Generation and Transmission of AC
Enroll to start learning
You’ve not yet enrolled in this course. Please enroll for free to listen to audio lessons, classroom podcasts and take practice test.
Interactive Audio Lesson
Listen to a student-teacher conversation explaining the topic in a relatable way.
AC Generation
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

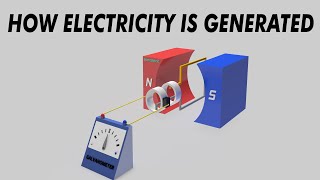
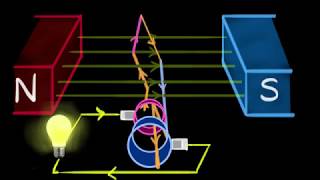
Today, we are going to discuss how Alternating Current, or AC, is generated in power stations. The primary device used for this purpose is called an alternator. Can anyone tell me what an alternator does?

Is it something that generates electricity?

Exactly! An alternator converts mechanical energy into electrical energy by rotating a coil within a magnetic field. This is key to how we generate AC. What must happen to control the frequency and amplitude of the generated AC?

We need to adjust the rotational speed of the generator and the number of coils?

Great! That's correct. By adjusting those factors, we can control both the frequency and the amplitude of the generated AC.

So, if we want higher voltage, do we just increase the speed of the alternator?

Not necessarily just the speed. Both factors play a role. Now, let's move on to how AC is transmitted.

In summary, AC is generated using alternators that convert mechanical energy to electrical energy, with controllable frequency and amplitude.
Transmission of AC
🔒 Unlock Audio Lesson
Sign up and enroll to listen to this audio lesson

Once AC is generated, the next step is transmission. Why do you think high-voltage transmission lines are used?

Is it to minimize energy loss in the wires?

Exactly! High voltage reduces energy loss due to heating in the wires. Would anyone care to share how we achieve these high voltages for transmission?

By using step-up transformers, right?

Correct! Step-up transformers increase the voltage to a high level for efficient transmission. And what happens when it reaches its destination?

It gets decreased to a safer level with step-down transformers.

That's right! Step-down transformers make the voltage safe for use in homes and businesses. To recap, AC is transmitted using high-voltage lines that utilize transformers to manage voltage efficiently.
Introduction & Overview
Read summaries of the section's main ideas at different levels of detail.
Quick Overview
Standard
In this section, we explore how AC is generated in power stations with alternators, which convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. Additionally, we learn about the role of high-voltage transmission lines in efficiently transporting AC over long distances, utilizing step-up and step-down transformers to manage voltage levels.
Detailed
Detailed Summary
Alternating Current (AC) is generated primarily in power stations using devices known as alternators. An alternator converts mechanical energy from a rotating coil within a magnetic field into electrical energy. The frequency and amplitude of the AC produced can be controlled by adjusting the rotational speed of the alternator and the number of coils used within it.
Once generated, AC is transmitted over long distances through high-voltage transmission lines. This method significantly reduces energy losses that occur due to heating in the wires. To facilitate this high-voltage transmission, step-up transformers are utilized to increase the voltage of the AC, allowing for efficient travel over distances. When the electricity reaches its destination, step-down transformers are employed to decrease the voltage to a safer level for household and commercial use.
Understanding the generation and transmission of AC is crucial since it underpins the vast majority of electrical systems in use today, including power grids and household appliances.
Youtube Videos



Audio Book
Dive deep into the subject with an immersive audiobook experience.
AC Generation
Chapter 1 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
AC Generation
Alternating current (AC) is generated in power stations using alternators, which convert mechanical energy into electrical energy by rotating a coil within a magnetic field.
The frequency and amplitude of the generated AC can be controlled by adjusting the rotational speed of the generator and the number of coils.
Detailed Explanation
AC generation occurs in power stations where large machines called alternators work to produce electrical energy. These alternators consist of coils that are rotated within a magnetic field. When the coils move, they cut through the magnetic lines of force, which induces an electrical current according to Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction.
By controlling the rotational speed of the coils, the frequency of the AC can be adjusted. Additionally, changing the number of coils can affect the amplitude, or height, of the electrical wave produced. This means that power stations have the ability to fine-tune the electricity generated to meet demand.
Examples & Analogies
Think of it like pedaling a bicycle. When you pedal faster, the bike goes faster (like increasing the frequency), and if you change gears, you can either make it easier to climb hills or go faster on flat ground (comparable to adjusting the number of coils to control amplitude).
Transmission of AC
Chapter 2 of 2
🔒 Unlock Audio Chapter
Sign up and enroll to access the full audio experience
Chapter Content
Transmission of AC
AC is transmitted over long distances using high-voltage transmission lines. High voltage is used to reduce energy loss due to heating in the wires.
Step-up transformers increase the voltage for efficient transmission, and step-down transformers decrease the voltage for safe use in homes and businesses.
Detailed Explanation
When transmitting AC over long distances, it’s important to send it at high voltages. This technique minimizes energy loss, which occurs due to resistance in the wires that generates heat. To achieve high voltage, step-up transformers are used at the generation point. These devices increase the voltage of the AC current, allowing for more efficient long-distance travel.
Once the electricity reaches near its destination, step-down transformers reduce the voltage to safe levels for use in residential and commercial settings. This two-step approach ensures that electricity can be transmitted with minimal loss, while still being usable at lower, safer voltages.
Examples & Analogies
Imagine you’re transporting water through pipes. If you send water through a narrow pipe, it creates friction and loses pressure (akin to energy loss in low-voltage AC lines). However, if you use a wider pipe (analogous to high voltage), pressure is maintained over a longer distance. Transforming the water back to a manageable flow at the destination represents how step-down transformers work.
Key Concepts
-
AC Generation: The process of generating alternating current using alternators.
-
High-voltage transmission: Reducing energy loss during transportation of electrical power by using high voltage.
-
Step-up transformer: A transformer that increases AC voltage for efficient transmission.
-
Step-down transformer: A transformer that decreases AC voltage to safe levels for usage.
Examples & Applications
A power plant using an alternator to generate AC electricity from mechanical energy derived from coal or gas turbines.
Transmission lines carrying high-voltage AC electricity across kilometers to reach urban centers, where step-down transformers reduce the voltage for domestic use.
Memory Aids
Interactive tools to help you remember key concepts
Rhymes
AC flows here and there, generated with flair, in alternators with care.
Stories
Once upon a time in a power station, there was a magical machine called an alternator. It turned the spinning energy from turbines into flowing electricity, sending it via high-voltage roads, just like how a train transports passengers carefully across cities.
Memory Tools
Remember 'GREAT' for AC generation: G for Generator, R for Rotational speed, E for Electrical energy, A for Alternator, T for Transmission.
Acronyms
AC can be remembered as 'A Cool' for Alternating Current!
Flash Cards
Glossary
- Alternator
A device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy, primarily used to generate alternating current (AC).
- Highvoltage transmission
The transmission of electrical power at high voltages to reduce energy loss due to heating in the wires.
- Stepup transformer
A transformer that increases the voltage of AC for transmission purposes.
- Stepdown transformer
A transformer that decreases the voltage of AC to safer levels for distribution to homes and businesses.
Reference links
Supplementary resources to enhance your learning experience.
