift heavy weights. Then, they shift to an AC-powered conveyor belt that adjusts power effortlessly, making the workflow smooth and efficient.
Acronyms
R.E.C.
Remember 'Reliable Easy Current' for why AC is easier and more reliable than DC.
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Alternating Current (AC)
A type of electric current where the flow of charge periodically reverses direction.
- Direct Current (DC)
An electric current that flows in one direction only.
- Transformer
A device that changes the voltage of an AC signal, allowing for efficient transmission.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
